Over the past few centuries, we have made countless discoveries that have greatly improved the quality of our daily lives and understanding how the world around us works. Assessing the full importance of these discoveries is very difficult, if not almost impossible. But one thing is certain, some of them have literally changed our lives once and for all. From penicillin and the screw pump to X-rays and electricity, here is a list of the 25 greatest discoveries and inventions of mankind.
25. Penicillin
If the Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming had not discovered penicillin, the first antibiotic, in 1928, we would still be dying from diseases such as stomach ulcers, abscesses, streptococcal infections, scarlet fever, leptospirosis, Lyme disease and many others.
24. Mechanical watch
Photo: pixabay
There are conflicting theories about what the first mechanical watches actually looked like, but most often researchers adhere to the version that in 723 AD, the Chinese monk and mathematician Ai Xing (I-Hsing) created them. It was this fundamental invention that allowed us to measure time.
23. Heliocentrism of Copernicus
Photo: WP / wikimedia
In 1543, almost on his deathbed, the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus unveiled his landmark theory. According to the works of Copernicus, it became known that the Sun is our planetary system, and all its planets revolve around our star, each in its own orbit. Until 1543, astronomers believed that the Earth was the center of the universe.
22. Blood circulation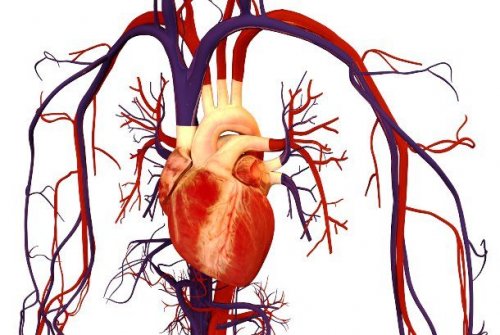
Photo: Bryan Brandenburg
One of the most important discoveries in medicine was the discovery of the circulatory system, which was announced in 1628 by the English physician William Harvey. He was the first person to describe the entire circulation system and properties of the blood that the heart pumps throughout our body from the brain to the fingertips.
21. Screw pump
Photo: David Hawgood / geographic.org.uk
One of the most famous ancient Greek scientists, Archimedes, is considered the author of one of the world's first water pumps. His device was a rotating corkscrew that pushed water up a pipe. This invention took irrigation systems to the next level and is still used today in many wastewater treatment plants.
20. Gravity
Photo: wikimedia
Everyone knows this story - Isaac Newton, the famous English mathematician and physicist, discovered gravity after an apple fell on his head in 1664. Thanks to this event, we first learned why objects fall down, and why the planets revolve around the Sun.
19. Pasteurization
Photo: wikimedia
Pasteurization was discovered in the 1860s by the French scientist Louis Pasteur. It is a heat treatment process during which pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed in certain foods and drinks (wine, milk, beer). This discovery had a significant impact on public health and the development of the food industry around the world.
18. Steam engine
Photo: pixabay
Everyone knows that modern civilization was forged in factories built during the Industrial Revolution, and that it was all done using steam engines. The steam-powered engine was invented a long time ago, but over the past century it has been significantly improved by three British inventors: Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen, and the most famous of them, James Watt (Thomas Savery, Thomas Newcomen, James Watt).
17. Conditioner
Photo: Ildar Sagdejev / wikimedia
The primitive climate control system has existed since ancient times, but it changed significantly when the first modern electric air conditioner appeared in 1902. It was invented by a young engineer named Willis Carrier, a native of Buffalo, New York (Buffalo, New York).
16. Electricity
Photo: pixabay
The fateful discovery of electricity is credited to the English scientist Michael Faraday. Among his key discoveries, it is worth noting the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Faraday's experiments also led to the creation of the first generator, which became the forerunner of the huge generators that today produce the electricity we are used to in everyday life.
15. DNA
Photo: pixabay
Many believe that it was the American biologist James Watson and the English physicist Francis Crick (James Watson, Francis Crick) who discovered in the 1950s, but in fact, this macromolecule was first identified back in the late 1860s by the Swiss chemist Friedrich Meischer (Friedrich Miescher). Then, several decades after Meisher's discovery, other scientists conducted a series of studies that finally helped us figure out how an organism passes its genes to the next generation, and how its cells work.
14. Anesthesia
Photo: Wikimedia
Simple forms of anesthesia such as opium, mandrake and alcohol have been used by humans for a long time, and the first references to them date back to 70 AD. But since 1847, pain relief has been taken to a new level, when the American surgeon Henry Bigelow first introduced ether and chloroform into his practice, making extremely painful invasive procedures much more bearable.
13. Theory of relativity
Photo: Wikimedia
Incorporating Albert Einstein's two interrelated theories, special and general relativity, published in 1905, the theory of relativity transformed the entire theoretical physics and astronomy of the 20th century and eclipsed the 200-year-old theory of mechanics proposed by Newton. Einstein's theory of relativity has become the basis for much of the scientific work of modern times.
12. X-rays
Photo: Nevit Dilmen / wikimedia
German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen accidentally discovered X-rays in 1895 when he was observing the fluorescence produced by a cathode ray tube. For this landmark discovery in 1901, the scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize, the first of its kind in the field of physical sciences.
11. Telegraph
Photo: wikipedia
Since 1753, many researchers have been conducting their experiments to establish communication at a distance using electricity, but a significant breakthrough did not come until a few decades later, when in 1835 Joseph Henry and Edward Davy (Joseph Henry, Edward Davy) invented the electrical relay. With this device, they created the first telegraph 2 years later.
10. Periodic system of chemical elements
Photo: sandbh / wikimedia
In 1869, the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that if you sort chemical elements by their atomic mass, they conditionally line up in groups with similar properties. Based on this information, he created the first periodic table, one of the greatest discoveries in chemistry, which was later called the periodic table in his honor.
9. Infrared rays
Photo: AIRS / flickr
Infrared radiation was discovered by the British astronomer William Herschel in 1800, when he was studying the heating effect of light of different colors, using a prism to spread the light into a spectrum, and measuring the changes with thermometers. Today, infrared radiation is used in many areas of our lives, including meteorology, heating systems, astronomy, tracking heat-intensive objects, and many other areas.
8. Nuclear magnetic resonance
Photo: Mj-bird / wikimedia
Today, nuclear magnetic resonance is constantly used as an extremely accurate and efficient diagnostic tool in the field of medicine. This phenomenon was first described and calculated by the American physicist Isidor Rabi in 1938 while observing molecular beams. In 1944, the American scientist was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery.
7. Moldboard plow
Photo: wikimedia
Invented in the 18th century, the mouldboard plow was the first plow that not only turned up the soil, but also stirred it up, which made it possible to cultivate even very stubborn and stony land for agricultural purposes. Without this tool, agriculture as we know it today would not exist in northern Europe or central America.
6 Camera Obscura
Photo: wikimedia
The forerunner of modern cameras and camcorders was the camera obscura (translated as dark room), which was an optical device used by artists to create quick sketches while traveling outside their studios. A hole in one of the walls of the device served to create an inverted image of what was happening outside the chamber. The picture was displayed on the screen (on the opposite wall of the dark box from the hole). These principles have been known for centuries, but in 1568 the Venetian Daniel Barbaro modified the camera obscura with converging lenses.
5. Paper
Photo: pixabay
Papyrus and amate, used by ancient Mediterranean peoples and pre-Columbian Americans, are often considered the first examples of modern paper. But it would not be entirely correct to consider them real paper. References to the first writing paper production date back to China during the Eastern Han Empire (AD 25-220). The first paper is mentioned in the annals dedicated to the activities of the judicial dignitary Cai Lun (Cai Lun).
4. Teflon
Photo: pixabay
The material that keeps your frying pan from burning was actually invented completely by accident by American chemist Roy Plunkett when he was looking for a replacement for refrigerants to make your home safer. During one of his experiments, the scientist discovered a strange slippery resin, which later became better known as Teflon.
3. The theory of evolution and natural selection
Photo: wikimedia
Inspired by his observations during his second exploratory journey in 1831-1836, Charles Darwin began to write his famous theory of evolution and natural selection, which, according to scientists from around the world, has become a key description of the mechanism of development of all life on Earth.
2. Liquid crystals
Photo: William Hook / flickr
If the Austrian botanist and physiologist Friedrich Reinitzer had not discovered liquid crystals while testing the physico-chemical properties of various cholesterol derivatives in 1888, today you would not know what LCD TVs or flat LCD monitors are.
1. Polio vaccine
Photo: GDC Global / flickr
On March 26, 1953, American medical researcher Jonas Salk announced that he had successfully tested a vaccine against polio, a virus that causes severe chronic illness. In 1952, an epidemic of this disease diagnosed 58,000 people in the United States, and the disease claimed 3,000 innocent lives. This spurred Salk to seek salvation, and now the civilized world is safe at least from this disaster.
Advances in technology are rapidly gaining momentum, leaving far behind the days when people had to use candles as a source of light. Today, people can shop from the comfort of their homes, travel thousands of miles in a few hours, even travel into space. At the same time, not many people remember the geniuses who are the founders of the current civilization. Let's pay tribute to the development of unique inventions and discoveries to the ancestors who contributed to all this. We present the rating, which presents the most famous inventors.
10 most famous and great inventors of the world
10
aircraft project
Mikhail Vasilievich Lomonosov opens the top of the most famous inventors. Among his discoveries are:
- The prototype of modern aircraft;
- Aerodynamic machine;
At one time, an outstanding Russian physicist was fond of geography, astronomy and chemistry. Achieved high results in the study of astronomy and philology. He was fond of geology and the history of his state. The essence of his main work - an aerodynamic machine - is the ability to lift meteorological devices into the air. This project served as a good basis for many modern discoveries.

Of course, the name of the creator of radio engineering should appear in the ranking of the best inventors. His name is Alexander Stepanovich Popov, and this is another person we can be proud of. The Russian genius has been awarded many prizes in the field of science. In 1898 he received an award from the Imperial Technical Society for the presentation of a telegraphy receiver. Thanks to its development, mankind was able to use the telegraph at a distance, without wires. In addition, Popov was an excellent teacher. Taught:
- physics;
- mathematics;
- electrical engineering;
He treats any work scrupulously and very responsibly!
Aerodynamic tube

Konstantin Stepanovich Tsiolkovsky is the only scientist who has no education. Self-taught created a wind tunnel. At the same time, the well-known scientist of the USSR is the founder of theoretical astronautics. Moreover, at the end of the 19th century, he introduced the world to the first design of an airplane equipped with a metal body. By no means, it was possible to launch this vehicle only after 20 years. It is worth noting that Konstantin Tsiolkovsky contributed not only to the development of science, but also to poetry. At the end of the 19th century, he presented a number of interesting works of art. There are many quotes from this talented person on the net.
lightning rod

The list of famous inventors includes Benjamin Franklin, who is both a politician, a writer and a talented designer. It was he who managed to create a lightning rod, a Franklin furnace, a glass harmonica. Franklin's contribution to the field of medicine deserves special attention. He created a flexible urinary catheter. It's funny that Benjamin did not patent any of his inventions. But this does not prevent him from representing a hundred dollar bill in the 21st century. This fact confirms the significance of the life of the inventor in the history of mankind. This scientist has repeatedly spoken out about the fact that inventions must be released free of charge.
Siege weapons

Of course, Archimedes of Syracuse is a man of genius, whose contribution to science will never be overestimated. First of all, this outstanding inventor became famous as a mathematician who created many theories and computational formulas. In addition, Archimedes created a siege weapon and mirrors, through which beams can be focused to ignite objects. Surely, many have heard about the existence of such an invention as the Archimedean screw. Currently, many use the invention to transfer water from reservoirs to irrigation canals. It was he who introduced the theory of leverage. In addition, the mathematician contributed to the development of mechanics.
Video recorder

The most famous inventors also include Jellal Hal Lemelson. Is a recognized mind in the US. He was able to submit over six hundred patents in his life. His works include:
- Wireless radiotelephones;
- Industrial robots;
- Tape cassettes;
- VCRs;
- Automated warehouses;
- fax machines;
- Video cameras.
At one time, Lemelson was one of the outstanding people. Actively defended the rights of independent scientists. He was constantly criticized by the patent offices. He worked 14 hours a day.
Current generator

One of the outstanding ones is Nikola Tesla - a scientist who was not recognized during his lifetime, who was able to make a huge contribution to science. Unfortunately, the significance of his work was appreciated only after his death. Nikola presented to the public a huge number of inventions that operate on alternating current. Many of his works led to the second revolution in the field of industry. A lot of Tesla introduced unique robots that could be controlled remotely. He is also the author of one hundred patents for various power plants and a generator.
Automobile

Many believe that Bell is the best inventor because of the creation of the car. By no means, it is impossible to confidently say that he made the most important contribution, since the mobile apparatus presented by Alexander would not have existed without the contributions of his predecessors, which we will discuss below. Nevertheless, he can be attributed to the top three, because he is the author of a car called Mersedes Benz, which is still included in the rating.
Famous inventors of the world have created a lot of useful things for mankind. Their benefit to society is difficult to overestimate. Many ingenious discoveries have saved more than one life. Who are they - inventors known for their unique developments?
Archimedes
This man was not only a great mathematician. Thanks to him, the whole world learned what a mirror and a siege weapon are. One of the most famous developments is the Archimedean screw (auger), with which you can effectively scoop out water. It is noteworthy that this technology is still used today.
Leonardo da Vinci
Inventors, known for their brilliant ideas, did not always have the opportunity to bring ideas to life. For example, drawings of a parachute, an airplane, a robot, a tank and a bicycle, which appeared as a result of the painstaking work of Leonardo da Vinci, remained unclaimed for a long time. At that time, there simply were no engineers and opportunities to implement such grandiose plans.
Thomas Edison
The inventor of the phonograph, kinescope and telephone microphone was the most famous. In January 1880, he filed a patent for an incandescent lamp, which later glorified Edison throughout the planet. However, some do not consider him a genius, noting that the inventors known for their developments worked alone. As for Edison, a whole group of people helped him.

Nikola Tesla
The great inventions of this genius were brought to life only after his death. Everything is explained simply: Tesla was so that no one knew about his work. Thanks to the efforts of the scientist, a multi-phase electric current system was discovered, which led to the emergence of commercial electricity. In addition, he formed the foundations of robotics, nuclear physics, computer science, and ballistics.

Alexander Graham Bell
Many inventors known for their discoveries have helped make our lives even better. The same can be said about Alexander Bell. Thanks to him, people were able to communicate freely, being thousands of kilometers apart, and all thanks to the phone. Bell also invented an audiometer - a special device that determines deafness; a device for searching for a treasure - a prototype of a modern metal detector; the world's first airplane; a model of a submarine, which Alexander himself called a hydrofoil boat.

Karl Benz
This scientist successfully realized the main idea of his life: a vehicle with a motor. It is thanks to him that we now have the opportunity to drive cars. Another valuable invention of Benz is the internal combustion engine. Later, a car manufacturing company was organized, which today is known throughout the world. This is Mercedes Benz.
Edwin Land
This famous French inventor devoted his life to photography. In 1926, he managed to discover a new type of polarizer, which later became known as the Polaroid. Land founded Polaroid and filed patents for 535 more inventions.
Charles Babbage
This English scientist worked on the creation of the first computer back in the nineteenth century. It was he who called the unique device a computer. Since at that time humanity did not have the necessary knowledge and experience, Babbage's efforts were not crowned with success. Nevertheless, brilliant ideas did not sink into oblivion: Konrad Zuse was able to realize them in the middle of the twentieth century.
Benjamin Franklin
This famous politician, writer, diplomat, satirist and statesman was also a scientist. The great inventions of mankind, which saw the light thanks to Franklin, are both a flexible urinary catheter and a lightning rod. An interesting fact: Benjamin basically did not patent any of his discoveries, because he believed that all of them were the property of mankind.

Jerome Hal Lemelson
Such great inventions of mankind as the facsimile machine, cordless telephone, automated warehouse and magnetic tape cassette were introduced to the general public by Jerome Lemelson. In addition, this scientist developed the technology of diamond coating and some medical devices that help in the treatment of cancer.

Mikhail Lomonosov
This recognized genius of various sciences organized the first university in Russia. The most famous personal invention of Mikhail Vasilyevich is an aerodynamic machine. It was intended to raise special meteorological instruments. According to many experts, it is Lomonosov who is the author of the prototype of modern aircraft.
Ivan Kulibin
It is not for nothing that this man is called the brightest representative of the eighteenth century. Ivan Petrovich Kulibin from early childhood was interested in the principles of mechanics. Thanks to his work, we now use navigational instruments, alarm clocks, and water-powered engines. For that time, these inventions were something from the category of science fiction. The surname of the genius even became a household name. Kulibin is now called a person with the ability to make amazing discoveries.
Sergei Korolev
His interests included manned astronautics, aircraft engineering, the design of rocket and space systems, and missile weapons. Sergei Pavlovich greatly contributed to the exploration of outer space. He created the Vostok and Voskhod spaceships, the 217 anti-aircraft missile and the 212 long-range missile, as well as a rocket plane equipped with a rocket engine.
Alexander Popov
And the radio receiver is this Russian scientist. The unique discovery was preceded by years of research into the nature and propagation of radio waves.
A brilliant physicist and electrical engineer was born in the family of a priest. Alexander had six more brothers and sisters. Already in childhood, he was jokingly called a professor, since Popov was a shy, thin, awkward boy who could not stand fights and noisy games. In the Perm Theological Seminary, Alexander Stepanovich began to study physics based on Gano's book. His favorite pastime was assembling simple technical devices. The acquired skills were subsequently very useful to Popov when creating physical instruments for his own most important research.
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
The discoveries of this great Russian inventor made it possible to bring aerodynamics and astronautics to a new level. In 1897, Konstantin Eduardovich finished working on a wind tunnel. Thanks to the allocated subsidies, he calculated the resistance of the ball, cylinder and other bodies. The data obtained were subsequently widely used in his work by Nikolai Zhukovsky.
In 1894, Tsiolkovsky designed an airplane with a metal frame, but the opportunity to build such an apparatus appeared only twenty years later.

Controversial question. Who is the inventor of the light bulb?
The creation of a device that gives light has been worked on since ancient times. The prototype of modern lamps were clay vessels with wicks made of cotton threads. The ancient Egyptians poured olive oil into such containers and set it on fire. The inhabitants of the coast of the Caspian Sea used another fuel material - oil - in similar devices. The first candles made in the Middle Ages consisted of beeswax. The notorious Leonardo da Vinci worked hard to create, however, the world's first safe lighting device was invented in the nineteenth century.
Until now, disputes about who should be awarded the honorary title of "Inventor of the Light Bulb" have not subsided. The first is often called Pavel Nikolaevich Yablochkov, who worked as an electrical engineer all his life. He created not only a lamp, but also an electric candle. The latter device is widely used in street lighting. The miracle candle burned for an hour and a half, after which the janitor had to change it for a new one.
In 1872-1873. Russian engineer-inventor Lodygin created an electric lamp in its modern sense. At first, it emitted light for thirty minutes, and after pumping air out of the device, this time increased significantly. In addition, Thomas Edison and Joseph Swan claimed the championship in the invention of the incandescent lamp.
Conclusion
Inventors around the world have given us many devices that make life more comfortable and varied. Progress does not stand still, and if a few centuries ago there were simply not enough technical capabilities to implement all the ideas, today it is much easier to bring ideas to life.
Two decades ago, people could not even dream of such a level of technological development as it exists today. Today, it takes only half a day to fly half the globe, modern smartphones are 60,000 times lighter and thousands of times more powerful than the first computers, today agricultural productivity and life expectancy are higher than ever in the history of mankind. Let's try to figure out which inventions have become the most important and, in fact, changed the history of mankind.
1. Cyanide

Although cyanide seems rather controversial to include on this list, the chemical has played an important role in human history. While the gaseous form of cyanide has caused the deaths of millions of people, it is this substance that is the main factor in the extraction of gold and silver from ore. Since the world economy has been tied to the gold standard, cyanide is an important factor in the development of international trade.
2. Plane

Today, no one doubts that the invention of the "metal bird" had one of the greatest impacts on human history by radically reducing the time needed to transport goods or people. The invention of the Wright brothers was enthusiastically received by the public.
3. Anesthesia

Until 1846, any surgical procedure was more like some kind of excruciating torture. Although anesthetics have been used for thousands of years, their earliest forms were nothing more than alcohol or mandrake extract. The invention of modern anesthesia in the form of nitrous oxide and ether allowed doctors to safely operate on patients without the slightest resistance from them (after all, patients did not feel anything).
4. Radio
The origins of radio history are highly controversial. Many claim that Guglielmo Marconi was its inventor. Others claim that it was Nikola Tesla. In any case, these two people have done a lot to enable people to successfully transmit information through radio waves.
5. Phone

The telephone has been one of the most important inventions in our modern world. As with all major inventions, there is still debate about who invented it. One thing is clear: the US Patent Office granted the first telephone patent to Alexander Graham Bell in 1876. This patent served as the basis for future research and development of electronic sound transmission over long distances.
6. World Wide Web

While everyone thinks it's a very recent invention, the Internet existed in its archaic form in 1969 when the United States military developed the ARPANET. But it was Tim Berners-Lee who created the network of hyperlinks to documents at the University of Illinois and created the first World Wide Web browser in its relatively modern form.
7. Transistor

Today it seems that picking up the phone and calling someone in Mali, the US or India is very easy, but it would not be possible without transistors. Semiconductor transistors, which amplify electrical signals, have made it possible to send information over long distances. The man who pioneered this research, William Shockley, is credited with creating Silicon Valley.
8. Atomic clock

While this invention may not seem as revolutionary as many of the previous points, the invention of the atomic clock was crucial in the advancement of science. Using microwave signals emitted by varying levels of electron energy, atomic clocks and their accuracy have made possible a wide range of modern modern inventions, including GPS, GLONASS, and the Internet.
9. Steam turbine

The steam turbine of Charles Parsons literally changed the development of mankind, giving impetus to the industrialization of countries and making it possible for ships to quickly overcome the ocean. In 1996 alone, 90% of electricity in the US was generated by steam turbines.
10. Plastic

Despite the ubiquity of plastic in our modern society, it only appeared in the last century. The waterproof and highly pliable material is used in almost every industry, from food packaging to toys and even spacecraft. While most modern plastics are made from petroleum, there are increasing calls to go back to the original version, which was partly organic.
11. Television

Television has had a long and storied history that dates back to the 1920s and continues to this day. This invention has become one of the most popular consumer products around the world - almost 80% of families have a TV.
12. Oil

Most people do not think at all when they fill the tank of their car. Although people have been extracting oil for millennia, the modern oil and gas industry emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century. After industrialists saw all the advantages of oil products and the amount of energy generated by burning them, they raced to make wells for the extraction of "liquid gold".
13. Internal combustion engine

Without the discovery of the efficiency of combustion of petroleum products, the modern internal combustion engine would not have been possible. Given that it has started to be used literally everywhere: from cars to agricultural combines and mining machines, these engines have allowed people to replace back-breaking, painstaking and time-consuming work with machines that can do this work much faster. The internal combustion engine also gave people freedom of movement since it was the one used in automobiles.
14. Reinforced concrete

The boom in the construction of high-rise buildings happened only in the middle of the nineteenth century. By embedding steel reinforcing bars (reinforcing bars) into concrete before it was poured, people were able to build reinforced concrete artificial structures many times larger in weight and size than before.

There would be far fewer people living on planet Earth today if there were no penicillin. Officially discovered by Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming in 1928, penicillin was one of the most important inventions/discoveries that made the modern world possible. Antibiotics were among the first drugs that were able to fight staphylococci, syphilis and tuberculosis.
16. Refrigerator

Harnessing heat was perhaps the most important discovery to date, but it took many millennia. Although people have long used ice for cooling, its practicality and availability has been limited. In the nineteenth century, scientists invented artificial refrigeration using chemicals. By the early 1900s, almost every meatpacking plant and major food distributor was using artificial refrigeration to preserve food.
17. Pasteurization

Half a century before the discovery of penicillin, a new process discovered by Louis Pasteur, pasteurization, or heating food (originally beer, wine, and dairy products) to a temperature high enough to kill most spoilage bacteria, helped save many lives. Unlike sterilization, which kills all bacteria, pasteurization only reduces potential pathogens to a level that makes most foods edible without fear of contamination, while still preserving the taste of the food.
18. Solar battery

Just as the oil industry sparked a boom in the industry as a whole, the invention of the solar battery allowed people to use a renewable form of energy in a much more efficient way. The first practical solar battery was developed in 1954 by Bell Telephone scientists, but today the popularity and efficiency of solar panels has increased dramatically.
19. Microprocessor

Today, people would have to forget about their laptop and smartphone if the microprocessor had not been invented. One of the most widely known supercomputers, ENIAC, was built in 1946 and weighed 27,215 tons. Intel engineer Ted Hoff created the first microprocessor in 1971, putting all the functions of a supercomputer into one tiny chip, making portable computers possible.
20. Laser

The stimulated light emission amplifier or laser was invented in 1960 by Theodor Meyman. Modern lasers are used in a variety of inventions, including laser cutters, barcode scanners, and surgical equipment.
21. Nitrogen fixation

Although it may seem overly pompous, nitrogen fixation, or fixation of molecular atmospheric nitrogen, is "responsible" for the explosion of the human population. By converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, the production of highly effective fertilizers was made possible, which increased agricultural production.
22. Conveyor

Today it is difficult to overestimate the importance of assembly lines. Before their invention, all products were made by hand. The assembly line or conveyor allowed the development of large-scale production of the same parts, greatly reducing the time it took to create a new product.
23. Oral contraceptives

Although the pill and pill has been one of the main methods of medicine that has been around for thousands of years, the invention of the oral contraceptive has been one of the most significant innovations. It was this invention that became the impetus for the sexual revolution.
24. Mobile phone / smartphone

Now, many of you are probably reading this article from your smartphone. Thanks to Motorola for this, back in 1973 they released the first wireless pocket mobile phone, which weighed as much as 2 kg, and it took as much as 10 hours to recharge it. To make matters worse, at that time one could only chat quietly for 30 minutes.
25. Electricity

Most modern inventions would simply be impossible without electricity. Pioneers such as William Gilbert and Benjamin Franklin laid the initial foundation upon which inventors such as Volt and Faraday launched the second industrial revolution.
03.05.2013
No. 10. Leonardo da Vinci
 Don't be surprised that this famous inventor in 10th place. The reason is this: he invented technologies that were many years ahead of the science of that time and could not actually be implemented. Leonardo was more of a futurist who imagined various innovations rather than a man who could actually create real things with his own hands. In addition, his interest changed rapidly and none of the theories received deep study. His inventions include a submarine, a tank, a glider.
Don't be surprised that this famous inventor in 10th place. The reason is this: he invented technologies that were many years ahead of the science of that time and could not actually be implemented. Leonardo was more of a futurist who imagined various innovations rather than a man who could actually create real things with his own hands. In addition, his interest changed rapidly and none of the theories received deep study. His inventions include a submarine, a tank, a glider.
No. 9. Edwin Land
 Physicist and great inventor Edwin Land of Connecticut didn't invent photography, of course, but he invented or perfected just about everything else about it. In his freshman year at Harvard University in 1926, he developed a new kind of polarizer by aligning and embedding crystals in a plastic sheet, which he called Polaroid. He applied the polarization principle to light filters, optical devices and motion picture processes and founded the Polaroid Corporation. Holder of at least 535 US patents.
Physicist and great inventor Edwin Land of Connecticut didn't invent photography, of course, but he invented or perfected just about everything else about it. In his freshman year at Harvard University in 1926, he developed a new kind of polarizer by aligning and embedding crystals in a plastic sheet, which he called Polaroid. He applied the polarization principle to light filters, optical devices and motion picture processes and founded the Polaroid Corporation. Holder of at least 535 US patents.
No. 8. Benjamin Franklin
 Seriously? Ben Franklin? Absolutely! Not many people know that among his many skills (Franklin was a famous polymath: writer, satirist, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, public figure, statesman, diplomat), he was amazing great inventor. Among his many creations are a lightning rod that has saved countless homes from lightning fires, Armonica glass, a Franklin stove, bifocals, and even a flexible urinary catheter. Franklin did not patent his inventions, believing that innovation should be available to everyone, which is why his inventions are often forgotten.
Seriously? Ben Franklin? Absolutely! Not many people know that among his many skills (Franklin was a famous polymath: writer, satirist, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, public figure, statesman, diplomat), he was amazing great inventor. Among his many creations are a lightning rod that has saved countless homes from lightning fires, Armonica glass, a Franklin stove, bifocals, and even a flexible urinary catheter. Franklin did not patent his inventions, believing that innovation should be available to everyone, which is why his inventions are often forgotten.
No. 7. Hero of Alexandria
 If he knew that his invention could turn the world upside down and start an industrial revolution, he would have told the whole world about it back in 50 AD. Alas, he thought that the invented steam engine was just a toy, and besides, in the presence of slaves, why invent a steam engine for widespread use? Some of the best minds of the Roman Empire also developed other useful things, including a pump, a syringe, a fountain, a windmill - all during the pre-industrial era. It is a pity that he did not develop his inventions for wide application.
If he knew that his invention could turn the world upside down and start an industrial revolution, he would have told the whole world about it back in 50 AD. Alas, he thought that the invented steam engine was just a toy, and besides, in the presence of slaves, why invent a steam engine for widespread use? Some of the best minds of the Roman Empire also developed other useful things, including a pump, a syringe, a fountain, a windmill - all during the pre-industrial era. It is a pity that he did not develop his inventions for wide application.
#6 Jerome "Jerry" Hal Lemelson
One of the most fruitful famous inventors of the world in history - 605 patents. What did he invent? Things like automated warehouses, industrial robots, cordless phones, fax machines, VCRs, camcorders, and magnetic drive tapes, the tapes used in Sony's Walkman players. Lemelson has also filed patents in the areas of medical equipment, cancer detection and treatment, diamond plating, and consumer electronics and television.
No. 5. George Westinghouse
 The main invention was electrical systems that ran on AC (the work of Nikola Tesla, by the way), which eventually surpassed Edison's DC devices and paved the way for the modern power grid. But before he surpassed Edison, he invented railroad brakes based on air masses. And, of course, he tried to develop a perpetual motion machine. However, without success. 361 patents.
The main invention was electrical systems that ran on AC (the work of Nikola Tesla, by the way), which eventually surpassed Edison's DC devices and paved the way for the modern power grid. But before he surpassed Edison, he invented railroad brakes based on air masses. And, of course, he tried to develop a perpetual motion machine. However, without success. 361 patents.
No. 4. Alexander Graham Bell
 Everyone knows the famous inventor of telephones, but not many people know that he also invented devices that help in the detection of icebergs, as well as a modern metal detector.
Everyone knows the famous inventor of telephones, but not many people know that he also invented devices that help in the detection of icebergs, as well as a modern metal detector.
No. 3. Thomas Edison
 What? The most prolific and one of great inventors of the world in modern history, with over a thousand patents and not number one? The inventor of the electric light bulb, the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and the man who electrified New York, literally? Can not be! In fact, although Edison was a gifted man, many of his most famous inventions were developed by other people working for him or in collaboration with an entire team, making him responsible for the development of projects, but not their main inventor.
What? The most prolific and one of great inventors of the world in modern history, with over a thousand patents and not number one? The inventor of the electric light bulb, the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and the man who electrified New York, literally? Can not be! In fact, although Edison was a gifted man, many of his most famous inventions were developed by other people working for him or in collaboration with an entire team, making him responsible for the development of projects, but not their main inventor.
No. 2. Nikola Tesla
 A man little known in his lifetime, in fact, was responsible for the birth of commercial electricity more than anyone. His patents and theoretical work formed the basis of modern AC electrical power systems, including the multi-phase AC electrical distribution system that helped usher in the second industrial revolution. He also contributed in varying degrees to the science of robotics, laid the groundwork for the development of remote control, radar, and computer science, and even participated in the expansion of ballistics, nuclear physics, and theoretical physics. Some people also believe that he worked on anti-gravity, teleportation, and lasers, but this has not been proven. In any case, he has 111 patents and is recognized as one of the best and most innovative minds in history.
A man little known in his lifetime, in fact, was responsible for the birth of commercial electricity more than anyone. His patents and theoretical work formed the basis of modern AC electrical power systems, including the multi-phase AC electrical distribution system that helped usher in the second industrial revolution. He also contributed in varying degrees to the science of robotics, laid the groundwork for the development of remote control, radar, and computer science, and even participated in the expansion of ballistics, nuclear physics, and theoretical physics. Some people also believe that he worked on anti-gravity, teleportation, and lasers, but this has not been proven. In any case, he has 111 patents and is recognized as one of the best and most innovative minds in history.
No. 1. Archimedes of Syracuse
 How This Ancient Greek Scientist Ranked No. 1 in the Top 10 The most famous and great inventors of the world? First, he is recognized as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. He came close to accurately calculating the value of pi, figured out how to determine the area under the arc of a parabola, and came up with many other things that are now a nightmare for schoolchildren in math classes. In addition, he invented many machines, including siege weapons and perhaps even a device that was capable of setting fire to Roman ships with a mirror by focusing sunlight on the sails. Not unimportantly, he did all this over 2,000 years ago, without the help of computers or the technology available to many inventors today. In addition, despite the fact that he studied at Alexandria (although this is not confirmed), he acquired most of his knowledge the old fashioned way - from his own experience.
How This Ancient Greek Scientist Ranked No. 1 in the Top 10 The most famous and great inventors of the world? First, he is recognized as one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. He came close to accurately calculating the value of pi, figured out how to determine the area under the arc of a parabola, and came up with many other things that are now a nightmare for schoolchildren in math classes. In addition, he invented many machines, including siege weapons and perhaps even a device that was capable of setting fire to Roman ships with a mirror by focusing sunlight on the sails. Not unimportantly, he did all this over 2,000 years ago, without the help of computers or the technology available to many inventors today. In addition, despite the fact that he studied at Alexandria (although this is not confirmed), he acquired most of his knowledge the old fashioned way - from his own experience.