silicone mineral silicon a variety of silica - black, dark gray or light - is quite common in nature, and a person is well acquainted with it. But the healing properties of silicon became known only recently: in the late 70s of the XX century. Although mankind got acquainted with silicon for a very long time.
Flint is the stone that marked the beginning of human civilization. Throughout the Stone Age, flint served as a material for the manufacture of tools and hunting, fire was mined with its help. The healing properties of flint are mentioned in the treatises of ancient philosophers. It was used to cut warts, to decorate walls in rooms where meat was stored, to powder wounds in the form of a powder, which prevented gangrene, flint millstones in mills made it possible to obtain flour with excellent baking and taste qualities. From time immemorial, silicon has been used to line the bottom and inner surface wells, since it has been noticed that people who drink water from such wells get sick less, and such water is unusually clear, tasty and healing.
In nature, silicon occurs in the form of widely distributed minerals - quartz, chalcedony, opal and others. The group of these minerals includes cornelian, and jasper, rhinestone, agate, opal, amethyst and many other stones. The basis of these minerals is silicon dioxide or silica, but the density, color, and some other properties are different. The composition of flints, in addition to silica, includes about 20 chemical elements, the main of which are Mg, Ca, P, Sr, Mn, Cu, Zn, etc. Hence the so many names. But the most famous among the representatives of this family is undoubtedly flint. Most of the earth's crust is made up of organic compounds silicon (28 vol.%).
Silicon (Silicium - lat.) chemical element, atomic number 14, IV group of the periodic system. Silicon atoms form the basis of clay, sand and rocks. We can say that the entire inorganic world is associated with silicon. AT natural conditions silicon minerals are found in calcite and chalk.
Silicon is second only to oxygen in terms of reserves in earth's crust element and makes up about a third of its total weight. Every 6th atom in the earth's crust is a silicon atom. Sea water contains even more silicon than phosphorus, which is so necessary for life on Earth.
In our body, silicon is found in the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland. Its highest concentration is found in hair and nails.
Silicon is also part of collagen, the main protein in connective tissue. Its main role is to participate in chemical reaction, fastening individual fibers of collagen and elastin, giving the connective tissue strength and elasticity. Silicon is also part of the collagen of hair and nails, plays an important role in the fusion of bones in fractures.
Silicon has a special role in the life and health of people, as well as flora and fauna. Silicon is absorbed by plants in the form of dissolved silicic acids, silicates and colloidal silica. The lack of silicon adversely affects the germination, growth and yield of cereals, mainly rice, as well as sugar cane, sunflower, crops such as potatoes, beets, carrots, cucumbers and tomatoes. With vegetables, fruits, milk, meat and other products, a person should consume 10-20 mg of silicon daily. This amount is necessary for normal life, growth and development of the body.
Scientific research about the role of silicon for human health are covered in the monographs of V. Krivenko and others "Lithotherapy", M., 1994, E. Mikheeva "Healing properties of silicon", S-P, 2002, the works of M. Voronkov and I. Kuznetsov (AS USSR , Sib. otd., 1984), A. Panicheva, L. Zardashvili, N. Semenova, etc. It is shown that silicon is involved in the exchange of fluorine, magnesium, aluminum, and other mineral compounds, but interacts especially closely with strontium and calcium. One of the mechanisms of action of silicon is that, due to its chemical properties, it creates electrically charged colloidal systems that have the ability to adsorb viruses and pathogens that are unusual for humans.
Some plants are able to concentrate silicon. This is Jerusalem artichoke, radish, olive a, currant, horsetail etc. A lot of silicon accumulates in grain crops, especially in the seed coat (bran): rice, oats, millet, barley, soybeans. When grinding grains in a mill, they are freed from the shell, which deprives them of silicon and thereby devalues them.
Rich in silicon and mineral waters. But refined sugar is practically devoid of silicon. Only unrefined yellow sugar has silicon and is therefore of great value.
Horsetails are distinguished by a high content of silicon - widespread plants of the domestic flora, which have been used more and more often in recent times in folk medicine. In this regard, burdock oil extract, horsetail extract, organic silicon compounds (ceramides), which are part of a medicine called burdock oil with horsetail extract (with ceramides), have proven themselves well. Special studies have shown that this medicine:
Recommendations for use: in violation of the structure of the hair, due to external or internal factors, as well as thinning and dull appearance hair.
Mode of application: apply warm oil on the hair and scalp, gently and thoroughly rub for at least 15 minutes (while avoiding sudden and intense movements, as this breaks and pulls out the hair), then evenly distribute the oil over the entire length of the hair. Apply for 1 hour, then wash off with a mild shampoo.
Silicon is also responsible for providing protective functions, metabolic processes and detoxification. It works as a biological "cross-linking" agent involved in the formation of the molecular "architecture" of polysaccharides and their complexes with proteins, gives elasticity to connective tissues, is part of the elastin of blood vessels, gives strength, elasticity and impermeability to their walls and prevents the penetration of lipids into the blood plasma. .
Studies have shown that silicon in water suppresses bacteria that cause fermentation and decay, precipitates heavy metals, neutralizes chlorine, and absorbs radionuclides. In a living organism, biologically active substances of silicon, together with protein structures, contribute to the formation of enzymes, amino acids, and hormones. Silicon is especially needed in connective tissue; it is found in the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. A lot of silicon in the hair. Its highest concentration is found in hair and nails.
Silicon:
Lack of silicon in the body leads to:
A relationship has been found between the concentration of silicon in drinking water and cardiovascular diseases. Tuberculosis, diabetes, leprosy, hepatitis, hypertension, cataracts, arthritis, cancer are accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of silicon in tissues and organs, or disturbances in its metabolism.
Meanwhile, our body loses silicon daily - on average, we consume 3.5 mg of silicon per day with food and water, and lose about 9 mg!
Causes of silicon deficiency in the body:
Usually, a decrease in the content of silicon occurs against the background of general mineral deficiency and is accompanied by a deficiency of magnesium and calcium.
Signs of silicon deficiency:
It is known that the biological age of a person is determined by the rate of metabolic processes, i.e. rate of renewal as individual cells. And if many cosmetic preparations are able to solve the problem of moisturizing and protection to one degree or another, then the problem of accelerating metabolism requires a more intensive change in the outer layer of the skin.
The slowdown in skin regeneration processes begins at about 30 years of age. By this time, the body is already beginning to feel the lack of silicon. Our body cannot restore silicon deficiency on its own, since the natural silicon compounds surrounding us are mostly biologically inactive and are not able to participate in biochemical reactions inside the cell.
Silicon is an excellent cosmetic product. It cleanses the skin from pustular formations. It is especially useful to wash with silicon water, as well as take it inside with youthful acne. In the process of research, scientists have created a new class of organic silicon compounds that can accelerate metabolic processes in the skin and, by participating in the synthesis of elastin and collagen connective tissue proteins, increase skin elasticity and eliminate wrinkles.
Silicon-containing compounds patented by WGN accelerate metabolic processes in cells, regenerate elastin and collagen fibers. The results of the creation of active nanosilicon compounds formed the basis for the development of the NewAge line of so-called "nanosilicon" cosmetic preparations.
Bioactive nanosilicon penetrates into the deep layers of the skin, cleanses them and provides protection that preserves the natural permeability and breathability of the skin. Nonosilicon, stimulating the processes of proliferation and regeneration, accelerates the renewal of the epidermis and restores the functions of dermal cells - fibroblasts.
The advantages of silicon cosmetics are dermatological compatibility of the components; the possibility of using for any type of skin, including sensitive; high efficiency of action, soft stimulation of natural biochemical mechanisms of the functional state of the skin.
When interacting with water, flint changes its properties. Water activated by flint has a detrimental effect on microorganisms, suppresses bacteria that cause decay and fermentation, active precipitation of heavy metal compounds occurs in it, water becomes clean in appearance and pleasant in taste, it does not deteriorate for a long time and acquires many other healing qualities.
Flint belongs to the minerals of the quartz or chalcedony family. The group of these minerals includes carnelian, jasper, rock crystal, agate, opal, amethyst and many other stones. The basis of these minerals is silicon dioxide SiO2 or silica, but the density, color, and some other properties are different. The composition of flints, in addition to silica, includes about 20 chemical elements, the main of which are Mg, Ca, P, Sr, Mn, Cu, Zn, etc. Hence the so many names. But the most famous among the representatives of this family is undoubtedly flint.
The causes and mechanism of the interaction of flint with water have not been fully elucidated. Perhaps the healing effect of silicon is due to its ability to form special associates with water - colloids that absorb dirt and foreign microflora from the environment.
Speaking about the beneficial properties of silicon for the body, we first of all remember water. The human body contains about 70% water, and therefore it is difficult to imagine life without it. And if we take into account that all types of metabolism are carried out through the aquatic environment, that it is water that is the conductor of the vast majority of physiological life processes, that no form of life is possible without it - carbon, silicon or any other, then it becomes clear that water activated by flint acquires special meaning.
“... in the flint system - aqueous solutions Inorganic salts, intensive precipitation of a number of metals occurs: aluminum, iron, cadmium, cesium, zinc, lead, strontium.- P. Aladovsky, head of the laboratory of the Central Research Institute for the Use of Water Resources, Doctor of Chemical Sciences. In other words, flint displaces harmful metals from water, purifying it. They stay at the bottom, and clean water is on top.
“Water treated with flint affects the adsorption capacity of radionuclides. This, perhaps, will allow using it to solve some radiochemical problems on the territory of Belarus contaminated with radionuclides.”- Doctor of Chemistry Yu. Davydov - head of the laboratory of the Institute of Radiological Problems of the National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Belarus.
“Silicon water, starting from the fifth day of storage, has the ability to strengthen the hemostatic capabilities of blood, increases its ability to coagulate.” E. Ivanov - Director of the Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, MD. Hemophilia immediately comes to mind - a disease in which the blood does not clot well. And this means that a person who has received even a small scratch can die from blood loss.
“For several years, I have not observed cancer in many patients who consumed silicon-activated water (ACB). We found that on the 5th-6th day of taking batteries (6-8 times a day) in patients with numerous trophic ulcers of the lower extremities, the number of T- and B-lymphocytes increases. And this indicates the ability to renew lost and weakened immunity. In addition, AKB reduces the amount of cholesterol in the blood, especially in obesity. Thus, the battery serves to prevent atherosclerosis"- M. Sinyavsky Professor of the Department of Medical Training of Mogilevsky state university them. A.A. Kuleshova.
What is it - silicon water? Silicon water is a dark brown flint tincture that is used internally and externally. The method of preparing flint water is quite simple. In a 2-3 liter container, preferably glass, add 40-50 g of small flint pebbles, preferably intensely bright brown (but not black), pour in water from the water supply network, but better after normal filtration, and put it in a protected from direct sunlight place and outside the terrestrial pathogenic radiation.
Such water for drinking will be ready in 2-3 days. Subject to the same technology, but if you tie the neck with 2-3 layers of gauze and put water in a bright place at a temperature above 5 ° C for 5-7 days, then this water, by its properties, can be used not only as drinking water, but also for medical purposes. preventive purposes. It is useful to use it for cooking - tea, soups, etc. You can drink silicon water without restrictions (normally 1.5-2 liters per day). If it is not possible, then at least 3-5 times a day for half a glass and always in small sips and preferably in a cool form.
Use flint, as already mentioned, only bright brown (not black) color.
Only natural minerals should be used. The fact is that flint contains the remains of microorganisms, which at one time formed flint from the silt of the Cretaceous and more ancient eras.
After one or two uses, the stone should be washed with cool water and ventilated in the fresh air for 2 hours. If deposits or deposits appear on the surface of the stones, they must be immersed in a 2% solution of acetic acid or salted water for 2 hours; then rinse 2-3 times with ordinary water and dip for 2 hours in a solution of baking soda and rinse again.
Specific properties silicon water allow you to engage in the prevention of many diseases. Silicon water has a positive effect on the general condition of the body as a whole.
If you drink flint-activated water or cook food on it, the following happens:
- strengthening of the immune system, the number of T- and B-blood lymphocytes increases;
The condition of people suffering from liver diseases improves, because. water helps the outflow of bile;
Rapid healing of burns, cuts, bruises, trophic ulcers;
Helps with indigestion, relieves inflammation in the digestive tract and gastritis;
Decreased blood sugar levels, as well as weight, predisposed to overweight diabetics;
Lowering the level of cholesterol in the blood, especially in obesity, prevention of atherosclerosis and improving kidney function;
Normalizes the condition of patients suffering from hypertension;
Normalizes metabolism;
The general tone increases.
At outdoor application silicon water stimulates the body's recovery processes in:
- treatment of tonsillitis, runny nose, inflammation of the gums (gargling of the throat and mouth after eating);
With viral diseases of the oral cavity, stomatitis and gingivitis;
Treatment of allergies, boils, diathesis, dermatitis, various skin irritations (lotions and washing);
With conjunctivitis relieves itching and inflammation;
Washing with such water helps to improve the condition of the skin, reduce the number of wrinkles and prevent the appearance of new ones, helps eliminate bumps, blackheads, acne;
Rinsing the head and hair, rubbing into the scalp helps to strengthen and grow hair;
With some skin diseases (simple vesicular, herpes zoster and rose deprive).
- In case of falling out and "split" hair, rinse your head with "flint" water;
To relieve irritation after shaving, rinse your face with the same water;
With "youthful acne" wash and apply inside the "water";
Wipe the skin of the face with frozen "flint" water with pieces of ice;
To prevent paradanthosis, rinse the gums with "water" when brushing your teeth.
The use of “flint” water for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes contributes to the rapid healing of wounds, the prevention of the formation of tumors with regular intake of water, the improvement of blood composition, the restoration of adrenal function, the removal of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract and gastritis, the normalization of blood sugar, and the reduction weight, cure for fractures (bones grow together faster and without complications), improve kidney function and metabolism, separation and excretion of bile. Silicon water kills viruses; for prevention during respiratory epidemics, it is recommended to instill "water" into the nose. This helps with insomnia.
In the household, it is recommended to water the flowers, which lengthens the flowering period; accelerates the fruiting period of fruit trees and vegetable crops; increases yield by 10%. Kills mold, gray mold, in particular on strawberries, and other fungi. Soaking seeds in such water increases germination. Flowers are best stored in a container with silicon pebbles, their shelf life increases dramatically. In an aquarium, flint prevents the water from blooming. Silicon helps to purify water on a hike, which is important for tourists to know.
It is also useful to drink silicon water for atherosclerosis (vessels are cleared of sclerotic deposits), various metabolic disorders, tonsillitis, influenza, pharyngitis (rinsing with silicon water significantly reduces the duration of these diseases - after all, silicon acts as an antibiotic here), rheumatism, Botkin's disease (silicon kills pathogenic viruses), diseases of the teeth and joints (because silicon restores the integrity of bone tissues).
And now the most important point - contraindications. Silicon water has contraindications, and it must be handled very carefully. Doctors have noticed that those who have a predisposition to cancer, it is better to completely abandon it.
Silicon was discovered and obtained in 1823 by the Swedish chemist Jens Jakob Berzelius.
The second most abundant element in the earth's crust after oxygen (27.6% by mass). Found in compounds.
|
The structure of the silicon atom in the ground state 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 2 |
The structure of the silicon atom in an excited state 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 3p 3 Oxidation states: +4, -4. |
Allotropy of silicon
Amorphous and crystalline silicon are known.
polycrystalline silicon
Crystal - dark gray substance with a metallic sheen, high hardness, brittle, semiconductor; ρ \u003d 2.33 g / cm 3, t ° pl. =1415°C; t°boiling = 2680°C.
It has a diamond-like structure and forms strong covalent bonds. Inert.
Amorphous - brown powder, hygroscopic, diamond-like structure, ρ = 2 g/cm 3 , more reactive.
Getting silicon
1) Industry – heating coal with sand:
2C + SiO 2 t ˚ → Si + 2CO
2) Laboratory – heating sand with magnesium:
2Mg + SiO 2 t ˚ → Si + 2MgO Experience
Typical non-metal, inert.
As a restorer:
1) With oxygen
Si 0 + O 2 t ˚ → Si +4 O 2
2) With fluorine (without heating)
Si 0 + 2F 2 → SiF 4
3) With carbon
Si 0 + C t ˚ → Si +4 C
(SiC - carborundum - hard; used for pointing and grinding)
4) Does not interact with hydrogen.
Silane (SiH 4) is obtained by decomposition of metal silicides with acid:
Mg 2 Si + 2H 2 SO 4 → SiH 4 + 2MgSO 4
5) Does not react with acids (tonly with hydrofluoric acid Si+4 HF= SiF 4 +2 H 2 )
It dissolves only in a mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids:
3Si + 4HNO 3 + 18HF →3H 2 + 4NO + 8H 2 O
6) With alkalis (when heated):
As an oxidizing agent:
7) With metals (silicides are formed):
Si 0 + 2Mg t ˚ →Mg 2 Si -4
Silicon is widely used in electronics as a semiconductor. Silicon additions to alloys increase their corrosion resistance. Silicates, aluminosilicates and silica are the main raw materials for the production of glass and ceramics, as well as for the construction industry.Silicon in engineering
The use of silicon and its compounds
Silane - SiH 4
Physical properties: Colorless gas, poisonous, t°pl. = -185°C, bp = -112°C.
Obtaining silicic acid
The action of strong acids on silicates - Na 2 SiO 3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H 2 SiO 3 ↓
Chemical properties:
When heated, it decomposes: H 2 SiO 3 t ˚ → H 2 O + SiO 2
Salts of silicic acid - silicates.
1) with acids
Na 2 SiO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2 \u003d Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 SiO 3

2) with salts
Na 2 SiO 3 + CaCl 2 \u003d 2NaCl + CaSiO 3 ↓
3) Silicates, which are part of minerals, are destroyed under natural conditions under the action of water and carbon monoxide (IV) - weathering of rocks:
(K 2 O Al 2 O 3 6SiO 2) (feldspar) + CO 2 + 2H 2 O → (Al 2 O 3 2SiO 2 2H 2 O) (kaolinite (clay)) + 4SiO 2 (silica (sand)) + K2CO3
The use of silicon compounds

Natural silicon compounds - sand (SiO 2) and silicates are used for the production of ceramics, glass and cement.

|
Ceramics |
|
|
Porcelain= kaolin + clay + quartz + feldspar. The birthplace of porcelain is China, where porcelain has been known since 220. In 1746, the production of porcelain was established in Russia
|
Faience - from the name of the Italian city of Faenza. Where ceramic handicrafts were developed in the 14th and 15th centuries. Faience - differs from porcelain in a high content of clay (85%), a lower firing temperature. |
SILICON (Latin Silicium), Si, a chemical element of the IV group of the short form (the 14th group of the long form) of the periodic system; atomic number 14, atomic mass 28.0855. Natural silicon consists of three stable isotopes: 28 Si (92.2297%), 29 Si (4.6832%), 30 Si (3.0872%). Radioisotopes with mass numbers 22-42 are artificially obtained.
History reference. Silicon compounds, widespread on earth, have been used by man since the Stone Age; for example, from ancient times to the Iron Age, flint was used to make stone tools. The processing of silicon compounds - the manufacture of glass - began in the 4th millennium BC in Ancient Egypt. Elemental silicon was obtained in 1824-25 by J. Berzelius during the reduction of fluoride SiF 4 with metallic potassium. The name "silicon" was given to the new element (from the Latin silex - flint; the Russian name "silicon", introduced in 1834 by G. I. Hess, also comes from the word "flint").
Distribution in nature. In terms of prevalence in the earth's crust, silicon is the second chemical element (after oxygen): the silicon content in the lithosphere is 29.5% by weight. It does not occur in the free state in nature. The most important minerals containing silicon are aluminosilicates and natural silicates (natural amphiboles, feldspars, micas, etc.), as well as silica minerals (quartz and other polymorphic modifications of silicon dioxide).
Properties. The configuration of the outer electron shell of the silicon atom is 3s 2 3р 2 . In compounds, it exhibits an oxidation state of +4, rarely +1, +2, +3, -4; electronegativity according to Pauling 1.90, ionization potentials Si 0 → Si + → Si 2+ → Si 3+ → Si 4+, respectively, are 8.15, 16.34, 33.46 and 45.13 eV; atomic radius 110 pm, Si 4+ ion radius 40 pm (coordination number 4), 54 pm (coordination number 6).
Silicon is a dark gray hard brittle crystalline substance with a metallic sheen. The crystal lattice is cubic face-centered; t pl 1414 ° С, t kip 2900 ° С, density 2330 kg / m 3 (at 25 ° С). Heat capacity 20.1 J/(mol∙K), thermal conductivity 95.5 W/(m∙K), dielectric constant 12; Mohs hardness 7. Under normal conditions, silicon is a brittle material; noticeable plastic deformation is observed at temperatures above 800 °C. Silicon is transparent to infrared radiation with a wavelength greater than 1 micron (refractive index 3.45 at a wavelength of 2-10 microns). Diamagnetic (magnetic susceptibility - 3.9∙10 -6). Silicon is a semiconductor, the band gap is 1.21 eV (0 K); specific electrical resistance 2.3 ∙ 10 3 Ohm ∙ m (at 25 ° C), electron mobility 0.135-0.145, holes - 0.048-0.050 m 2 / (V s). The electrical properties of silicon are highly dependent on the presence of impurities. To obtain silicon single crystals with p-type conductivity, dopants B, Al, Ga, In (acceptor impurities) are used, with n-type conductivity - P, As, Sb, Bi (donor impurities).
Silicon in air is covered with an oxide film, therefore, at low temperatures it is chemically inert; when heated above 400 ° C, it interacts with oxygen (oxide SiO and dioxide SiO 2 are formed), halogens (silicon halides), nitrogen (silicon nitride Si 3 N 4), carbon (silicon carbide SiC), etc. Silicon compounds with hydrogen - silanes are obtained indirectly. Silicon interacts with metals to form silicides.
Finely dispersed silicon is a reducing agent: when heated, it interacts with water vapor to release hydrogen, reduces metal oxides to free metals. Non-oxidizing acids passivate silicon due to the formation of an acid-insoluble oxide film on its surface. Silicon dissolves in a mixture of concentrated HNO 3 with HF, and fluorosilicic acid is formed: 3Si + 4HNO 3 + 18HF \u003d 3H 2 + 4NO + 8H 2 O. Silicon (especially finely dispersed) interacts with alkalis to release hydrogen, for example: Si + 2NaOH + H 2 O \u003d Na 2 SiO 3 + 2H 2. Silicon forms various organosilicon compounds.
biological role. Silicon belongs to microelements. The daily human need for silicon is 20-50 mg (an element is necessary for the proper growth of bones and connective tissues). Silicon enters the human body with food, as well as with inhaled air in the form of dusty SiO 2 . With prolonged inhalation of dust containing free SiO 2, silicosis occurs.
Receipt. Silicon of technical purity (95-98%) is obtained by reduction of SiO 2 with carbon or metals. High-purity polycrystalline silicon is obtained by reduction of SiCl 4 or SiHCl 3 with hydrogen at a temperature of 1000-1100 ° C, thermal decomposition of Sil 4 or SiH 4; single-crystal silicon of high purity - by zone melting or by the Czochralski method. The volume of world production of silicon is about 1600 thousand tons / year (2003).
Application. Silicon is the main material of microelectronics and semiconductor devices; used in the manufacture of glasses that are transparent to infrared radiation. Silicon is a component of alloys of iron and non-ferrous metals (in low concentrations, silicon increases the corrosion resistance and mechanical strength of alloys, improves their casting properties; in high concentrations, it can cause brittleness); iron, copper and aluminum silicon-containing alloys are of the greatest importance. Silicon is used as a starting material for the production of organosilicon compounds and silicides.
Lit .: Baransky P. I., Klochkov V. P., Potykevich I. V. Semiconductor electronics. Properties of materials: Handbook. K., 1975; Drozdov A. A., Zlomanov V. P., Mazo G. N., Spiridonov F. M. Inorganic chemistry. M., 2004. T. 2; Shriver D., Atkins P. Inorganic Chemistry. M., 2004. T. 1-2; Silicon and its alloys. Yekaterinburg, 2005.
CPU? Sand? What associations do you have with this word? Or maybe Silicon Valley?
Be that as it may, we encounter silicon every day, and if you are interested in knowing what Si is and what it is eaten with, please under cat.
Introduction
As a student of one of the Moscow universities with a degree in Nanomaterials, I wanted to introduce you, dear reader, to the most important chemical elements of our planet. I chose for a long time where to start, carbon or silicon, and yet I decided to focus on Si, because the heart of any modern gadget is based on it, so to speak, of course. I will try to express my thoughts in an extremely simple and accessible way, by writing this material I was counting mainly on beginners, but more advanced people will be able to learn something interesting, I would also like to say that the article was written solely to broaden the horizons of those interested. So let's get started.Silicium
Silicon (lat. Silicium), Si, a chemical element of group IV of the periodic system of Mendeleev; atomic number 14, atomic mass 28.086.In nature, the element is represented by three stable isotopes: 28Si (92.27%), 29Si (4.68%) and 30Si (3.05%).
Density (N.C.) 2.33 g/cm³
Melting point 1688 K

Powder Si
History reference
Silicon compounds, widely distributed on earth, have been known to man since the Stone Age. The use of stone tools for labor and hunting continued for several millennia. The use of silicon compounds associated with their processing - the manufacture of glass - began around 3000 BC. e. (in ancient Egypt). The earliest known Silicon compound is SiO2 oxide (silica). In the 18th century, silica was considered a simple body and referred to as "earths" (which is reflected in its name). The complexity of the composition of silica was established by I. Ya. Berzelius. He was the first, in 1825, to obtain elemental silicon from silicon fluoride SiF4, reducing the latter with metallic potassium. The name "silicon" was given to the new element (from Latin silex - flint). The Russian name was introduced by G.I. Hess in 1834.
Silicon is very common in nature in the composition of ordinary sand.
Distribution of silicon in nature
In terms of prevalence in the earth's crust, silicon is the second (after oxygen) element, its average content in the lithosphere is 29.5% (by mass). In the earth's crust, silicon plays the same primary role as carbon in animals and flora. For the geochemistry of silicon, its exceptionally strong bond with oxygen is important. About 12% of the lithosphere is silica SiO2 in the form of the mineral quartz and its varieties. 75% of the lithosphere is composed of various silicates and aluminosilicates (feldspars, micas, amphiboles, etc.). Total number minerals containing silica exceeds 400.Physical properties of Silicon
I don't think it's worth stopping here. physical properties are freely available, but I will list the most basic ones.Boiling point 2600 °C
Silicon is transparent to long-wave infrared rays
Dielectric constant 11.7
Silicon Mohs Hardness 7.0
I would like to say that silicon is a brittle material, noticeable plastic deformation begins at temperatures above 800°C.
Silicon is a semiconductor, which is why it is of great use. The electrical properties of silicon are highly dependent on impurities.
Chemical Properties of Silicon
There's a lot to be said, of course, but I'll focus on the most interesting. In Si compounds (similar to carbon) is 4-valent.Due to the formation of a protective oxide film, silicon is stable in air even at elevated temperatures. In oxygen, it oxidizes starting from 400 °C, forming silicon oxide (IV) SiO2.
Silicon is resistant to acids and dissolves only in a mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids, easily dissolves in hot alkali solutions with hydrogen evolution.
Silicon forms 2 groups of oxygen-containing silanes - siloxanes and siloxenes. Silicon reacts with nitrogen at temperatures above 1000 ° C, Important practical value has Si3N4 nitride, which does not oxidize in air even at 1200 °C, is resistant to acids (except nitric acid) and alkalis, as well as to molten metals and slags, which makes it a valuable material for the chemical industry, as well as for the production of refractories. Silicon compounds with carbon (silicon carbide SiC) and boron (SiB3, SiB6, SiB12) are characterized by high hardness, as well as thermal and chemical resistance.
Obtaining Silicon
I think this is the most interesting part, here we will stop in more detail.Depending on the purpose, there are:
1. Silicon of electronic quality(so-called "electronic silicon") - the highest quality silicon with a silicon content of more than 99.999% by weight, the electrical resistivity of electronic quality silicon can be in the range from about 0.001 to 150 ohm cm, but the resistance value must be provided exclusively a given impurity, i.e., the ingress of other impurities into the crystal, even if they provide a given electrical resistivity, as a rule, is unacceptable.
2. Solar Grade Silicon(the so-called "solar silicon") - silicon with a silicon content of more than 99.99% by weight, used for the production of photovoltaic converters (solar batteries).

3. Technical silicon- silicon blocks of polycrystalline structure obtained by carbothermal reduction from pure quartz sand; contains 98% silicon, the main impurity is carbon, it has a high content of alloying elements - boron, phosphorus, aluminum; mainly used to obtain polycrystalline silicon.
Silicon of technical purity (95-98%) is obtained in an electric arc by the reduction of silica SiO2 between graphite electrodes. In connection with the development of semiconductor technology, methods have been developed for obtaining pure and extra pure silicon. This requires a preliminary synthesis of the purest initial silicon compounds, from which silicon is extracted by reduction or thermal decomposition.
Polycrystalline silicon ("polysilicon") - the purest form of industrially produced silicon - a semi-finished product obtained by cleaning technical silicon by chloride and fluoride methods and used for the production of mono- and multi-crystalline silicon.
Traditionally, polycrystalline silicon is obtained from technical silicon by converting it into volatile silanes (monosilane, chlorosilanes, fluorosilanes), followed by separation of the resulting silanes, distillation purification of the selected silane, and reduction of the silane to metallic silicon.
Pure semiconductor silicon is obtained in two forms: polycrystalline(reduction of SiCl4 or SiHCl3 with zinc or hydrogen, thermal decomposition of SiI4 and SiH4) and monocrystalline(crucible-free zone melting and "pulling" of a single crystal from molten silicon - the Czochralski method). 
Here you can see the process of growing silicon using the Czochralski method.
Czochralski method- a method of growing crystals by pulling them up from the free surface of a large volume of the melt with the initiation of the onset of crystallization by bringing a seed crystal (or several crystals) of a given structure and crystallographic orientation into contact with the free surface of the melt.
Silicon Application
Specially doped silicon is widely used as a material for the manufacture of semiconductor devices (transistors, thermistors, power rectifiers, thyristors; solar photocells used in spaceships, as well as a lot of stuff).Since silicon is transparent to rays with a wavelength of 1 to 9 microns, it is used in infrared optics.
Silicon has diverse and ever-expanding applications. In metallurgy Si
used to remove oxygen dissolved in molten metals (deoxidation).
Silicon is an integral part a large number alloys of iron and non-ferrous metals.
Silicon usually gives alloys increased resistance to corrosion, improves their casting properties and increases mechanical strength; however, at higher levels, silicon can cause brittleness.
Highest value have iron, copper and aluminum alloys containing silicon.
Silica is processed by glass, cement, ceramic, electrical and other industries.
Ultra-pure silicon is mainly used for the production of single electronic devices (for example, your computer processor) and single-chip microcircuits.
Pure silicon, ultra-pure silicon waste, refined metallurgical silicon in the form of crystalline silicon are the main raw materials for solar energy.
Monocrystalline silicon - in addition to electronics and solar energy, it is used to make mirrors for gas lasers.

Ultrapure silicon and its product
Silicon in the body
Silicon is found in the body in the form of various compounds involved mainly in the formation of solid skeletal parts and tissues. Especially a lot of silicon can be accumulated by some marine plants (for example, diatoms) and animals (for example, silicon-horned sponges, radiolarians), which form powerful deposits of silicon oxide (IV) when dying on the ocean floor. In cold seas and lakes, biogenic silts enriched with silicon predominate, in tropical seas - calcareous silts with a low content of silicon. Among terrestrial plants, cereals, sedges, palms, and horsetails accumulate a lot of silicon. In vertebrates, the content of silicon oxide (IV) in ash substances is 0.1-0.5%. Silicon is found in the largest quantities in dense connective tissue, kidneys, and pancreas. AT daily diet human contains up to 1 g of silicon. With a high content of silicon oxide (IV) dust in the air, it enters the lungs of a person and causes a disease - silicosis.Conclusion
Well, that's all, if you read to the end and delved a little, then you are one step closer to success. I hope I wrote not in vain and at least someone liked the post. Thank you for your attention.Silicon compounds, widely distributed on earth, have been known to man since the Stone Age. The use of stone tools for labor and hunting continued for several millennia. The use of silicon compounds associated with their processing - the manufacture of glass - began around 3000 BC. e. (in ancient Egypt). The earliest known Silicon compound is SiO 2 oxide (silica). In the 18th century, silica was considered a simple body and referred to "earths" (which is reflected in its name). The complexity of the composition of silica was established by I. Ya. Berzelius. He was the first, in 1825, to obtain elemental silicon from silicon fluoride SiF 4 , reducing the latter with metallic potassium. The new element was given the name "silicon" (from the Latin silex - flint). The Russian name was introduced by G.I. Hess in 1834.
Distribution of Silicon in nature. In terms of prevalence in the earth's crust, silicon is the second (after oxygen) element, its average content in the lithosphere is 29.5% (by mass). In the earth's crust, silicon plays the same primary role as carbon in the animal and plant kingdoms. For the geochemistry of silicon, its exceptionally strong bond with oxygen is important. About 12% of the lithosphere is silica SiO 2 in the form of the mineral quartz and its varieties. 75% of the lithosphere is composed of various silicates and aluminosilicates (feldspars, micas, amphiboles, etc.). The total number of minerals containing silica exceeds 400.
Silicon is weakly differentiated during magmatic processes: it accumulates both in granitoids (32.3%) and in ultramafic rocks (19%). At high temperatures and high pressures, the solubility of SiO 2 increases. It can also migrate with water vapor; therefore, pegmatites of hydrothermal veins are characterized by significant concentrations of quartz, which is often associated with ore elements (gold-quartz, quartz-cassiterite, and other veins).
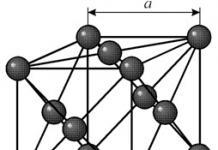
Physical properties of Silicon. Silicon forms dark gray crystals with a metallic sheen, having a cubic face-centered diamond-type lattice with a period a = 5.431Å, density 2.33 g/cm 3 . At very high pressures a new (apparently hexagonal) modification with a density of 2.55 g/cm 3 was obtained. Silicon melts at 1417°C and boils at 2600°C. Specific heat capacity (at 20-100 °C) 800 J/(kg K), or 0.191 cal/(g deg); thermal conductivity, even for the purest samples, is not constant and is in the range (25 ° C) 84-126 W / (m K), or 0.20-0.30 cal / (cm s deg). Temperature coefficient linear expansion 2,33·10 -6 K -1 below 120 K becomes negative. Silicon is transparent to long-wave infrared rays; refractive index (for λ = 6 μm) 3.42; dielectric constant 11.7. Silicon is diamagnetic, atomic magnetic susceptibility -0.13-10 -6. Silicon hardness according to Mohs 7.0, according to Brinell 2.4 Gn / m 2 (240 kgf / mm 2), modulus of elasticity 109 Gn / m 2 (10 890 kgf / mm 2), compressibility coefficient 0.325 10 -6 cm 2 /kg. Silicon is a brittle material; noticeable plastic deformation begins at temperatures above 800°C.
Silicon is a semiconductor with a wide range of applications. The electrical properties of Silicon are highly dependent on impurities. The intrinsic specific volume electrical resistance of Silicon at room temperature is assumed to be 2.3·10 3 ohm·m (2.3·10 5 ohm·cm).
Semiconductor Silicon with p-type conductivity (additives B, Al, In or Ga) and n-type (additives P, Bi, As or Sb) has a much lower resistance. The band gap according to electrical measurements is 1.21 eV at 0 K and decreases to 1.119 eV at 300 K.
Chemical properties of Silicon. In accordance with the position of Silicon in periodic system Mendeleev, 14 electrons of the silicon atom are distributed over three shells: in the first (from the nucleus) 2 electrons, in the second 8, in the third (valence) 4; electron shell configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 2 . Sequential ionization potentials (eV): 8.149; 16.34; 33.46 and 45.13. Atomic radius 1.33Å, covalent radius 1.17Å, ionic radii Si 4+ 0.39Å, Si 4- 1.98Å.
In compounds Silicon (similar to carbon) is 4-valent. However, unlike carbon, Silicon, along with a coordination number of 4, exhibits a coordination number of 6, which is explained by the large volume of its atom (silicone fluorides containing a 2- group are an example of such compounds).
The chemical bonding of the Silicon atom with other atoms is usually carried out through hybrid sp 3 orbitals, but it is also possible to involve two of its five (vacant) 3d orbitals, especially when Silicon is six-coordinated. Having a low electronegativity value of 1.8 (against 2.5 for carbon; 3.0 for nitrogen, etc.), silicon in compounds with non-metals is electropositive, and these compounds are polar in nature. The high bonding energy with oxygen Si - O, equal to 464 kJ / mol (111 kcal / mol), determines the stability of its oxygen compounds (SiO 2 and silicates). The Si-Si bond energy is low, 176 kJ/mol (42 kcal/mol); unlike carbon, silicon is not characterized by the formation of long chains and a double bond between Si atoms. Due to the formation of a protective oxide film, silicon is stable even at elevated temperatures in air. In oxygen, it oxidizes starting from 400 ° C, forming silicon oxide (IV) SiO 2. Silicon oxide (II) SiO is also known, which is stable at high temperatures in the form of a gas; as a result of rapid cooling, a solid product can be obtained, which easily decomposes into a thin mixture of Si and SiO 2 . Silicon is resistant to acids and dissolves only in a mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids; easily dissolves in hot alkali solutions with evolution of hydrogen. Silicon reacts with fluorine at room temperature, with other halogens - when heated to form compounds general formula SiX4. Hydrogen does not directly react with Silicon, and silicon hydrides (silanes) are obtained by decomposition of silicides (see below). Silicon hydrogens are known from SiH 4 to Si 8 H 18 (similar in composition to saturated hydrocarbons). Silicon forms 2 groups of oxygen-containing silanes - siloxanes and siloxenes. Silicon reacts with nitrogen at temperatures above 1000 ° C. Si 3 N 4 nitride is of great practical importance, it does not oxidize in air even at 1200 ° C, it is resistant to acids (except nitric acid) and alkalis, as well as to molten metals and slags , which makes it a valuable material for the chemical industry, for the production of refractories and others. Silicon compounds with carbon (silicon carbide SiC) and boron (SiB 3 , SiB 6 , SiB 12) are characterized by high hardness, as well as thermal and chemical resistance. When heated, silicon reacts (in the presence of metal catalysts, such as copper) with organochlorine compounds (for example, with CH 3 Cl) to form organohalosilanes [for example, Si(CH 3) 3 Cl], which are used for the synthesis of numerous organosilicon compounds.
Silicon forms compounds with almost all metals - silicides (compounds were not found only with Bi, Tl, Pb, Hg). More than 250 silicides have been obtained, the composition of which (MeSi, MeSi 2 , Me 5 Si 3 , Me 3 Si, Me 2 Si and others) usually does not correspond to classical valencies. Silicides are distinguished by their refractoriness and hardness; of greatest practical importance are ferrosilicon (a reducing agent in the smelting of special alloys, see Ferroalloys) and molybdenum silicide MoSi 2 (electric furnace heaters, gas turbine blades, etc.).
Getting Silicon. Silicon of technical purity (95-98%) is obtained in an electric arc by the reduction of silica SiO 2 between graphite electrodes. In connection with the development of semiconductor technology, methods have been developed for obtaining pure and especially pure silicon This requires a preliminary synthesis of the purest initial silicon compounds, from which silicon is extracted by reduction or thermal decomposition.
Pure semiconductor Silicon is obtained in two forms: polycrystalline (by reduction of SiCl 4 or SiHCl 3 with zinc or hydrogen, thermal decomposition of SiI 4 and SiH 4) and single-crystal (by crucibleless zone melting and "pulling" a single crystal from molten silicon - the Czochralski method).
The use of silicon. Specially doped silicon is widely used as a material for the manufacture of semiconductor devices (transistors, thermistors, power rectifiers, thyristors; solar photocells used in spacecraft, etc.). Since silicon is transparent to rays with a wavelength of 1 to 9 microns, it is used in infrared optics,
Silicon has diverse and ever-expanding applications. In metallurgy, silicon is used to remove oxygen dissolved in molten metals (deoxidation). Silicon is an integral part of a large number of iron and non-ferrous alloys. Silicon usually gives alloys increased resistance to corrosion, improves their casting properties and increases mechanical strength; however, at higher levels, silicon can cause brittleness. The most important are iron, copper and aluminum alloys containing Silicon. All large quantity Silicon is used for the synthesis of organosilicon compounds and silicides. Silica and many silicates (clays, feldspars, micas, talcs, etc.) are processed by the glass, cement, ceramic, electrical and other industries.
Silicon is found in the body in the form of various compounds involved mainly in the formation of solid skeletal parts and tissues. Some marine plants (for example, diatoms) and animals (for example, silicon-horned sponges, radiolarians) can accumulate especially much silicon, forming thick deposits of silicon (IV) oxide on the ocean floor when they die. In cold seas and lakes, biogenic silts enriched with Silicon predominate in the tropical. seas - calcareous silts with a low content of Silicon. Among terrestrial plants, grasses, sedges, palms, and horsetails accumulate a lot of Silicon. In vertebrates, the content of silicon oxide (IV) in ash substances is 0.1-0.5%. Silicon is found in the largest quantities in dense connective tissue, kidneys, and pancreas. The daily human diet contains up to 1 g of Silicon. With a high content of silicon oxide (IV) dust in the air, it enters the lungs of a person and causes a disease - silicosis.
Silicon in the body. Silicon is found in the body in the form of various compounds involved mainly in the formation of solid skeletal parts and tissues. Some marine plants (for example, diatoms) and animals (for example, silicon-horned sponges, radiolarians) can accumulate especially much silicon, forming thick deposits of silicon (IV) oxide on the ocean floor when they die. In cold seas and lakes, biogenic silts enriched with Silicon predominate in the tropical. seas - calcareous silts with a low content of Silicon. Among terrestrial plants, grasses, sedges, palms, and horsetails accumulate a lot of Silicon. In vertebrates, the content of silicon oxide (IV) in ash substances is 0.1-0.5%. Silicon is found in the largest quantities in dense connective tissue, kidneys, and pancreas. The daily human diet contains up to 1 g of Silicon. With a high content of silicon oxide (IV) dust in the air, it enters the lungs of a person and causes a disease - silicosis.