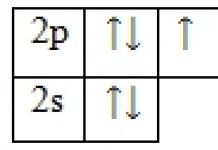
What is biochemistry? Biological or physiological biochemistry is the science of chemical processes that underlie the life of an organism and those that occur inside a cell. The purpose of biochemistry (the term comes from Greek word"bios" - "life") as science is the study chemical substances, structure and metabolism of cells, the nature and methods of its regulation, the mechanism of energy supply for processes within cells.
Medical biochemistry: the essence and goals of science
Medical biochemistry is a section that studies the chemical composition of the cells of the human body, the metabolism in it (including in pathological conditions). After all, any disease, even in an asymptomatic period, will inevitably leave its mark on the chemical processes in cells and the properties of molecules, which will be reflected in the results of biochemical analysis. Without knowledge of biochemistry, it is impossible to find the cause of the disease and the way to effectively treat it.
Biochemical blood test
What is a blood chemistry test? Biochemical blood testing is one of the laboratory diagnostic methods in many areas of medicine (for example, endocrinology, therapy, gynecology).
It helps to accurately diagnose the disease and examine a blood sample using the following parameters:
Alanine aminotransferase (ALAT, ALT);
Cholesterol or cholesterol;
Bilirubin;
Urea;
Diastasis;
Glucose, lipase;
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AST);
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), gamma GT (glutamyl transpeptidase);
Creatinine, protein;
Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus.
For the health of every person, it is important to know what blood biochemistry is and to understand that its indicators will not only provide all the data for an effective treatment regimen, but will also help prevent disease. Deviations from normal values are the first signal that something is wrong in the body.
blood for liver research: significance and goals

In addition, biochemical diagnostics will allow monitoring the dynamics of the disease and the results of treatment, creating a complete picture of metabolism, deficiency of microelements in organ function. For example, liver biochemistry will be a mandatory test for people with liver dysfunction. What is this? That's what they call it biochemical analysis blood to study the quantity and quality of liver enzymes. If their synthesis is impaired, then this condition threatens the development of diseases and inflammatory processes.
Specifics of liver biochemistry
Biochemistry of the liver - what is it? The human liver consists of water, lipids, and glycogen. Its tissues contain minerals: copper, iron, nickel, manganese, so the biochemical study of liver tissue is a very informative and quite effective analysis. The most important enzymes in the liver are glucokinase and hexokinase. The following liver enzymes are most sensitive to biochemical tests: alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST). As a rule, the study is guided by the indicators of these substances.
For complete and successful monitoring of their health, everyone should know what “biochemistry analysis” is.
Areas of biochemistry research and the importance of correct interpretation of analysis results
What does biochemistry study? First of all, metabolic processes, the chemical composition of the cell, chemical nature and the function of enzymes, vitamins, acids. It is possible to evaluate blood parameters using these parameters only if the analysis is correctly interpreted. If everything is fine, then blood parameters for various parameters (glucose level, protein, blood enzymes) should not deviate from the norm. Otherwise, this should be regarded as a signal of a malfunction of the body.
Decoding biochemistry
How to decipher the numbers in the analysis results? Below are the main indicators.

Glucose
The glucose level shows the quality of the carbohydrate metabolism process. The limiting norm of content should not exceed 5.5 mmol/l. If the level is lower, this may indicate diabetes, endocrine diseases, and liver problems. Increased level glucose may be due to diabetes, physical activity, or hormonal medications.
Protein
Cholesterol
Urea
This is the name given to the end product of protein breakdown. U healthy person it must be completely excreted from the body in urine. If this does not happen, and it gets into the blood, then you should definitely check your kidney function.
Hemoglobin
This is a red blood cell protein that saturates the body's cells with oxygen. Norm: for men - 130-160 g/l, for girls - 120-150 g/l. Low level hemoglobin in the blood is considered one of the indicators of developing anemia.
Biochemical blood test for blood enzymes (ALAT, AST, CPK, amylase)
Enzymes are responsible for the proper functioning of the liver, heart, kidneys, and pancreas. Without the required amount, a complete exchange of amino acids is simply impossible.
The level of aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AST - a cellular enzyme of the heart, kidneys, liver) should not be higher than 41 and 31 units/l for men and women, respectively. Otherwise, this may indicate the development of hepatitis and heart disease.
Lipase (an enzyme that breaks down fats) plays an important role in metabolism and should not exceed 190 units/l. An elevated level indicates a malfunction of the pancreas.
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of biochemical analysis for blood enzymes. Every person who cares about their health must know what biochemistry is and what it studies.
Amylase
This enzyme is found in the pancreas and saliva. It is responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrates and their absorption. Norm - 28-100 units/l. Its high level in the blood may indicate renal failure, cholecystitis, diabetes mellitus, peritonitis.
The results of a biochemical blood test are recorded on a special form, which indicates the levels of substances. Often this analysis is prescribed as an additional one to clarify the intended diagnosis. When deciphering the results of blood biochemistry, keep in mind that they are also influenced by the patient’s gender, age and lifestyle. Now you know what biochemistry studies and how to correctly interpret its results.
How to properly prepare for donating blood for biochemistry?
Acute diseases internal organs;
Intoxication;
Vitamin deficiency;
Inflammatory processes;
For the prevention of diseases during pregnancy;
To clarify the diagnosis.
Blood for analysis is taken early in the morning, and you cannot eat before coming to the doctor. Otherwise, the analysis results will be distorted. A biochemical study will show how correct your metabolism and salts in the body are. In addition, refrain from drinking sweet tea, coffee, or milk at least an hour or two before blood sampling.
Be sure to answer the question of what biochemistry is before taking the test. Knowing the process and its significance will help you correctly assess your health status and be competent in medical matters.
How is blood taken for biochemistry?
The procedure does not last long and is practically painless. From a person in a sitting position (sometimes they offer to lie down on the couch), the doctor takes it after applying a tourniquet. The injection site must be treated with an antiseptic. The collected sample is placed in a sterile tube and sent for analysis to the laboratory.

Quality control of biochemical research is carried out in several stages:
Preanalytical (patient preparation, analysis, transportation to the laboratory);
Analytical (processing and storage of biomaterial, dosing, reaction, result analysis);
Post-analytical (filling out a form with the result, laboratory and clinical analysis, sending to the doctor).
The quality of the biochemistry result depends on the appropriateness of the chosen research method, the competence of laboratory technicians, the accuracy of measurements, technical equipment, the purity of reagents, and adherence to diet.
Biochemistry for hair
What is biochemistry for hair? Biocurling is a method of long-term curling of curls. The difference between a regular perm and a bioperm is fundamental. In the latter case, hydrogen peroxide, ammonia, and thioglycolic acid are not used. The role of the active substance is played by a cystine analogue (biological protein). This is where the name of the hair styling method comes from.

The undoubted advantages are:
Gentle effect on the hair structure;
Blurred line between regrown and bio-permed hair;
The procedure can be repeated without waiting for its effect to completely disappear.
But before going to the master, you should consider the following nuances:
The biowave technology is relatively complex, and you need to be meticulous in choosing a specialist;
The effect is short-lived, about 1-4 months (especially on hair that has not been permed, dyed, or has a dense structure);
Biowave is not cheap (on average 1500-3500 rubles).
Biochemistry methods
What is biochemistry and what methods are used for research? Their choice depends on its purpose and the tasks set by the doctor. They are called upon to study bio chemical structure cells, examine the sample for possible deviations from the norm and thus help diagnose the disease, find out the dynamics of recovery, etc.

Biochemistry is one of the most effective tests for clarifying, making a diagnosis, monitoring treatment, and determining a successful treatment regimen.
Biochemistry (from the Greek “bios” - “life”, biological or physiological) is a science that studies chemical processes inside a cell that affect the functioning of the entire organism or its specific organs. The goal of the science of biochemistry is knowledge chemical elements, composition and process of metabolism, methods of its regulation in the cell.
According to other definitions, biochemistry is the science of the chemical structure of cells and organisms of living beings.
To understand why biochemistry is needed, let’s imagine the sciences in the form of an elementary table. As you can see, the basis for all sciences is anatomy, histology and cytology, which study all living things.
On their basis, biochemistry, physiology and pathophysiology are built, where they study the functioning of organisms and the chemical processes within them. Without these sciences, the rest that are represented in the upper sector will not be able to exist.
- There is another approach, according to which sciences are divided into 3 types (levels):
- Those that study the cellular, molecular and tissue level of life (the sciences of anatomy, histology, biochemistry, biophysics);
- Study pathological processes and diseases (pathophysiology, pathological anatomy);
Diagnose the body's external response to disease (clinical sciences such as medicine and surgery).
This is how we found out what place biochemistry, or, as it is also called, medical biochemistry, occupies among the sciences. After all, any abnormal behavior of the body, the process of its metabolism will affect the chemical structure of cells and will manifest itself during the LHC.
Why are tests taken? What does a biochemical blood test show?
Blood biochemistry is a laboratory diagnostic method that shows diseases in various areas of medicine (for example, therapy, gynecology, endocrinology) and helps determine the functioning of internal organs and the quality of metabolism of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates, as well as the sufficiency of microelements in the body.
BAC, or biochemical blood test, is an analysis that provides the broadest information regarding a variety of diseases.
 Based on its results, you can find out the functional state of the body and each organ in a separate case, because any ailment that attacks a person will one way or another manifest itself in the results of the LHC. Therefore, a distinction is made between standard and complex tanks. The standard one is prescribed in most cases, but the extended one with additional indicators is prescribed by the doctor if he needs to find out additional nuances depending on the symptoms of the disease and the purpose of the analysis.
Based on its results, you can find out the functional state of the body and each organ in a separate case, because any ailment that attacks a person will one way or another manifest itself in the results of the LHC. Therefore, a distinction is made between standard and complex tanks. The standard one is prescribed in most cases, but the extended one with additional indicators is prescribed by the doctor if he needs to find out additional nuances depending on the symptoms of the disease and the purpose of the analysis.
Basic indicators.
- Total protein in the blood (TP, Total Protein).
- Bilirubin.
- Glucose, lipase.
- ALT (Alanine aminotransferase, ALT) and AST (Aspartate aminotransferase, AST).
- Creatinine.
- Urea.
- Electrolytes (Potassium, K/Calcium, Ca/Sodium, Na/Chlorine, Cl/Magnesium, Mg).
- Total cholesterol.
The expanded profile includes any of these additional indicators (as well as others, very specific and narrowly focused, not indicated in this list).

Biochemical general therapeutic standard: adult norms
| Blood chemistry | Norms |
|---|---|
| (TANK) | |
| Total protein | from 63 to 85 g/liter |
| Bilirubin (direct, indirect, total) | total up to 5-21 µmol/liter |
| direct – up to 7.9 mmol/liter | |
| indirect - calculated as the difference between direct and indirect indicators | |
| Glucose | from 3.5 to 5.5 mmol/liter |
| Lipase | up to 490 U/liter |
| AlAT and AsAT | for men – up to 41 units/liter |
| for women – up to 31 units/liter | |
| Creatinine phosphokinase | up to 180 U/liter |
| ALKP | up to 260 U/liter |
| Urea | from 2.1 to 8.3 mmol/l |
| Amylase | from 28 to 100 U/l |
| Creatinine | for men – from 62 to 144 µmol/liter |
| for women – from 44 to 97 µmol/liter | |
| Bilirubin | from 8.48 to 20.58 µmol/liter |
| LDH | from 120-240 U/liter |
| Cholesterol | from 2.97 to 8.79 mmol/liter |
| Electrolytes | K from 3.5 to 5.1 mmol/liter |
| Ca from 1.17 to 1.29 mmol/liter | |
| Na from 139 to 155 mmol/liter | |
| Cl from 98 to 107 mmol/liter | |
| Mg from 0.66 to 1.07 mmol/liter |
Decoding biochemistry
The decoding of the data described above is carried out according to certain values and standards.
- Total protein is the amount of total protein found in the human body. Exceeding the norm indicates various inflammations in the body (problems of the liver, kidneys, genitourinary system, burn disease or cancer), with dehydration (dehydration) during vomiting, sweating in particularly large quantities, intestinal obstruction or multiple myeloma, deficiency - an imbalance in a nutritious diet, prolonged fasting, intestinal disease, liver disease, or in case of impaired synthesis as a result of hereditary diseases.
 Albumen‒ this is a highly concentrated protein fraction contained in the blood. It binds water, and its low amount leads to the development of edema - water is not retained in the blood and enters the tissues. Usually, if protein decreases, then the amount of albumin decreases.
Albumen‒ this is a highly concentrated protein fraction contained in the blood. It binds water, and its low amount leads to the development of edema - water is not retained in the blood and enters the tissues. Usually, if protein decreases, then the amount of albumin decreases.- General analysis of bilirubin in plasma(direct and indirect) - this is the diagnosis of a pigment that is formed after the breakdown of hemoglobin (it is toxic for humans). Hyperbilirubinemia (exceeding the level of bilirubin) is called jaundice, and clinical jaundice is subhepatic (including in newborns), hepatocellular and subhepatic. It indicates anemia, extensive hemorrhages subsequently hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, liver destruction, oncology and other diseases. It is scary because of liver pathology, but it can also increase in a person who has suffered blows and injuries.
- Glucose. Its level determines carbohydrate metabolism, that is, energy in the body, and how the pancreas works. If there is a lot of glucose, it may be diabetes, physical activity, or the effect of taking hormonal drugs; if there is little, it may be hyperfunction of the pancreas, diseases of the endocrine system.
- Lipase – It is a fat-breaking enzyme that plays an important role in metabolism. Its increase indicates pancreatic disease.
- ALT– “liver marker”; it is used to monitor pathological processes in the liver. An increased rate indicates problems with the heart, liver or hepatitis (viral).
- AST– “heart marker”, it shows the quality of the heart. Exceeding the norm indicates a disruption of the heart and hepatitis.
- Creatinine– provides information about the functioning of the kidneys. It is elevated if a person has acute or chronic kidney disease or there is destruction of muscle tissue or endocrine disorders. Increased in people who eat a lot of meat products. And therefore, creatinine is lowered in vegetarians, as well as in pregnant women, but it will not greatly affect the diagnosis.

 Urea analysis- This is a study of the products of protein metabolism, liver and kidney function. An overestimation of the indicator occurs when there is a malfunction of the kidneys, when they cannot cope with the removal of fluid from the body, and a decrease is typical for pregnant women, with diet and disorders associated with liver function.
Urea analysis- This is a study of the products of protein metabolism, liver and kidney function. An overestimation of the indicator occurs when there is a malfunction of the kidneys, when they cannot cope with the removal of fluid from the body, and a decrease is typical for pregnant women, with diet and disorders associated with liver function.- Ggt in biochemical analysis it informs about the metabolism of amino acids in the body. Its high rate is visible in alcoholism, as well as if the blood is affected by toxins or dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract is suspected. Low – if there are chronic liver diseases.
- Ldg The study characterizes the course of the energy processes of glycolysis and lactate. A high score indicates negative impact on the liver, lungs, heart, pancreas or kidneys (pneumonia, heart attack, pancreatitis and others). A low lactate dehydrogenase level, like low creatinine, will not affect the diagnosis. If LDH is elevated, the reasons in women may be the following: increased physical activity and pregnancy. In newborns, this figure is also slightly higher.
- Electrolyte balance indicates the normal process of metabolism into the cell and out of the cell back, including the process of the heart. Nutritional disorders are often the main cause of electrolyte imbalance, but vomiting, diarrhea, hormonal disbalance or kidney failure.
- Cholesterol(cholesterol) total - increases if a person has obesity, atherosclerosis, liver dysfunction, thyroid gland, and decreases when a person goes on a low-fat diet, with septicism or other infection.
- Amylase- an enzyme found in saliva and pancreas. High level will show if there are cholecystitis, signs of diabetes, peritonitis, mumps and pancreatitis. It will also increase if you consume alcoholic beverages or drugs - glucocorticoids, which is also typical for pregnant women during toxicosis.
There are a lot of biochemistry indicators, both basic and additional; complex biochemistry is also carried out, which includes both basic and additional indicators at the discretion of the doctor.
To take biochemistry on an empty stomach or not: how to prepare for the analysis?
A blood test for HD is a responsible process, and you need to prepare for it in advance and with all seriousness.

These measures are necessary so that the analysis is more accurate and no additional factors influence it. Otherwise, you will have to retake the tests, since the slightest changes in conditions will significantly affect the metabolic process.
Where do they get it from and how to donate blood?
Donating blood for biochemistry involves taking blood with a syringe from a vein on the elbow, sometimes from a vein on the forearm or hand. On average, 5-10 ml of blood is enough to measure basic indicators. If a detailed biochemistry analysis is needed, then a larger volume of blood is taken.
The norm of biochemistry indicators on specialized equipment from different manufacturers may differ slightly from the average limits. The express method involves obtaining results within one day.
The procedure for drawing blood is almost painless: you sit down, the treatment nurse prepares a syringe, puts a tourniquet on your arm, treats the area where the injection will be given with an antiseptic and takes a blood sample.
The resulting sample is placed in a test tube and sent to the laboratory for diagnosis. The laboratory doctor places the plasma sample into a special device that is designed to determine biochemical parameters with high accuracy.
He also processes and stores blood, determines the dosage and procedure for conducting biochemistry, diagnoses the results obtained, depending on the indicators required by the attending physician, and prepares a form for the results of biochemistry and laboratory chemical analysis.
The laboratory chemical analysis is transmitted within a day to the attending physician, who makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
The LHC, with its many different indicators, makes it possible to see an extensive clinical picture of a specific person and a specific disease.
Biochemical analysis is the study of a wide range of enzymes, organic and mineral substances. This analysis of metabolism in the human body: carbohydrate, mineral, fat and protein. Changes in metabolism show whether pathology exists and in which organ. This analysis is done if the doctor suspects a hidden disease. The result of the analysis of pathology in the body is actually initial stage development, and the specialist can navigate the choice.
medicines
Using this test, it is possible to detect leukemia at an early stage, when symptoms have not yet begun to appear. In this case, you can start taking the necessary medications and stop the pathological process of the disease.
Sampling process and analysis indicator values
Blood is taken from a vein for analysis, approximately five to ten milliliters. It is placed in a special test tube. The analysis is carried out on an empty stomach of the patient, for more complete veracity. If there is no health risk, it is recommended not to take medications before blood.
To interpret the analysis results, the most informative indicators are used:
- glucose and sugar levels - an increased level characterizes the development of diabetes mellitus in a person, a sharp decrease in it poses a threat to life;
- cholesterol – its increased content indicates the presence of vascular atherosclerosis and the risk of cardiovascular diseases;
- transaminases - enzymes that detect diseases such as myocardial infarction, liver damage (hepatitis), or the presence of any injury;
- urea and creatine - their excess indicates a weakening of the excretory function of the kidneys and liver;
- total protein - its indicators change when a serious illness or some negative process occurs in the body;
- amylase is an enzyme of the pancreas, an increase in its level in the blood indicates inflammation of the gland - pancreatitis.
In addition to the above, a biochemical blood test determines the content of potassium, iron, phosphorus and chlorine in the body. Only the attending physician can interpret the results of the analysis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
BIOCHEMISTRY. Lecture No. 1. Biochemistry as a science. Structure and functions of the main substances in the body. Subject and methods of research in biochemistry. Overview of main classes organic matter, their role in homeostasis.
Biochemistry (from the Greek βίος - “life” and Egyptian kēme - “Earth”, also biological or physiological chemistry) is the science of the chemical composition of organisms and their components and the chemical processes occurring in organisms. Science deals with the structure and function of substances that are components of cells and make up the body, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and other biomolecules. Biochemistry seeks to answer biological and biochemical questions using chemical methods.
Biochemistry is a relatively young science that arose at the intersection of biology and chemistry at the end of the 19th century. She studies the processes of development and functioning of organisms in the language of molecules, the structure and chemical processes that ensure the life of single- and multicellular creatures inhabiting the Earth. Outstanding discoveries in the field of enzyme science, biochemical genetics, molecular biology and bioenergetics have turned biochemistry into a fundamental discipline that allows solving many important problems of biology and medicine.
Although there is a wide range of different biomolecules, many of them are polymers, i.e. complex large molecules consisting of many similar subunits, monomers. Each class of polymer biomolecules has its own set of types of these subunits. For example, proteins are polymers made of amino acids. Biochemistry studies Chemical properties important biological molecules such as proteins, particularly the chemistry of reactions catalyzed by enzymes.
In addition, most of the research in biochemistry deals with cell metabolism and its endocrine and paracrine regulation. Other areas of biochemistry include research genetic code DNA and RNA, protein biosynthesis, transport across biological membranes and signal transmission.
The foundations of biochemistry were laid in the mid-19th century, when scientists such as Friedrich Violer and Anselm Paen were able to describe for the first time the chemical processes in living organisms and show that they are no different from ordinary ones chemical processes. Many works at the beginning of the 20th century led to an understanding of the structure of proteins, making it possible to carry out bio chemical reactions(alcoholic fermentation) outside the cell, etc. At the same time, the term “biochemistry” itself began to be used. The foundations of biochemistry in Ukraine were laid by Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky in the 20s of the last century.
Story
By the beginning of the 19th century there was a general belief that life was not subject to physical and chemical laws inherent in inanimate nature. It was believed that only living organisms are capable of producing molecules characteristic of them. It was only in 1828 that Friedrich Wöhler published work on the synthesis of urea, carried out in laboratory conditions, proving that organic compounds can be created artificially. This discovery dealt a serious defeat to vitalist scientists who had denied this possibility.
By that time, factual material already existed for primary biochemical generalizations, which accumulated in connection with the practical activities of people aimed at making food and wine, obtaining yarn from plants, cleaning the skin from wool with the help of microbes, studying the composition and properties of urine and other secretions healthy and sick person. After Wehler's work, such scientific concepts, like respiration, fermentation, fermentation, photosynthesis. The study of the chemical composition and properties of compounds isolated from animals and plants is becoming the subject of organic chemistry(chemistry of organic compounds).
The birth of biochemistry was also marked by the discovery of the first enzyme, diastase (now known as amylase) in 1833 by Anselm Paen. The difficulties associated with obtaining enzymes from tissues and cells were used by proponents of vitalism to argue that it was impossible to study cellular enzymes outside living beings. This statement was refuted by the Russian physician M. Manasseina (1871 - 1872), who proposed the possibility of observing alcoholic fermentation in extracts of ground (i.e., lacking structural integrity) yeast. In 1896, this possibility was confirmed by the German scientist Eduard Buchner, who was able to experimentally recreate this process.
The term “biochemistry” itself was first proposed in 1882, but it is believed that it gained widespread use after the work of the German chemist Carl Neuberg in 1903. By that time, this field of research was known as physiological chemistry. After this time, biochemistry developed rapidly, especially from the mid-20th century, primarily through the development of new techniques such as chromatography, X-ray diffraction analysis, NMR spectroscopy, radiolabeling, electron and optical microscopy, and finally molecular dynamics and other computational biology techniques. These methods allowed the discovery and detailed analysis of many molecules and metabolic pathways of the cell, such as glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Other important historical event in the development of biochemistry was the discovery of genes and their role in the transmission of information in the cell. This discovery laid the possibility of the emergence not only of genetics, but also of its interdisciplinary branch at the intersection with biochemistry - molecular biology. In the 1950s, James Watson, Francis Crick, Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins were able to decipher the structure of DNA and suggested its connection with the genetic transmission of information in the cell. Also in the 1950s, George Otley and Edward Tatum proved that a single gene is responsible for the synthesis of a single protein. With the development of DNA testing techniques such as genetic fingerprinting, in 1988 Colleen Pitchfork became the first person to be charged with murder using DNA evidence, marking the first major success of biochemical forensics. In the 200s, Andrew Fire and Craig Mello showed the role of RNA interference (RNAi) in suppressing gene expression.
Currently, biochemical research is proceeding in three directions, formulated by Michael Sugar. Plant biochemistry studies the biochemistry of predominantly autotrophic organisms and studies processes such as photosynthesis and others. General biochemistry includes the study of plants, animals and humans, while medical biochemistry focuses primarily on human biochemistry and abnormalities in biochemical processes, particularly as a result of disease.
55.0
For friends!
Reference
Word "biochemistry" came to us from the 19th century. But it became established as a scientific term a century later thanks to the German scientist Carl Neuberg. It is logical that biochemistry combines the provisions of two sciences: chemistry and biology. Therefore, she studies substances and chemical reactions that occur in a living cell. Famous biochemists of their time were the Arab scientist Avicenna, the Italian scientist Leonardo da Vinci, the Swedish biochemist A. Tiselius and others. Thanks to biochemical developments, methods such as the separation of heterogeneous systems (centrifugation), chromatography, molecular and cellular biology, electrophoresis, electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis have emerged.
Description of activity
The work of a biochemist is complex and multifaceted. This profession requires knowledge of microbiology, botany, plant physiology, medical and physiological chemistry. Specialists in the field of biochemistry are also involved in research into theoretical and applied biology and medicine. The results of their work are important in the field of technical and industrial biology, vitaminology, histochemistry and genetics. The work of biochemists is used in educational institutions, medical centers, biological production enterprises, in agriculture and other areas. Professional activity biochemists - this is mainly laboratory work. However, a modern biochemist deals not only with a microscope, test tubes and reagents, but also works with various technical instruments.
Wage
average for Russia:Moscow average:average for St. Petersburg:
Job responsibilities
The main responsibilities of a biochemist are to carry out scientific research and subsequent analysis of the results obtained.
However, a biochemist not only takes part in research work. He can also work at medical industry enterprises, where he conducts, for example, work on studying the effects of drugs on the blood of humans and animals. Naturally, such activities require compliance with the technological regulations of the biochemical process. The biochemist monitors reagents, raw materials, chemical composition and properties of the finished product.
Features of career growth
A biochemist is not the most in-demand profession, but specialists in this field are highly valued. Scientific developments of companies in various industries (food, agricultural, medical, pharmacological, etc.) cannot be done without the participation of biochemists.
Domestic research centers cooperate closely with Western countries. A specialist who is confident in foreign language and confidently working at a computer can find work in foreign biochemical companies.
A biochemist can realize himself in the field of education, pharmacy or management.