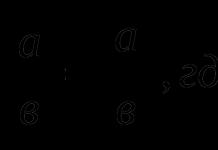
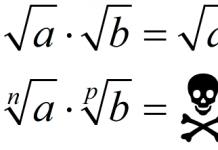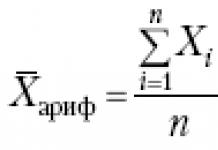The materials located on this page are copyrighted. Copying for posting on other sites is permitted only with the express consent of the author and site administration.
Lesson topic: “Health-saving technologies and their use in lessons physical culture in a modern school"
Methodological development
physical education teacher
first qualification category
Alexandrova E.L.
1. Relevance of the problem
The main indicator of the well-being of society and the state is the student’s health status, which reflects reality and gives a forecast for the future. According to data obtained by experts, no more than 10% of modern schoolchildren are considered practically healthy. The most common pathologies are: postural disorders and spinal curvature, visual impairment, diseases of the cardiovascular system, allergic manifestations, and digestive disorders. Diseases of the nervous system do not go unnoticed.
The causes of student health problems are:
- lack of physical activity among students, leading to physical inactivity;
- intensity of the educational process;
- technologies for conducting a lesson and assessing students’ knowledge, leading to stressful situations;
- the impossibility of teachers in conditions modern organization educational process to implement an individual approach to students, taking into account their psychological and physiological characteristics.
The main feature of health-saving pedagogy is the priority of health, that is, a sensitive and attentive attitude to health.
Principles of health-saving pedagogy
The main principle is “do no harm”;
- caring for the health of students, that is, a positive impact on both the health in general and the emotional sphere of children;
- continuity and continuity;
- inclusion of health issues in the content of programs;
- unity of physical, mental and spiritual health;
- compliance of the content and organization of training with the age of students;
- priority of positive influence over negative;
- students’ responsibility for their health;
- control over results.
We can solve the problem of organizing physical activity and preventing physical inactivity in physical education lessons. Modern schoolchildren sit for hours over notebooks and textbooks, the workload is colossal, plus they have a passion computer games, Internet. As a result, there is no time left for physical education and sports. This leads to retarded growth and development, and decreased immunity.
Ways to solve the problem
- At least 3 physical education lessons per week
- The content of the lessons is aimed at instilling in children an interest in physical exercise and movement.
- Mandatory breaks during the school day (physical breaks, physical education minutes).
- Adaptive physical education classes.
- Opportunity to study outside of school hours.
Physical education and health technologies.
They are aimed at the physical development of students. These include: hardening, training strength, endurance, speed, flexibility and other qualities that distinguish a healthy, trained person from a physically weak one.
Based on the nature of the action, the following technologies are distinguished:
Stimulating.
They allow you to activate the body’s own forces and use its resources to get out of an undesirable state. Examples could be temperature hardening, physical activity.
Protective and preventive.
This is compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards and requirements. Limiting the maximum load to prevent overwork.
The use of safety equipment and protective devices in gyms to prevent injury. And so on.
Compensatory-neutralizing technologies. These are physical education minutes, physical education breaks, which to some extent neutralize the adverse effects of static lessons.
Information and learning technologies.
Provides students with the level of literacy necessary to effectively manage their health.
Hygienic conditions for ensuring the educational processAn important element of health-saving technologies is ensuring optimal conditions at school.
The teacher’s responsibilities include the ability and willingness to see and identify obvious violations of the hygienic conditions of conducting a physical education lesson. It has been established that optimizing sanitary and hygienic conditions improves health by 11%. A physical education teacher must: - monitor the condition of workplaces, educational equipment
, visual aids, sports equipment; - do not allow training sessions
, work of circles and sections in premises not equipped for these purposes and not accepted for operation;
- before the start of classes, conduct a thorough check of the location of the class, make sure that the equipment is in good working order, and that the equipment is securely installed and fastened.
Sanitary and hygienic requirements for gyms
The number of seats in the gym during classes should be set at the rate of 0.7 m per student.
- Floors must be elastic, without cracks, have a flat, horizontal, non-slip surface.
- The floors must be dry and clean before the start of classes. Wet cleaning should be carried out after 2 hours of classes.
- The walls must be even and smooth, the paint must be resistant to ball impacts.
- The ceiling of the hall should have a non-fading color.
- Illumination should be no less than: 200-300 lux.
Fluorescent lamps or lamps with incandescent lamps with fully reflected light distribution should be used as a light source.
- Ventilation should be carried out in a natural through way.
- Lighting control must provide the ability to partially turn off the lighting installation.
- Safety plugs must be installed on all socket outlets.
- There should be an evacuation plan in a visible place in the room.
- The gym must have at least 2 exits.
Sanitary and hygienic requirements for outdoor sports grounds
Must be located at a distance of at least 10 m from educational buildings.
- The sites must be level, of established dimensions, and solid.
- Running tracks must be specially equipped, smooth, non-slip and continue for at least 15 m after the finish.
- Jumping pits should be filled with loosened sand to a depth of 20-40m.
- The sand must be clean.
- Places for throwing are located in a clearly visible place, at a considerable distance from public places. The length of the sector must be at least 60-70m.
Sanitary and hygienic requirements for inventory and equipment
All sports equipment and equipment installed in training areas must be in full working order.
- Gymnastic apparatus should not have any backlash, swings, or deflections in the units and joints; the fastening parts must be securely fixed.
- The bars of the parallel bars must be repaired along their entire length each time before starting classes. If the pole is cracked, it must be replaced.
- The bar of the crossbar must be wiped with a dry cloth before performing the exercise and after completion.
- The gymnastic beam should not have cracks or burrs.
- The supports of the gymnastic goat must be firmly fixed in the boxes of the body. When extending, the goat's legs must be firmly secured.
- Gymnastic mats must be placed closely together.
- The gymnastic bridge must be lined with rubber.
- Medicine balls are used according to numbers, strictly in accordance with age and physical activity.
- The weight of projectiles when throwing must correspond to age and gender according to the rules of the competition.
Requirements for school educational technologies
Health-saving educational technologies are assessed under the following conditions:A system of operational, current and stage-by-stage monitoring of the health status of students has been developed;
- the teaching content includes issues related to health protection;
- the learning process is built taking into account the anatomical, physiological and mental characteristics of the body;
- preference is given to meaningful, meaningful material;
- taken into account individual characteristics students;
- independent work and independent choice are stimulated, that is, what contributes to the child’s self-development;
- a sufficient level of motivation is ensured;
- the educational process is focused on the formation of ideas, and not on the transfer of knowledge;
- prevents overwork;
- positive impacts prevail over negative ones;
- the success rate is used to develop positive principles;
- assessment plays a stimulating role;
- the level of teacher communicative culture is ensured.
Rational organization of the lesson
The functional state of schoolchildren in the process depends on compliance with hygienic and psychological-pedagogical conditions. educational activities. A lesson lasting 40 minutes is considered physiologically justified (except for 1st grade students - 35 minutes).The assessment of hygienic requirements is carried out according to regulated items using timing:
- lesson density (% of time spent on academic work);
- number of types of educational activities (listening, performing physical exercises, changing lanes, etc.);
- duration of each type of activity (minutes);
- frequency of changes in activities (minutes);
- number of types of teaching (verbal, visual, TSO), duration of independent activity;
- places, duration and conditions of application of TSO;
- frequency of alternation of types of teaching.
To prevent fatigue, it is necessary to take into account that the first 3-5 minutes of any lesson are spent working on (in physical education lessons 8-10 minutes), stable performance lasts 10-15 minutes for junior schoolchildren, 15-20 minutes for middle school students, 20-30 minutes for high school students. After this, pre-fatigue sets in; if teaching tactics are not changed, then fatigue sets in.
Physical activity of schoolchildren
The physical activity of students consists of daily (morning exercises, walking, active breaks and breaks in the daily routine) and periodic.For schoolchildren, physical education classes should be 8-12 hours a week. Even 3 lessons are not enough to satisfy the biological needs of a growing organism. The physical activity of children should be organized to prevent physical inactivity and at the same time not lead to overwork. Replenishment of physical activity of students at school occurs mainly in physical education lessons. Depending on the form of delivery, topic and specificity, students realize their daily need for physical activity in different ways. The construction of physical education lessons in the interests of health lies on the shoulders of physical education teachers.
“Physical education without exemptions” is a principle that should guide physical education teachers. Physical activity should be organized in two directions:
- Large form classes - physical education lessons and work in sports sections outside of school hours.
- Lessons of small forms, introduced into the structure of the school day (introductory gymnastics before classes, physical education minutes and physical education breaks, physical exercises during an extended break).
Assessment of student health dynamics
Methods for diagnosing student health (socio-psychological, psychological-pedagogical)The health assessment should include the results of:
- teacher-provided: observations and evaluations;
- results provided by parents;
- results provided by the students themselves;
- results of regular medical examinations.
Test questionnaire for teachers
Test questionnaire for an indicative assessment of the risk of a student’s health problems.The teacher gives the assessment himself. 0 — the sign is not expressed; 1 - weakly expressed; 2 - the sign appears periodically or is moderately expressed; 3 - clearly expressed.
- Poor health has been evident since childhood.
- Previously suffered serious illness, injury, and surgery.
- Growing up in a dysfunctional family.
- The family has financial difficulties.
- An asocial environment (friends, neighbors, relatives) is typical.
- Leads an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Leads a sedentary lifestyle.
- Low intellectual level.
- Low cultural level.
- Immaturity of hygiene skills is characteristic.
- Carefree, irresponsible.
- Weak willed.
- Lack of initiative.
- Shows no interest in his health.
- Has increased excitability of the nervous system.
- Poor communication with teachers.
- Increased fatigue.
- Uses (used) intoxicating substances.
- Smokes.
- He often complains about his health.
Municipal budgetary educational institution
"Savasley Secondary School"
Generalization of work experience on the topic
“Use of health-saving technologies
in physical education lessons"
Completed by: Snorovikhin I.V.
Physical education teacher
With. Savasleika
year 2014
Main characteristics of the experience………………………………………………………..
The essence of experience………………………………………………………………..
Relevance of experience…………………………………………………………….
Conditions for the formation of experience………………………………………………………
Novelty of experience………………………………………………………………………………..
Labor intensity of experience……………………………………………………………….
Theoretical basis of experience………………………………………………………
Technology of experience………………………………………………………………………………….
3.1 Goals and objectives………………………………………………………………………………………
3.2 Means and methods…………………………………………………………………………………
3.3 Conducting health monitoring and
physical fitness of students………………………………………………………...
4. Effectiveness of experience………………………………………………………..
5. References……………………………………………………………...
Applications………………………………………………………………………………..
1. Main characteristics of the experience
The Essence of Experience
The essence of the experience is to ensure physical health and a healthy lifestyle for students through an optimal combination of theory and practice, the choice of modern means, methods and forms in the process of teaching physical education.
Relevance of experience
Health and a healthy lifestyle do not yet occupy first place in the hierarchy of human needs in our society.
Nowadays you almost never meet a completely healthy child. The intensity of students' educational work is very high, which is a significant factor in weakening health and an increase in the number of various deviations in the body's condition. The causes of these deviations are a sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia), accumulation negative emotions without physical release, as a result of which psycho-emotional changes occur: isolation, imbalance, excessive excitability. Anxiety about the result and its expectation lead to an increase in mental stress, nervous shock, school stress and discourage the desire to be active.
All of the above reasons lead to the fact that the child not only has health problems, but also develops personal problems. Lack of persistent interests and hobbies related to expanding one’s horizons, apathy, and closedness are the few symptoms that are associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Due to the deteriorating level of health of the younger generation, there is a need to organize a physical education lesson with an emphasis on solving health problems physical education without disturbing the educational component of the process.
In accordance with the Law “On Education”, the health of schoolchildren refers to priority areas state policy in the field of education. The issue of preserving the health of students at school today is very acute. Doctors note a trend towards an increase in the number of students with various functional abnormalities and chronic diseases. However, in curriculum there is only one item that can to a certain extent compensate for the negative impact of intensification educational process: an increase in physical inactivity, a decrease in the motor activity of students - this is the subject “Physical Education”.
Therefore, every physical education teacher faces questions: how to organize the activities of schoolchildren in the classroom in order to give each student the optimal load, taking into account his preparedness and health group? How to develop students’ interest in physical education lessons and the need for a healthy lifestyle, taking into account the emergence of stronger interests in the lives of schoolchildren? How to make physical education lessons attractive for all children? How to achieve the optimal combination of health, training, and educational components of physical education activities in a lesson? How to ensure that the subject “Physical Education” has a holistic impact on schoolchildren, stimulating their conscious self-development, self-improvement, and self-realization. When solving these questions, questions arise contradictions. On the one hand, a physical education teacher in the process of his activities must take into account the multifunctionality of the lesson, on the other hand, increasing the requirements for its valueological orientation; on the one hand, a high level of requirements for the physical fitness of graduates, on the other, a decrease in interest in physical education lessons.
Therefore there arises problem, relevant for both pedagogical science and practice: how to effectively organize the educational process without harming the health of schoolchildren? It is possible to answer this if we approach the organization of training from the perspective of the three principles of valeology: preservation, strengthening and formation of health.
The relevance of the experience lies in solving this problem of preserving and strengthening the health of schoolchildren; it can be achieved by implementing the following tasks:
Creating conditions that promote the development of schoolchildren’s motivation for physical education and a conscious attitude towards health.
Providing students with the necessary reliable information and technologies in the field of developing a healthy lifestyle.
Prevention of misunderstanding of the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
1.3 Conditions for the formation of experience
The experience of working on the topic “Health-saving technologies in physical education lessons” developed gradually. The experience was formed in an ordinary rural secondary school. In Savasleyskaya secondary school I've been working for 7 years. I've been working on this problem for two years. The topic I have chosen is consonant with the problem that the teaching staff of our school is working on: “Humanization of the learning process is an important condition for the formation of a harmoniously developed personality.”
1.4 Novelty of experience
The novelty of the experience lies in the implementation of innovative health-saving technologies in physical education lessons:
Using valeological techniques to motivate a healthy lifestyle;
Using ICT to more clearly demonstrate the benefits of a healthy lifestyle.
1.5 Labor intensity of experience
The main problem that faced me was creating conditions for physical development, strengthening and preserving the health of children.By conditions I mean increasing students’ motivation for physical education lessons, creating material base for classes.
School students, especially high school girls, were reluctant to attend physical education classes and often skipped classes for any reason.
The presence of a good sports base at the school made it possible to work on a comprehensive physical education program at the school.
The work system for implementing a comprehensive program can be presented in the form of a diagram (see Diagram 1).
Questioning
Medical checkup
Implementation of a comprehensive program
Physical education lesson
Extracurricular forms of work
Monitoring
Result
2. Theoretical basis of experience
The theoretical basis for the presented experience can be found in the works of V.I. Kovalko. The manual by the famous teacher contains theoretical and practical information about current state health preservation pedagogy, a specific program for a healthy lifestyle is provided. Also, based on the proposed experience, I use the work of N.K. Smirnov, the main content of the concept of “health-saving educational technology.” The experience is based on a comprehensive physical education program for grades 1-11, authored by Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences V.I. Lyakh, and candidate of pedagogical sciences A.A. Zdanevich.
2.1 Health-saving technologies at school
One of the serious, not yet fully resolved tasks is preparing teachers to work on introducing health-saving technologies in schools. Health-saving educational technologies are many of the psychological and pedagogical techniques, methods, and technologies familiar to most teachers that do not cause direct or indirect harm to health (Smirnov N.K.). Preparing a child for a healthy lifestyle based on health-saving technologies should become a priority in the activities of every educational institution for school-age children.
Reasons leading to poor health in children (see Diagram 2).
Student health
Problems
Disease of the musculoskeletal system.
Poor posture, flat feet.
Decreased vision.
Neuropsychiatric disorders.
Causes
Sedentary lifestyle
Wrong habit. Ignorance of means, forms.
Insufficient lighting. Study overload.
Accumulation of negative ones. emotions
Scheme 2. Causes leading to health problems.
IN AND. Kovalko writes that the success of the implementation of health-saving technologies depends on many components:
Active participation of students themselves in this process;
Creation of a health-preserving environment;
High professional competence and literacy of teachers;
Systematic work with parents;
Close interaction with the socio-cultural sphere.
The entire learning process in the conditions of health-saving pedagogy includes three stages, which differ from each other both in particular tasks and in the features of the methodology.
First. The stage of initial familiarization with basic concepts and ideas.
The goal is to form in the student the basics of a healthy lifestyle and achieve the implementation of basic health rules.
Main goals:
To form a semantic understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
Create basic understanding of the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
Achieve compliance with basic health rules (at the level of initial skill).
Prevent misunderstanding of the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
Second. Stage in-depth study.
The goal is to develop a full understanding of the basics of a healthy lifestyle.
Main goals:
Clarify your understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
Achieve conscious implementation of basic health rules.
Formation of practically necessary knowledge, abilities, skills, rational methods of thinking and activity.
Third. The stage of consolidating knowledge, skills and abilities in health conservation and their further improvement.
The goal is the ability to translate into a skill that has the ability to be used for its intended purpose.
Main goals:
Achieve stability and automaticity in the implementation of health rules.
Achieve compliance with health rules in accordance with their requirements practical use.
Ensure variable use of healthy lifestyle rules depending on specific practical circumstances.
3. Technology experience
Goals and objectives of educational activities
The main goal pedagogical activity I believe in creating conditions for the physical development, preservation and strengthening of schoolchildren’s health.
The main objective of educational activities is:
Comprehensive implementation of the basic components of the program.
Solving the main problems of physical education at each stage of education.
When selecting content, I am guided by a comprehensive physical education program.
My job as a teacher is to implement the basic components of the program. When planning educational material, I am guided by the following:
The educational material, first of all, must meet the requirements
program, goals and objectives of the lesson and is focused on the final result;
I take as a basis the basic level of educational content, but at the same time
Each student is given the opportunity to choose the content of the activity
in class, based on the level of physical fitness of his motor skills
abilities and health status.
I definitely plan the material
This is exactly how I see the creation of a health-saving space in physical education lessons.
To implement a health-saving space, consider Scheme 4
Physical education lesson

Diagram 4. Impact of physical education lessons on schoolchildren
3.2 Tools and methods
To achieve the goals of health-saving technologies, the following groups of means are used:
hygiene factors;
healing powers of nature;
means of motor orientation.
The first condition for recovery is the creation of a hygienic regime in physical education lessons. For clarity, we use diagram 3. My responsibilities include the ability and willingness to see and identify obvious violations of the requirements for hygienic conditions for conducting a lesson and, if possible, change them in better side– myself, with the help of the administration and doctors.

Scheme 3. Hygienic means to achieve health preservation
The second is the use of the healing powers of nature, which has a significant impact on achieving the goals of health-saving technologies in the classroom. Carrying out activities in the fresh air promotes activation biological processes, increase the overall performance of the body, slow down the process of fatigue, etc.
The most important condition is to ensure optimal motor mode in physical education lessons, which allows you to satisfy physiological need in motion, contributes to the development of basic motor qualities and maintaining performance at a high level throughout the school day, week and year.
Only the integrated use of these funds will help solve the problem of recovery.
I understand perfectly well that it is impossible to force all schoolchildren to engage in physical education and their health; this requires certain incentives and motives.
To create conditions for motivation to engage in physical education, I use:
valeological education of students and their parents;
non-traditional lessons;
modern means physical culture;
combination of methods and techniques of physical education.
extracurricular forms of physical education
1. Valueological education of students and their parents.
On parent meetings I widely cover issues related to the state of health, the conditions for its preservation and strengthening. I include parents in the process of discussing problems and provide statistical data.
In class I practice conversations about a healthy lifestyle. When performing various exercises, I explain to the children the meaning of each of them.
For the purpose of a more visual representation of a healthy lifestyle, I use computer presentations. This is particularly stimulating cognitive activity students, increases interest in the topic, promotes the acquisition of basic rules for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Presentation of one topic (see Appendix 1).
During all lessons, I instill hygiene skills in the child, and provide for his participation in regulating the general daily routine, in particular, the routine of movements during the day. I bring up the correct attitude of children towards hardening the body. For this purpose, I practice classes in shorts and T-shirts, skiing, playing in the fresh air, walking barefoot, drying off after classes, etc. etc. I teach children proper breathing and massage techniques (self-massage).
2. Main types non-traditional lessons are role-playing lessons, health lessons (see Appendix 2). During health lessons, I divide children into groups; in groups of weakened children, I follow the principles and norms of providing children with exercises that help relieve mental stress, excluding long-term static loads. I use physical exercises that are aimed not only at the physical development of children, but also have a therapeutic and educational effect, corrective, corrective exercises. For example, walking on foot stairs, bumps, or ropes strengthens and develops the muscles of the foot and prevents the development of flat feet. Exercises with a skipping rope and a hoop promote the formation of correct posture and have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Sets of exercises (see Appendix 3).
I regularly use special complexes that create elegance, grace, and plasticity. I make sure to include exercises on psychoregulation and relaxation in each lesson (see Appendix 4). I include story-based games and game tasks in my lessons.
3. I use modern means of physical education. I use these tools when working with high school girls.
Working with girls occupies a special place in my teaching activity. How to create conditions that promote motivation of high school girls to engage in physical education and be conscious of their health? I found a solution to the problem in the choice of physical education means:
Rhythmic gymnastics;
aerobics;
shaping classes;
exercises in the gym.
To increase interest and emotional mood in my lessons, I use technical means: tape recorder, computer.
4. I successfully combine gaming, competitive and circular methods. When using one or another method, I take into account the age characteristics of students, prevent overwork, direct their actions and control the load.
For the purpose of complete and accurate description exercise techniques, I show the sequence of actions clearly. In my practice, I use methods of analyzing exercises, I suggest, I help perform them, but at the same time I take into account the physical development and level of physical fitness of the child. I am convinced that methods of persuasion and encouragement have a special effect on children.
I teach you to consciously evaluate physical development own body and create sets of exercises. Students themselves monitor their own state of well-being during classes and create their own sets of exercises. I explain to students that the systematicity of special exercises and the sequence of their implementation consolidate the results achieved during the lessons. This arouses interest in classes, activity and the desire to work on oneself independently.
When choosing methods and techniques, I take into account general pedagogical and methodological requirements. Explaining new material While learning and consolidating it, I draw children’s attention to the main mistakes in the technique of performing exercises, teach them to analyze and evaluate them.
I pay a lot of attention to homework; I have developed and compiled homework sets. Thanks to them, students learn to be independent and actively participate in the process of self-improvement.
It is on children’s interest in activities that it is necessary to build lessons, thereby developing skills and abilities that provide motivation for health. In my lessons, I try to create such conditions so that the child “develops an appetite” for physical education and sports, so that he understands the benefits of movement for his health.
Extracurricular work on the subject
Schoolchildren need to master the basics of personal physical culture, which is understood as the unity of knowledge, needs, motives to achieve an optimal level of health, physical development, comprehensive development of motor abilities, and the ability to carry out their own motor, physical education, health and sports activities. And here extracurricular forms of physical education, recreation and sports work play a big role. They allow you to increase the volume of physical activity and contribute to a more complete realization of their individual abilities and motor potential.
In order to increase the physical activity of students extracurricular activities I build in a certain sequence. It is aimed at consolidating the skills and abilities acquired in the lessons. All activities, as a rule, are carried out according to sections of the curriculum. The main forms of physical education are (see Diagram 5).




Gymnastics before classes.
Outdoor games during breaks.
Physical education minutes.
Sports hour in extended day groups
Generally - physical training.
Sport sections.
Days of health and sports
Tourist rallies and
Physical education holidays
Intraschool competitions
Scheme 5. Forms of physical education
The school organizes and hosts sports festivals, health days, friendly meetings, tourist rallies, and organizes the preparation of teams for school and regional competitions. We try to involve as many children as possible in mass sports events and competitions. Taking part in competitions at the school and district level greatly contributes to attracting schoolchildren to sectional classes.
This is my fifth year running the cross-country skiing section. Work in this direction has an effective impact on the physical development, preservation and strengthening of the health of schoolchildren. My students, as a rule, do not get sick and show a high level of physical fitness, fulfill all the standards for passing tests and tests.
Together with students, we carry out active propaganda work to promote physical education and sports, set up sports corners: “Health Corner”, “Sports Life of the School”, and publish information newspapers. We have developed and the school administration approved the “Regulations on the best sports class.” At the end of the school year, the best sports class is awarded a certificate and gifts.
3.4 Monitoring the state of physical fitness
students
Monitoring tasks:
To identify the state of physical fitness and health of schoolchildren.
To analyze the effectiveness of work on physical education, maintaining and strengthening the health of students at school.
Technology for monitoring the state of physical fitness(See Diagram 6).
 Scheme 6. Model for monitoring the state of physical fitness
Scheme 6. Model for monitoring the state of physical fitness
To monitor and identify the level of physical fitness, I test students. Monitoring the completion of tests allows you to more effectively manage the educational process, draw conclusions and make adjustments in a timely manner. To the generally accepted control tests, proposed by the program, I add tests of presidential competitions, I conduct them not twice a year, but every quarter.The tests are aimed at developing basic motor qualities: flexibility, endurance, strength, speed, coordination abilities.
Based on testing data, groups of students in need of adjustment are identified, and I carry out corrective work with them. To do this, I develop sets of exercises aimed at developing lagging physical qualities.
I record the test results of each class in the “Health Passport”. The level of physical fitness of students is determined based on the results of testing according to the presidential test program and is determined as a whole for the school at the end of the school year.
4. Effectiveness of the experience
Analyzing the results of my experience, I note that the introduction of a system of work on health-saving educational technologies made it possible to:
1. Improve your performance in the subject.
Increase the dynamics of growth in students' physical fitness.
To increase students' interest in physical education and motivation to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Increase the dynamics of student health
Health-saving technologies should undoubtedly be used in the process of improving the health of schoolchildren, in particular, in physical education lessons.
Literature
1. Derekleeva N.I. Motor games, training and health lessons. Moscow
"VAKO", 2004.
2. Kovalko V.I. Health-saving technologies. Publishing house "VAKO",
2004.
3. Kodzhaspirov Yu.G. Educational games in physical education lessons.
LLC "Drofa", 2003.
4. Mishin B.I. Handbook for physical education teachers. AST Arstel
Moscow 2003.
5.Lyakh V.I., Zdanevich A.A. Comprehensive physical education program
students of grades 1-11 Moscow “Enlightenment” 2007.
6. Smirnov N.K. “Health-saving educational technologies in
modern school", Moscow, 2002.
APPENDIX 2
Lesson summary on physical education in 2nd grade
Program section:"Gymnastics", "Fundamentals of Knowledge"
Goals: Introduce students to the concept of “daily routine”; to introduce students to regular physical exercise for the purpose of physical development and a healthy lifestyle.
Lesson objectives:
consolidate exercises in balance;
improve the skills and abilities of climbing exercises;
cultivate discipline, hard work, and collectivism.
Organization method: individual, frontal, in-line.
Location: gym
Inventory and equipment: multi-projector, tape recorder, audio cassette, gymnastic mats, 2 foot ladders, 4 gymnastic benches, 18 wet towels, 18 inflatable balls.
Dosage
Preparatory part
15 minutes
Construction, communication of lesson objectives
View slides. Conversation with children.
What is a daily routine?
Where do you start your daily routine?
Having woken up and done our morning exercises, we... (children continue)
We had breakfast, and then... (children continue)
Returning from school, we... (children continue)
What do you do in your free time?
What time do we guys have dinner and go to bed?
What do you need to remember when following your daily routine?
Why is a daily routine important for a person?
Place children on benches
Slide 9, 10
Slide 11, 12
Poetic exercises for morning exercises
Now guys, stand up!
They quickly raised their hands up (hands up through the sides)
To the sides, forward 2p
Turn to the right, left, (torso turns, arms alternately forward)
Right left
1-2 Well done
And to the right and also over the left shoulder
Stomp your right foot (side step, arms forward to the sides)
Stomp your left foot.
Again - with the right foot,
Again - with the left foot,
After - with the right foot
Then with your left foot,
Leaned to the left, to the right (torso tilted to the sides, arms above the head)
Left, right
It turns out great
Left, right, left, right
Bent over from the heart (lean forward)
One - bent over, two - bent over (lean forward, backward, hands on the belt)
He spread his arms to the sides,
To reach the sun,
You need to stand on your toes. (stretch up on your toes, arms out to your sides)
One, two, three, four, five (jumping in place, hands on the belt)
We want to become stronger (lunges to the sides, clench fists with our hands)
Fine! Well done
Stretch from the heart (lean forward, hugging your knees)
Rearranging into a column
Musical accompaniment.
Stretch on your toes.
Palms facing yourself.
Raise your head.
Dancing.
Reach out for your hand
Watch your posture
Stretch up.
Arms straight
Walking
On your toes, hands up
On your heels, hands behind your head
Running with game tasks
Ground (squat)
Air (climb the gymnastics wall)
Water (arms forward rotation)
Breathing exercise
Back straight
Elbows apart
Inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth
Main part
25 min
Walking on the narrow rail of a gymnastic bench.
a) Walk towards each other; when meeting, separate without leaving the bench.
b) While walking, take a certain position at a sudden signal from the teacher.
Foot exercises
a) Grabbing a small ball with your feet.
b) Walking on stairs for feet.
Climbing on an incline bench
a) Emphasis crouching
b) Standing on your knees
Game "Daily Mode"
Students stand in a circle representing a clock face. The teacher calls the activity “getting up”, the children say “7 o’clock” and clap their hands 7 times. Students who stand on the numbers “7” and “12” raise their hands up, indicating that they are ready to run and, after waiting for the teacher’s signal, the number “12” catches up with the number “7”, etc.
Watch your posture
Watch your back position
Monitor execution technique
Game "Rules of Hygiene"
Children form a circle. The teacher gives everyone a task:
What do we do in the morning when we wake up?
The player identified by the teacher answers and shows.
We do exercises, wash ourselves, brush our teeth. (performs in motion and everyone repeats his movements)
The next player completes the next task... and so on.
Psychoregulation and relaxation game
with inflatable balls.
"Walk in the Meadow"
(Calm music)
We are walking in the meadow
You can hear the rustling of leaves, the singing of birds
Movements are smooth, slow
Creates a joyful mood
We smile at each other
(Music is more fun)
Various movements with balls are performed to cheerful music.
Musical accompaniment song “Smile”
Everyone sings the chorus of the song “Smile”
Final part
5 minutes
1. Homework.
2. Lesson summary.
3. Wiping with a damp towel to the waist.
Give everyone their own daily routine.
Rubdown in locker rooms
Lesson summary
Topic: Rhythmic gymnastics, shaping.
Tasks:
Formation of posture and its correction.
Improving coordination abilities.
Training in elements of self-massage and psychoregulation.
Location: gym.
Inventory and equipment: tracks, video recording, tape recorder, chairs – 9 pcs.
Duration: 45 min.
Lesson parts
dosage
Guidelines
I hour
Part II
Building a class.
Lesson objectives.
A conversation about the formation of posture and its correction.
What is posture?
How to improve your posture?
What exercises do you know to improve posture?
Moving to the place of classes, staggered formation
Rhythmic gymnastics:
a) Varieties of walking on toes, sharp step, high step, side step, cross step.
b) Varieties of running and jumping: simple, on toes, high, with straight lines to the sides, forward, backward, sweeping the shin back.
c) Breathing exercise, relaxation.
Shaping(video recording).
Part I
a) Standing exercise for the upper and lower body.
b) Exercise with a chair.
c) Relaxation exercise, breathing.
Part II
Preparation of paths.
Exercises for the abdominal muscles.
Self-massage of the legs (legs, thighs) stroking with the edge of the palm, one hand on the other, patting, shaking.
I. Breathing exercises
a) Breathing through one “nostril”.
b) “Fast breathing.”
c) “Cleansing breath.”
Autogenic training(psychoenergetic version)
a) Mentally see spots of light: red, green, blue, black, select one of them and keep it in your field of vision
red – warm
black - sadness
blue – cold
green – peace
b) See yourself from the outside, imagine yourself on the seashore, in the forest.
Lesson summary:
D/z
1) Continue doing rhythmic gymnastics on your own.
2) Prepare for the torso elevation test
Organized care.
30s
30s
5-7min.
30s
4min.
4min.
1 min.
each exercise is repeated 10 times
3 min.
4min.
2 times
2 times
1-2min.
Pay attention to the form.
Appendix No. 1
Musical accompaniment
Raise your head, straight back, spread your shoulders, pull your stomach in.
Start of movements to the right.
Watch your posture.
Pull the toe.
Breathe through your nose.
Watch your posture and breathing.
Perform the exercise smoothly.
Monitor correct execution. The massage is performed from bottom to top. Appendix No. 2
Appendix No. 3.
Watch your back and head.
Watch your belly breathing.
First perform the exercise with your eyes closed, and then with your eyes open.
APPENDIX 3
Posture exercises
Exercises for a flat back
1. Bend backwards, bending from a kneeling position.
2.Lying on your stomach, grabbing your feet with your hands, try to pull them to your head (“basket”); do the same alternately with the right and left foot.
3.Standing on your right, grab your left foot and, bending it at the knee, try
pull back and up; the same with the other leg.
4. Bridge from a prone position.
5. Hangs bent over the gymnastics wall.
6. Mixed hangs in a bending position.
Eliminations for increased lumbar curve
1. Bend backwards while kneeling. Maintain a straight line from knees to head; do the same, successively touching your heels with your hands, then the floor.
2. Sit on your heels, arms forward, shoulders touching your knees.
3. In a sitting or standing position, grasping the foot, pull the knee to the shoulder; the same with the other leg.
4.Sit with your legs crossed, lean forward, alternately touching your knees with your head.
5. From an emphasis position, squatting, extending your legs at the knees, hands at the toes.
6. Hanging with your legs bent, turning them to the right, left, with your legs extended into a corner.
7. Lying on the floor, touch the floor with as much of your body as possible.
8. Raising legs while sitting.
9.Alignment of the torso against the wall (tighten the stomach).
Exercises for increased thoracic curve
1.Kneeling, arms along the body, bend back, bending, reach
heels with hands.
2. Standing on your knees, tilt your torso to the right, reaching right hand heel of the left foot;
the same to the left.
3.Lying on your stomach, bending over, circling with your arms outstretched to the sides.
Complex of general developmental exerciseswith short jump ropes “Sun”
I. I.p. - basic stance, rope folded in four in downy hands. Pulling the rope, we raised our hands up and lowered them.
2.I.p. - standing with your feet apart, a double-folded jump rope in bent arms behind your head. While pulling the rope, turn your torso left and right.
3.I.p. - standing on the rope with your feet apart, hold the rope by the ends. Tilt your torso to the left, pulling the rope with your right hand. The same in the other direction.
4. I.p. - standing, jump rope folded in four in front of you. Without resting your hands on the floor or lowering them, you sat on the floor and straightened your legs. We stood up without using our hands.
5. I.p. - standing, a jump rope folded in four behind your back with your hands down. Tilt the torso forward, arms back to the limit. We returned to IP.
6. Jumping over a rotating rope from foot to foot.
A set of special exercises “Smooth back”.
1. We dispersed around the hall.
I.p. - stand against the wall, touching it with the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks, heels and elbows.
Maintaining the accepted position, take a step forward, then a step back; repeat several
2. I.p. -Same.
Walking around the hall in different directions; return to IP
Take your places in two lines.
3.I.p. - main stand. Bend your right leg forward, arms to the sides, clap your hands
behind your back, cotton under your foot; return to i.p.; the same, bending the left one forward.
4.I.p. - main stand.
Sit on your toes, knees apart, back straight, arms forward - to the sides - position
landings when jumping; return to IP
5. I.p. - main stand.
Half squat, arms back, swing arms forward, small jump up, soft squat while maintaining balance; return to IP
6. The same exercise, but jump up and half a step forward.
Formation into one line - the second line takes two steps forward.
7.Running alternating with walking.
A set of special exercises “Beautiful Posture”.
1.Spread around the hall.
I.p. - stand against the wall, touching it with the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks, heels and elbows. Sliding
hands along the wall, hands through the sides up, then through the sides down. Keeping the right
posture, take your place.
2.I.p. - Same. Touching the wall with the back of your head and back, raise your hands in front and half-squat;
Focus on health-saving technologies in education is one of the main and urgent tasks of the entire education system. The relevance of the topic is predetermined by the fact that health is the main human value. Exactly at school age the foundations of health-saving thinking and behavior of the individual are laid. On the other hand, the school environment most often does not create conditions for promoting health. !
Download:
Preview:
Health-saving technologies in physical education lessons and in extracurricular activities. (slide No. 1)
At the core of development modern standards school education lies the idea of education as an institution for the socialization of the individual.The new standard focuses teachers' attention on the need to usemodern educational technologies,which can provide development schoolchildren. It is no coincidence that the use of advanced technologies becomes the most important criterion for a teacher’s success. Thanks to modern technologies, lessons unfold activity students. Focus on health-saving technologies in education is one of the main and urgent tasks of the entire education system. The relevance of the topic is predetermined by the fact that health is the main human value. It is at school age that the foundations of health-saving thinking and behavior of an individual are laid. On the other hand, the school environment most often does not create conditions for promoting health.Caring for the health of students is the responsibility of every school, every teacher.The teacher can do
To save
And strengthening the health of schoolchildren
More than a doctor! (slide No. 2")
. The concept of “health-saving educational technologies” (HST) has appeared in the pedagogical lexicon in the last few years and is still perceived by many teachers as an analogue of sanitary and hygienic measures. This indicates a distorted understanding of the term “health-saving educational technologies”, primitive ideas about the content of the work that a school should carry out to implement its the most important task- maintaining and strengthening the health of students.
Teachers of general education subjects also understand this term differently. Some believe that ZOT is one or more new pedagogical technologies, alternative to all others, and therefore you can choose whether to work, for example, using KUZ, IOSO technologies, etc. or using “health-saving technology”. Health conservation cannot, by definition, act as the main and only goal of the educational process, but only as a condition, one of the tasks associated with achieving the main goal.
Health-saving technologies -
this is a quality component of any educational technology, its “health safety certificate”"(slide No. 3)
Health-saving educational technology is understood as a system that creates the maximum possible conditions for preserving, strengthening and developing the spiritual, emotional, intellectual, personal and physical health of all subjects of education (students, teachers, etc.).
Health-saving educational technologies are a set of techniques, forms and methods for organizing the education of schoolchildren without harming their health..(slide No. 4)
The goal of health-saving pedagogy is to provide school graduates with a high level of real health, equipping him with the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, and cultivating in him a culture of health. If caring for the health of students is one of the priorities of the entire teaching staff and is carried out on a professional basis, then only then can we talk about the implementation of health-saving technologies at school, and the result of their implementation will be the protection of the health of students and teachers from the influence of negative factors, primarily related to the educational process.
In physical education lessons, health-saving technologies are the basis. The activity of a physical education teacher to preserve the health of children is one of the components of the quality of the result.
The traditional system of physical education, focused on the program recommended by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation, is designed to provide a certain amount of premises, specialized equipment and inventory. In the absence of such conditions, the program becomes completely impossible to implement and the physical education teacher transfers the entire burden of its development to the standards proposed in the program, that is, in fact, he transfers the burden of responsibility for the effectiveness of physical education from himself to the students. Moreover, taking into account the prevailing attitude in our education towards standards focused on the “average” student, they themselves, in the current interpretation, are the most important factor not in the education of physical culture in students, but in alienation from it. At the same time, resolving this issue, and on the basis of individual guidelines, does not cause any fundamental difficulties.
The main goal of the work of physical education teachers is to provide the student with the opportunity to maintain health during the period of study at school. To do this you need:
Form among students necessary knowledge, skills and abilities for a healthy lifestyle(Slide No. 5)
Teach schoolchildren to use the acquired knowledge in Everyday life;
To teach schoolchildren the techniques of mobilization, relaxation and spiritual self-improvement.
Develop a value-based attitude towards your health.
Create a need for a healthy lifestyle.(Slide No. 6)
The assigned tasks are solved through:
1) improving the methodology of teaching a lesson,
2) individual work with low-achieving and physically developed students,
3) correction of schoolchildren’s activities based on diagnostics of development, abilities and natural inclinations,
- motivating schoolchildren to study.
The teacher’s activities in the aspect of implementing health-saving technologies in physical education lessons should include familiarization with the results of medical examinations of children, taking them into account in teaching and educational work; Helping parents build healthy lives for students and families as a whole.
The theory and practice of physical education convincingly demonstrate that exercises aimed at developing endurance (running, jumping, outdoor games, tourism, orienteering) are of particular importance for promoting health, promoting the expansion of the functional capabilities of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and improving the activity of the central nervous system. and, thereby, overall strengthening of health and increasing the performance of the body.
Those exempt from physical education, as well as children classified as preparatory group, it is necessary to offer to prepare reports and messages on healthy lifestyle.
In some lessons, use questions and tasks to find out whether children understand the basic concepts and rules of “health conservation”:
1. Define the concepts of “Health” and “Healthy lifestyle”.
2.Name the main components of a healthy lifestyle. How do you implement them in your life?
3.Name 10 reasons to say “No” to drugs.
4.What methods of managing your well-being and performance do you know?
5.How to breathe correctly:
Mouth
Nose
Classes, participation in competitions, in a word, physical education is one of the foundations of our health.
It is physical education teachers who must help children get rid of stooped shoulders and sunken chests, and develop their strength, speed, flexibility, and agility. This is especially important in modern conditions with a sharply worsened environmental situation and increased stress.
However, in teaching physical education there are several typical problems that force teachers to turn to the experience of their colleagues, to innovative ideas, and to science.
2. Weak material and technical base
3. Overloaded halls.
Physical exercises aimed at mastering proper walking, running, jumping, throwing, and balance skills make it possible to organize the work of children in the main medical group and the preparatory group, taking into account the dosage of physical activity and the age characteristics of schoolchildren, and to form vital motor skills in them.
From early spring to late autumn, classes should be conducted outdoors whenever possible. All lessons must have high motor density. Use frontal and group methods in lessons. At the same time, the thread-group method proved to be most effective. The creative atmosphere in the lesson depends to a large extent on preparation for it, which includes carefully thought out explanations educational material, setting tasks in the sequence of their implementation and solution, explaining the essence of motor action, the relationship and interdependence of its elements. The lesson material must be arranged in a strict logical sequence from simple to complex: the relay race is replaced by dribbling a basketball, imitation exercises by rope climbing, jumping running by passing the ball in pairs.
Widely use various options for outdoor games based on competitive elements, all kinds of game relay races with objects. Use small sports equipment: gymnastic sticks, tennis and medicine balls, jump ropes. Independent activity of students, introducing elements of play into intense work, the necessary distraction, switching, calming, temporary rest to regulate the respiratory and cardiovascular functions of the body - all this creates a situation of success, instilling confidence in the children in their abilities.
For individual sections of the program, you can use cards with exercises of three degrees of difficulty. If a student does not perform this or that exercise well enough, he receives a task card with a difficulty coefficient of “1”, indicating a deadline for completion. At the end of the specified period, the student is required to pass the training standard or complete the learned exercise. After this, he receives a card with a coefficient of “2”, and after completing this task, a card with a coefficient of “3”. In addition, cards can contain movement patterns and a description of the order of performing various exercises from all sections of the curriculum. This allows for a differentiated and individual approach to learning.
As for health, in lessons with appropriate content it is necessary to create an idea of physical development and a healthy lifestyle, teach independent physical exercises using them for leisure and recreation. The children clearly see the connection between the subject “Physical Education” and the preservation of their health and normal physical development in the future.
To ensure an effective health-saving process, it is necessary to comply with sanitary and hygienic conditions of training, normalize the educational load and training schedule, use health-saving technologies taking into account the age and individual characteristics of the child;
It is necessary to create a favorable emotional and psychological climate at school, as well as by all means to promote the formation of the needs for a healthy lifestyle among students, teachers and parents.The starting position is that each student is an individual. The student is the subject of his education.(slide No. 7)
It is very important for the teacher to organize the lesson correctly, because... it is the main form of the pedagogical process.(slide No. 8) The level of hygienic rationality of the lesson largely determines the functional state of schoolchildren in the process of educational activities, the ability to maintain mental performance at a high level for a long time and prevent premature fatigue. We must not forget that hygienic conditions affect the teacher’s condition and his health. And this, in turn, affects the condition and health of students. The main modern requirements for a lesson with a complex of health-saving technologies: - the rational density of the lesson (the time spent by schoolchildren on academic work) should be at least 60% and no more than 75-80%; - the content of the lesson should include issues related to the health of students, contributing to the formation of students’ values of a healthy lifestyle and the needs for it; - the number of types of educational activities should be 4-7, and their change should be carried out every 7-10 minutes; - the lesson must include activities that promote the development of memory, logical and critical thinking; - during the lesson, at least 2 teaching technologies must be used (when choosing technologies, it is necessary to take into account whether they contribute to the activation of initiative and creative self-expression of students); - training should be carried out taking into account the leading channels of information perception by students (audiovisual, kinesthetic, etc.); - the scientific nature of the material being studied must be monitored; - it is necessary to form external and internal motivation for students’ activities; - it is necessary to implement an individual approach to students, taking into account personal capabilities; - in the lesson it is necessary to create a favorable psychological climate and necessarily situations of success and emotional release, because the result of any work, and especially mental work, depends on the mood, on the psychological climate - in an unfriendly environment, fatigue sets in faster; - it is necessary to include in the lesson technological techniques and methods that promote self-knowledge and self-esteem of students; - it is necessary to carry out targeted reflection throughout the lesson and in its final part.
To prepare and conduct a lesson that meets all of the above requirements, it is necessary professional competence teachers in matters of health-saving educational technologies, in connection with which there is a need for additional training for teachers of any specialty and working with different populations of students. Creating conditions for an interested attitude to learning. Situations of success contribute to the formation of positive motivation for the learning process as a whole, thereby reducing emotional tension, improving the comfort of relationships among all participants in the educational process, thereby implementing the basics of health-saving technologies when organizing the educational process.
In physical education lessons, it is necessary to pay special attention to the organization of health-preserving factors. Control tests, assignments, tests, etc. should only provide initial (and current) information for the development of individual tasks, the essence of which is that the student must move further in each period of time, which will be confirmed by the next test. If this does not happen, then the teacher must add individual assignments appropriate adjustments. It is fundamentally important that the student does not compare with others on the principle of “better or worse than others,” but compares with himself: today I have become better than yesterday, and tomorrow I will try to become better than today. However, for this, tasks must be realistic and stimulate students to active work. In the meantime, evaluation criteria are based on comparing the results of mastering knowledge and skills with some contrived “average” values. In this case, the strong student does not feel the need for everyday educational work, and the weak one, feeling doomed, does not feel the desire for it. And if a student does not understand the importance of educational material, then the selectively working subconscious immediately after receiving a grade helps him to quickly forget unnecessary material. In this case, the consistency in mastering the basics of knowledge is disrupted and each new material appears to be divorced from the previous one, independent and even far-fetched. Incorporating elements of active recreation into the training process.
Elements of physical education, in addition to the physical education lesson itself, can be used in other lessons and breaks: physical education minutes, physical education breaks, dynamic (moving) breaks(Slide No. 9) Such active recreation is designed to solve a number of problems: preventing early mental fatigue and restoring mental performance by activating cerebral circulation and switching attention; elimination of congestion in the blood circulation and respiratory system through deep breathing exercises and rhythmic alternations of contractions and relaxations of the muscles that provide accommodation of the eye; eliminating the adverse effects of prolonged stretching and relaxation of the back muscles responsible for posture and more. Ensuring the necessary hygienic conditions in educational premises. Lighting and air characteristics in the gym, temperature conditions. All this is quite fully regulated by the relevant sanitary and hygienic standards.(Slide No. 10)
Introduction
1. Health-saving pedagogical technologies.
1.2. Types of educational technologies.
1.4.. Principles of health-saving pedagogy
2.Health-saving technologies in physical education
Conclusion.
List of sources used.
Introduction
On modern stage development of education, the transition from authoritarian, group approaches in physical education of students to personality-oriented methods of teaching and upbringing, based on individual capabilities, will help improve the situation with regard to children’s health.
A personal-oriented approach in the physical education system has not yet become the norm for many physical education teachers in their work.
Practice feels the need to develop methods for conducting lessons that use scientifically based, proven traditional and non-traditional means and methods of physical education.
Healthy children mean the well-being of society. Without a healthy younger generation, the nation has no future. Preserving the health of the nation and the health of the younger generation is an important social problem.
The main task of the school is to organize the educational process at all levels in such a way that quality training, development and education of students are not accompanied by damage to their health. And a physical education lesson at school is the main health lesson. Every year, doctors and teachers note the dynamics of deterioration in children’s health. The work of the school today is aimed at preserving and strengthening the health of students, where health-saving and health-forming technologies are implemented.
Health conservation and its role in the educational process are considered differently by teachers and scientists. M.A. Danilov, for example, saw entertainment as the role of stimulating a student to learn; B.P. Esipov viewed it as a means of intensifying educational activities; N.I. Hamburg considers the use of entertainment as a means of improving the quality of learning. In a study by G.I. For Shchukina, entertaining is an important stimulus for arousing interest in the subject.
The relevance of the work is to consider issues related to the use of health-saving technologies in the process of physical education in physical education lessons.
Purpose of the work: to theoretically develop and practically justify the use of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons at school.
The object of the work is the process of teaching children in physical education lessons in health-preserving conditions.
Subject of research: health-saving technologies as a means of preserving and strengthening the health of students during the learning process.
Job objectives:
1. Study the essence of pedagogical technologies.
2. Identify the principles and functions of health-saving technologies.
3. Consider the means of health-saving technologies in the learning process during physical education lessons.
4. Determine the optimal forms of organizing educational activities in a physical education lesson in conditions of health-saving pedagogy.
Practical significance The work is that the material presented by the author can be used by teachers to organize and conduct physical education classes in health-saving conditions.
1. Health-saving pedagogical technologies.
1.1. The essence of pedagogical technology.
Pedagogical technology is a strictly scientific design and accurate reproduction of pedagogical actions that guarantee the success. Since the pedagogical process is built on a certain system of principles, pedagogical technology can be considered as a set of external and internal actions aimed at the consistent implementation of these principles in their objective relationship, where the personality of the teacher is fully manifested. This is the difference between pedagogical technology and the methodology of teaching and educational work. If the concept of “methodology” expresses the procedure for using a set of methods and techniques of teaching and upbringing without regard to the person implementing them, then pedagogical technology involves adding to it the personality of the teacher in all its diverse manifestations. Any pedagogical problem can be effectively solved only with the help of adequate technology implemented by a qualified professional teacher.
Pedagogical technologies can be presented as teaching technologies and educational technologies. We can highlight the most essential features such technologies: the technology is developed for a specific pedagogical plan; it is based on a certain methodological, philosophical position of the author. In the literature, a distinction is made between technologies for the process of knowledge transfer and technologies for personal development; the technological chain of pedagogical actions, operations, communications is built strictly in accordance with target settings, which have the form of a specific expected result; technology provides for the interconnected activities of teachers and students on a contractual basis, taking into account the principles of individualization and differentiation, optimal implementation of human and technical capabilities, and dialogic communication; elements of pedagogical technology must, on the one hand, be reproduced by any teacher, and on the other hand, guarantee the achievement of the planned results (state standard) by all schoolchildren; An organic part of pedagogical technology are diagnostic procedures containing criteria, indicators and tools for measuring performance results.
Modern researchers have proven that scientifically based and well-developed educational technologies help the teacher achieve the planned result. professional activity with the maximum degree of approximation. But in the field of education, much depends on the person using this or that technology. Therefore, the personality of the teacher, his culture, professionalism, intuition - all these are conditions for the successful use of any educational technology. Teaching a teacher the ability to independently analyze their activities, as well as analysis, selection, and development of educational technologies is an important scientific and methodological problem.
It is necessary to apply a technological approach to the process of teacher self-analysis of his professional activities, in particular its humanistic orientation.
1.2 Types of educational technologies
According to the stages of solving a pedagogical problem, regardless of their content and time frame, it is possible to distinguish between interrelated general and specific technologies. General technologies include design technologies, for example, the learning process and its implementation. Private ones are technologies for solving such problems of teaching and upbringing as pedagogical stimulation of student activity, monitoring and evaluation of its results, and more specific ones - such as analyzing the educational situation, organizing the beginning of a lesson, etc.
One of the decisive conditions for the successful implementation of the pedagogical process is its design, which includes analysis, diagnosis, determination of prognosis and development of an activity project. At this stage of solving a pedagogical problem, it is possible to identify closely related types of teacher activities, which are relatively independently aimed at constructing the content, means and programs of action for themselves and their students. Accordingly, the technology of designing the pedagogical process can be represented as the unity of the technology of designing content (constructive-content activity), designing material or materialized means (structural-material) and designing activity (constructive-operational).
The technology for the direct implementation of the pedagogical process can be represented as a set of sequentially implemented technologies for transmitting information, organizing educational, cognitive and other types of developmental activities, stimulating the activity of students, regulating and correcting the course of the pedagogical process, its current control. The central place among them is occupied by the technology of organizing activities, which is, in essence, the implementation of the plan and project for the functioning of the pedagogical process.
The content of a teacher’s activity at the stage of implementation of the pedagogical process can be represented by an interconnected system of such pedagogical actions as setting goals for students and explaining the tasks of the activity; creating conditions for the acceptance of activity tasks by the team and individual students; application of selected methods, means and techniques for implementing the pedagogical process; ensuring interaction between subjects of the pedagogical process and creating conditions for its effective implementation; using the necessary techniques to stimulate student activity; establishing feedback and timely adjustment of the progress of the pedagogical process.
Taking into account the technological requirements and characteristics of children’s activities to be organized determines the specifics of relatively independent technologies for organizing children’s developmental activities.
In the organization of educational cognitive activity students crucial has a technology for teaching them to solve problems of various types. In the holistic technology of organizing educational and cognitive activity, which essentially boils down to managing the processes of students solving educational problems, an important element is teaching them the culture of defining concepts. In the course of this work, students begin to understand the organizing role of definitions in understanding the subject as a whole.
The universal initial method and basis of the technology for organizing developmental activities is the pedagogical requirement. The pedagogical requirement does not lose its purpose in connection with changes in the philosophy of education itself, since it is fully consistent with the principle of priority of subject-subject relations in the total volume of relations of the pedagogical process. When mastering a specific technology for organizing children's developmental activities, it is important to keep in mind that a pedagogical requirement in its development must go through a logical series of steps: from primary to initial, from it to a requirement-rule, then to a requirement-norm and finally develop into a requirement-rule. principle.
The technology for organizing the developmental activities of schoolchildren according to the type of reflexive management, in contrast to authoritarian management, involves placing the student in the position of an active subject of cognition, communication, work and social assessment carried out in a general system of collective work; development of the student’s ability to self-government (self-regulation, self-organization, self-control of one’s own activities); organization of the pedagogical process as a solution to educational, cognitive and other tasks (problems) based on creative interaction (dialogue) between teachers and students
In the classification of pedagogical technologies, the following can be distinguished:
1. Technology of management activities.
2. Technologies for organizing the educational process.
3. Technologies for organizing students’ cognitive activity.
4. Technologies of educational work.
5. Subject technologies.
6. Corrective technologies for children with temporary difficulties in learning and behavior.
7. Corrective technologies for children with problems in mental and physical development.
Technology of management activities - functional technology, technology of program-target planning, information technology.
The technology of organizing the educational process is:
a) change in structure educational institution;
b) selective differentiation technologies: specialized classes, classes with in-depth study of the subject;
c) technologies for organizing the educational process: Dalton technology, technological model of individual learning, project technology;
d) technologies for reconstructing educational material: technology for enlarging didactic units, technology for implementing mental actions (P.Ya. Galperina), technology for advanced advanced learning (S.N. Lysenkova).
The technology for organizing students’ cognitive activity is:
a) technology of personal orientation of pedagogical cooperation, humane-personal technology of Sh. Amonashvili, technology of developmental education according to the system of D.B. Elkonina - V.V. Davydov (holistic education system);
b) technologies for activating and intensifying the cognitive activity of students: gaming technology, technologies problem-based learning, technology of iconic models, information technology, technology of programmed learning (technologies for complete assimilation of material, block technologies, modular technologies), technology of a collective method of learning;
c) technology of effective differentiation: technology of elective differentiation, technology of intra-subject differentiation and compulsory level of education.
The technology of organizing the educational process is collective creative activity(associations different types activities and combinations of forms, means, methods of action of teachers and students), play (the child’s mastery of various social roles and norms of behavior during the game), modeling technology (constructing analogues of certain fragments of reality to practice the rules and norms of children’s behavior), design technology (targeted design of new methods, techniques and forms of education), technology free development(providing the child with freedom and independence in determining the goals of his development).
Subject technologies - technology of the Dialogue of Cultures, technology for improving general educational skills, technology based on effective lessons, technology of step-by-step teaching of the subject, etc.
Correctional technologies are actually corrective (the use of these technologies allows the child to catch up with their peers in development; compensatory technologies (the inclusion of a child in social life is possible through the formation of activity structures in him that allow him to exclude the use of those mechanisms of activity that cannot be restored - hearing, vision, etc. .), technology of adaptive pedagogy (individual adaptation classes, classes on the general somatic and sensorimotor development of the child, helping to strengthen the child’s health). Among the listed technologies, there is no term “health-saving technologies”, since this pedagogy cannot be expressed by any specific educational technology. At the same time, this concept combines all areas of activity of an educational institution to form, preserve and strengthen the health of students.
Health-saving educational technologies are psychological and pedagogical techniques and methods of work, technologies, approaches to the implementation of possible problems and the constant desire of the teacher himself for self-improvement. We can only say that the educational process is carried out using health-saving pedagogical technologies if the implementation of the pedagogical system used solves the problem of preserving the health of students and teachers.
The fundamental priorities for wellness pedagogy are as follows:
1. A healthy child is a practically achievable norm child development.
2. Health improvement is not a set of therapeutic and preventive measures, but a form of development of the psychophysical capabilities of children.
3. An individually differentiated approach is the main means of health-improving and developmental work with students.
1.3. The concept of health-saving technologies, their functions
The main question that faces the education system is: how to ensure the preservation, strengthening and restoration of the health of students? But in order to answer this question and successfully solve it, it is necessary to understand the actual human condition.
Education - culture - health are the fundamental basis of a health-preserving system, the strategic goal of which is the formation of a harmoniously developed personality.
Let us dwell only on a few conceptual positions.
1. The purposeful nature of the entire educational process to create a culture of health for students:
Acquiring and mastering knowledge about how to maintain your health and prevent its impairment;
Formation of spiritual and moral qualities of the individual (responsibility, honesty, kindness, mercy);
Development of skills and abilities for a safe, healthy life; fostering a culture of health (behavior, nutrition, communication, everyday life, work, rest, etc.);
Fostering hard work, spiritual culture, patriotism, national identity, tolerance;
Formation of stable immunity and negative attitude to tobacco, alcohol, drugs and the influence of destructive religious cults and organizations;
Education of humanistic behavior guidelines that exclude cruelty and violence against the individual;
Fostering the need for physical education, hardening and improving the physical abilities and capabilities of the human body;
Formation of a culture of interaction with nature and the world around us;
Development of first aid skills;
Formation of knowledge among students about a healthy family, the role of parents and raising healthy children.
2. Integrity of the educational process.
Integrity presupposes that all aspects of the educational process should be aimed at creating a culture of health for students.
This is a long process, it cannot be temporary and requires the use of all means, forms, and methods.
Integrity also means that healthy life We consider a person in the unity of all its components: mental, physical, social and spiritual health.
Integrity also implies that the process of forming a culture of health for students includes learning, development, and upbringing of children.
3. Updating the content of education and using health-saving technologies.
The content of education is being updated in connection with the introduction of new federal state educational standards, according to which both the school and teachers should pay serious attention, inter alia, to the education of the student’s physical culture, and ensure that he acquires the experience of a healthy lifestyle.
4. Creating a health-saving educational environment and using its pedagogical capabilities
A health-saving educational environment is of fundamental importance for the formation of a harmoniously developed personality. Only when such an environment is created at school (a climate of health, a culture of trust, personal creation), is it possible to fully preserve and strengthen health, teach health, form a culture of health, and assimilate its spiritual, moral, aesthetic, and physical components.
5. Development of motor activity and taking into account the individual personal capabilities of students in the conditions of a specific educational institution
As you know, spiritually and physically healthy people They adapt much faster in science and production, master new types of activities more successfully, and perform their work better. Therefore, the development of physical activity as a factor in promoting health should be considered mainly as social protection of the interests of the developing personality in relation to new socio-economic conditions, when a person offers his services in the labor market.
6. Involvement of all participants in the educational process in various forms of activities to preserve and promote health
Education will serve the function of strengthening the health of the younger generation if health is not only taught, but health becomes a way of life. Teachers, parents, and the public should set an example of this lifestyle.
To create a culture of student health, it is necessary, first of all, to have an interested and creative attitude to the work of the entire pedagogical community of the republic: from employees of the Ministry of Education to teachers, educators, lecturers and scientists in each educational institution.
1.4. Principles of health-saving pedagogy
The goals of health-saving educational learning technologies determine the principles of learning that reflect pressing social needs. They act in organic unity, forming a system that includes general methodological and specific principles that express the specific laws of health improvement pedagogy.
General methodological principles are the basic provisions that determine the content, organizational forms and methods of the educational process in accordance with the general goals of health-saving educational technologies.
Systematic influence on the body and psyche of students can be successful only if the methodology for using health-preserving means is consistent with the laws of this application.
The principle of consciousness and activity - aims at developing in students a deep understanding, sustainable interest, and a meaningful attitude towards cognitive activity. Increased awareness and activity is facilitated by the use of special methodological techniques by the teacher, problem solvers health pedagogy. Realizing the health-improving effects of vigorous activity on the body, the child learns to independently and creatively solve cognitive problems.
The principle of activity - presupposes a high degree of independence, initiative and creativity in students.
The principle of visibility obliges us to build the learning process with maximum use of forms of involving human senses in the process of cognition. The principle of visualization promotes targeted influence on the functions of sensory systems involved in cognitive process.
The principle of systematicity and consistency is manifested in the interconnection of knowledge, skills and abilities. Regularity, systematicity, and continuity in the educational process throughout the entire period of study in a comprehensive school are ensured by the principle of systematicity.
Mastering the benefits of health-saving measures requires their repetition.
The principle of repetition of skills is one of the most important. As a result of repeated repetitions, dynamic stereotypes are developed. The nature of the elements of activity can manifest itself in changes in exercises and the conditions for their implementation, in a variety of methods and techniques, various forms ah tasks.
The inclusion of variable changes in stereotypes presupposes adherence to the principle of gradualism. It assumes continuity from one stage of education to another.
The principle of accessibility and individualization has its own characteristics in the health-improving orientation of health-saving educational technologies.
The principle of individualization is carried out on the basis of general laws of training and education. Based on individual characteristics, the teacher comprehensively develops the child, plans and predicts his development. Taking into account the level of individual preparedness of the student, his motor abilities and health status, ways to improve skills and abilities, build a motor mode, and introduce him to various forms of cognitive activity are outlined. Using the child’s natural abilities, the teacher guides and stabilizes his all-round development. The purpose of the principle of accessibility and individualization is seen in the elimination of negative and harmful consequences for the students’ body due to excessive demands and tasks.
The principle of continuity expresses the patterns of constructing the pedagogy of health improvement as an integral process. It is closely related to the principle of systematic alternation of loads and rest. A combination of high activity and relaxation in different forms students’ activities increases their efficiency, which is expressed in the dynamism of natural changes in the content and form of functional load parameters from lesson to lesson, from stage to stage.
The principle of cyclicity contributes to streamlining the process of healing pedagogy. It consists of a repeating sequence of lessons, which improves the child’s preparedness for each subsequent stage of learning. The formation of motor abilities and skills, the child’s motor abilities, and the functional capabilities of the body develop in the process of using health-saving technologies based on the principle of taking into account the age and individual characteristics of students. The principle of comprehensive and harmonious development of the individual is of utmost importance. It promotes the development of psychophysical abilities, motor abilities and skills, carried out in unity and aimed at the comprehensive - physical, intellectual, spiritual, moral and aesthetic - development of the child’s personality.
The principle of health-improving orientation solves the problem of strengthening the child’s health in the learning process.
The principle of an integrated interdisciplinary approach to teaching schoolchildren involves close interaction between teachers and medical workers.
Principle active learning, which consists in the widespread use of active forms and methods of teaching (training in pairs, group work, “Icebreaker” technique, gaming technologies, etc.).
The principle of forming responsibility among students for their own health and the health of others.
The principle of connecting theory with practice calls for persistently teaching students to apply their knowledge on the formation, preservation and promotion of health in practice, using the surrounding reality not only as a source of knowledge, but also as a place for their practical application.
2.Health-saving technologies in physical education
2.1. Means of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons.
To achieve the goals of health-saving educational teaching technologies, the following groups of means are used:
1. Means of motor orientation;
2. The healing powers of nature;
3. Hygiene factors.
The integrated use of these tools allows us to solve the problems of health improvement pedagogy.
Motor-oriented means include motor actions that are aimed at implementing the tasks of health-saving educational teaching technologies. This is movement; physical exercise; physical education minutes and active breaks; emotional release and moments of “peace” gymnastics (health-improving, finger, corrective, breathing, for the prevention of colds, for vigor); physical therapy, outdoor games; specially organized physical activity of the child (health-improving physical education classes, timely development of the basics of motor skills); massage, self-massage; psycho-gymnastics, trainings, etc.
The use of the healing powers of nature has a significant impact on achieving the goals of health-saving educational teaching technologies. Conducting classes in the fresh air helps to activate biological processes caused by the learning process, increase the overall performance of the body, slow down the process of fatigue, etc.
Taking into account the influence of meteorological conditions (solar radiation, exposure to air and water temperature, changes in atmospheric pressure, movement and ionization of air, etc.) on certain biochemical changes in the human body, which lead to changes in the health and performance of students, can help relieve the negative impact of training on schoolchildren.
As relatively independent means of healing, one can single out sun and air baths, water procedures, herbal medicine, aromatherapy, inhalation, vitamin therapy (vitaminization of the diet, iodization of drinking water, use of the amino acid glycine twice a year - in December and spring in order to strengthen the memory of schoolchildren). It is possible to introduce new elements into the life of the school - herbal bars, a physiotherapy room, health training for teachers and students.
Hygienic means of achieving the goals of health-saving educational teaching technologies that promote health and stimulate the development of adaptive properties of the body include: compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements regulated by SanPiNs; personal and public hygiene (cleanliness of the body, cleanliness of places of activity, air, etc.); ventilation and wet cleaning of premises; compliance with the general regime of physical activity, diet and sleep; instilling in children basic skills in washing hands, using a handkerchief when sneezing and coughing, etc. teaching children basic healthy lifestyle techniques (HLS), the simplest skills of providing first aid medical care for cuts, abrasions, burns, bites); organizing the procedure for vaccinations of students in order to prevent infections; limiting the maximum level of study load to avoid overwork. Failure to comply with hygienic requirements for conducting classes reduces the positive effect of health-saving educational teaching technologies. One of the main requirements for the use of the above tools is their systematic and comprehensive use in the form of classes using preventive techniques; using functional music; audio accompaniment of lessons, alternating classes with high and low physical activity; in the form of rehabilitation measures; through mass recreational events, sports and health holidays; going out into nature, excursions, through health-saving technologies of the learning and development process in working with families in order to promote a healthy lifestyle in the system of organizational, theoretical and practical classes in parent lectures, in working with the teaching staff as training of the teaching staff in an innovative educational institution. .
Stages of the learning process in conditions of health-saving pedagogy
In the learning process, in accordance with the ideas of health-saving educational technologies, the task is to form in the student the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities on a healthy lifestyle, teach how to use the acquired knowledge, skills and abilities on a healthy lifestyle, and teach how to use the acquired knowledge in everyday life.
The entire learning process in the conditions of health-saving pedagogy includes three stages, which differ from each other both in particular tasks and in the features of the methodology.
1. The stage of initial familiarization with basic concepts and ideas. The goal is to form in the student the basics of a healthy lifestyle and achieve the implementation of basic health rules.
Main goals:
1. Form a semantic understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
2. Create basic ideas about the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
3. Achieve compliance with basic health rules (at the level of initial skill).
4. Prevent misunderstanding of the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
These tasks are solved one by one. Ideas about the basic rules of health preservation are formed as a result of the teacher’s explanation, perception of the demonstrated movements of the physical education complexes, viewing of visual aids, analysis of one’s own muscle and other sensations that arise during the first attempts to perform the complexes, and observations of the actions of other students. All this creates an indicative basis, without which it is impossible to master the rules of health conservation.
2. In-depth study stage. The goal is to develop a full understanding of the basics of a healthy lifestyle.
Main goals:
1. Clarify your understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
2. Achieve conscious implementation of basic health rules.
3. Formation of practically necessary knowledge, skills, rational methods of thinking and activity.
These tasks can be solved simultaneously. The effectiveness of training at this stage largely depends on the correct and optimal selection of methods, techniques and teaching aids. Using active learning methods, it is necessary, in combination with it, to widely use visualization aimed at creating feelings of a healthy lifestyle. The method of verbal influence changes its forms, the leading ones are analysis and analysis of the rules of health savings, conversation, and discussion.
At this stage, a complex of various means is widely used (motor-oriented means; healing forces of nature; hygienic factors).
The effectiveness of using various means is achieved with strict adherence to the following points: a) the goals and objectives of using a specific means in a specific lesson; b) the structural relationship of this tool and method with the main content of the lesson; c) control and self-control of compliance with health saving rules.
3. The stage of consolidating knowledge, skills and abilities in health conservation and their further improvement. The goal is the ability to translate into a skill that has the ability to use it for its intended purpose.
Main goals:
1. Achieve stability and automaticity in the implementation of health rules.
2. To achieve compliance with health protection rules in accordance with the requirements of their practical use.
3. Ensure variable use of healthy lifestyle rules depending on specific practical circumstances.
These tasks can be solved both simultaneously and sequentially, since they are interrelated.
At this stage, the number of repetitions of the use of basic concepts and ideas about a healthy lifestyle in ordinary and new, unusual conditions increases, which allows one to develop a flexible skill in applying existing knowledge in various conditions.
In order to improve knowledge, skills and abilities in health conservation, various methods and techniques are used: practical method, cognitive game, situational method, game method, competitive method, active methods training, educational, educational and educational programs. The teacher selects the means in accordance with specific working conditions. These could be basic movements during class; physical exercise; physical education minutes and active breaks; “minutes of peace”, various types of gymnastics (health-improving, finger, corrective, breathing, for the prevention of colds, for vigor); physiotherapy; outdoor games; specially organized physical activity of the child (health-improving physical education classes, timely development of the basics of motor skills); massage; self-massage; psycho-gymnastics, trainings, as well as elements of herbal medicine, aromatherapy, vitamin therapy, herbal bars within the school walls, a physiotherapy room, health training for teachers and students, various rehabilitation activities; mass recreational events, sports and recreational holidays, themed health holidays, etc.
2.2.Features of organizing educational activities in a physical education lesson in conditions of health-saving pedagogy.
Health-saving technologies in physical education are a set of techniques, methods, techniques, teaching aids and approaches to the educational process, in which at least 4 requirements are met:
1. Taking into account the individual characteristics of the child.
2. The teacher’s activities in the aspect of implementing health-saving technologies in physical education lessons should include familiarization with the results of medical examinations of children, taking them into account in teaching and educational work; Helping parents build healthy lives for students and families as a whole
3. Avoid excessively debilitating physical and emotional stress when mastering educational material.
4. Providing an approach to the educational process that would guarantee the maintenance of only a favorable moral and psychological climate in the team.
To implement high-quality physical education and recreational work and create health-protecting conditions for the development of a child, it is necessary to build the educational process on a diagnostic basis. Therefore, your activities at the beginning of the school year should begin with diagnostic examinations of the levels of physical development of children (methodology by N.N. Efimenko). In parallel with this diagnosis, medical workers monitor the health of children at the beginning of the school year, comparative analysis in these areas for 2 years. Together with the exercise therapy instructor, an additional study “Plantography” (N.N. Efimenko’s method) is being conducted to organize correctional and developmental work with children with musculoskeletal disorders. This extensive work is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of children’s development when planning and implementing the pedagogical process.
Together with the doctor, “Health Screens” are compiled for children in each group (class) with specific recommendations for teachers and parents. Based on this, a plan for physical education, health, treatment and preventive work is drawn up, which includes hardening activities, a physical activity regimen, taking into account the characteristics of the health status of children in this group (class), the requirements of the Sanitary Institution, and the specific diagnosis of each child. Such in-depth analysis and consideration of children’s health in ongoing activities allows us to solve the problem of preserving the child’s vital energy and monitoring the development and changes in the condition of each child.
And there should also be: strict dosed physical activity; using the technique of alternating intensity and relaxation in training; using the principle of clarity, gradualism, accessibility of the load, taking into account the age characteristics of students; taking into account the physical fitness of children and the development of physical qualities; building a lesson taking into account the dynamism of students and their performance; compliance with hygiene requirements; favorable emotional mood; creating comfort.
In physical education lessons, it is necessary to pay special attention to the organization of health-preserving factors.
Control tests, assignments, tests, etc. should only provide initial (and current) information for the development of individual tasks, the essence of which is that the student must move further in each period of time, which will be confirmed by the next test. If this does not happen, then the teacher must make appropriate adjustments to individual assignments. It is fundamentally important that the student does not compare with others on the principle of “better or worse than others,” but compares with himself: today I have become better than yesterday, and tomorrow I will try to become better than today. However, for this, tasks must be realistic and stimulate students to actively work. In the meantime, evaluation criteria are based on comparing the results of mastering knowledge and skills with some contrived “average” values. In this case, the strong student does not feel the need for everyday educational work, and the weak one, feeling doomed, does not feel the desire for it.
If a student does not understand the importance of educational material, then the selectively working subconscious immediately after receiving a grade helps him to quickly forget unnecessary material. In this case, the consistency in mastering the basics of knowledge is disrupted, and each new material appears to be divorced from the previous one, independent and even far-fetched.
Creating comfortable conditions for physical education consists of the following activities:
compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards;
rational lighting of the hall;
exclusion of monotonous sound stimuli;
wet cleaning of the hall every 2 hours of classes;
the presence of toilets and washbasins in girls' and boys' locker rooms;
availability of a first aid kit;
sports equipment by age (w/w balls average age No. 5, older age No. 7, ski equipment, medicine balls);
Each student has replacement sports shoes and sports uniforms for physical education lessons in the hall and appropriate uniforms for outdoor lessons (autumn-spring, winter).
Taking into account the dynamics of performance in the lesson.
1st phase operation 8-10 minutes.
Phase 2 of optimal performance 15-20 minutes.
Phase 3 of overcome fatigue.
Individually differentiated approach.
1. Taking into account health diagnosis in physical education and health work
2. Individual approach to hardening preschoolers
3. Taking into account the type of constitution of the child in the process of physical education
4. Manifestation of typological features of the nervous system in muscle activity
5. Relationship between the type of nervous system and the level of motor activity of the child
6. Gender approach in physical education
7. The relationship between individual and age-related characteristics of the development of motor qualities
8. Accounting for individual indicators of physical fitness
Solving the problem of health improvement from the point of view of these aspects has different implementation in accordance with the characteristics of each age.
Among all the opportunities for recreational work in school, physical exercise is the most effective.
Systematic physical exercise has a beneficial effect on the central nervous system, which is the main regulator of all physical and mental processes in our body. Constant physical exercise increases the vital capacity of the lungs, the mobility of the chest, improves the physique, the figure becomes slender and beautiful, movements become expressive and flexible.
Physical culture is a natural biological method, which is based on an appeal to the main biological function of the body - muscle movement.
Physical education lessons are the main link in the chain of student health improvement at school. They promote health promotion, proper physical development and hardening of the body, as well as mental and physical performance, the formation of correct posture, the elimination or permanent compensation of disorders caused by various diseases.
The modern school, with its academic workload, has a detrimental effect on not only the somatic, but also the mental health of students.
In my work I am based on modern psychological and pedagogical theories of training, education and personal development, I use active methods of teaching and upbringing, taking into account the personal characteristics of each child. Principles of activity and personal approaches consist in the fact that the student masters ways of using the wealth accumulated by humanity in the field of bodily and spiritual improvement.
Methodology for conducting classes with elements of rhythmic gymnastics. Simplicity, accessibility, safety, optimal alternation of load and rest, correct dosage of load - a prerequisite for every physical education lesson.
The complexes offered to students are age-appropriate and include accessible exercises. Exercises are selected in such a way that they influence the complex development of physical qualities through consistent impact on different muscle groups.
The existing physical education program provides for the active use of rhythmic gymnastics in lessons.
Everyone knows that gymnastics improves health. Muscular exercise strengthens the heart, lungs, blood vessels and other organs. Many people are attracted by the beauty of gymnastic exercises. This type of exercise is performed with musical accompaniment, which increases the emotional mood of those involved. However, the teacher faces the question: in what part of the lesson and in which classes is it best to use rhythmic gymnastics?
When the “Gymnastics” section begins, to eliminate sharpness and angularity in the movements of students, I have been using rhythmic gymnastics for several years since the 2nd grade and conduct it in the aquatic part of the lesson. The use of rhythmic gymnastics has a positive effect on the development of coordination, rhythm, ease and plasticity of movements. Exercises have a significant impact on the formation of correct posture, beautiful gait, and cultivate aesthetic concepts and a culture of movement. Its effectiveness lies in its diverse effects on the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In addition, practicing with music creates an emotional background. With the help of rhythmic gymnastics, you can develop physical qualities such as general endurance, strength, flexibility, and agility.
Jumping rope. In every lesson, regardless of the sections of the program, I conduct jumping rope. Everyone wants to have strong, slender, beautiful legs, and for this they need to be exercised. And a jump rope serves as an excellent simple sports equipment in physical education lessons. A jump rope is a very affordable and useful gymnastic equipment. Jumping with a rolling pin develops the leg muscles, makes them slim and beautiful, and serves as a preventive measure for flat feet; contribute to the formation of correct posture; strengthen the ligaments of internal organs; eliminate congestion in the body; develop the cardiovascular and respiratory systems; develop a sense of rhythm and coordination of movements; strengthens the pelvic floor muscles. The ease of use of the jump rope consists in its fairly easy learning and simplicity of the exercises performed. I start learning to jump rope in elementary school with the simplest jumps. There are many different exercises with a jump rope. The most common of them are jumps: on both legs, rotating the rope forward, on one leg; with alternate jumping on one and the other leg, with a running step, in place and with movement, with a crossed position of the arms, with a crossed position of the legs. The inclusion of jumping rope in every lesson held in the gym is not burdensome for students if the jumping exercises are varied in form, load and tasks facing them. Jumping in relay races and jumping according to instructions are of great interest. Such jumps serve to develop coordination abilities. These can be jumps moving forward, backward: with alternating directions - left-right; with objects in hands. Many years of experience in the daily use of jumping rope allows us to talk about a positive result, more effective compared to the use of running in the gym and the interest of students in this gymnastic apparatus. Jumping rope is tested every quarter and many students set a class record. The tables show that for some students there is a significant jump in results.
Formation of posture in lessons. Good physical development and good health of schoolchildren are possible by maintaining correct posture, which ensures the favorable course of physiological processes in the body. Correct posture is slightly lowered shoulders, laid back, head held straight, tucked stomach, straightened knees, slightly protruding chest. Violations of correct posture are the result of changes in the shape of the spine: round, stooped back, arched back, scoliosis. Posture is the habitual posture of a casual standing person. Posture is not innate. It is formed in the process of growth, development of the child, study, labor activity and physical exercise. Poor posture occurs under the influence of a wide variety of reasons. One of them, I think, is that in schools there is a cabinet system. All day long, a student, moving from office to office, sits at a desk or table that does not correspond to his height. Another reason is reading for many hours in poor lighting; this forces the student to lean lower over the book, spoiling not only his posture, but also his vision. And the main reason is physical inactivity. It is no secret that many subject teachers do not conduct physical education lessons in their lessons. Systematic reasonable physical education and sports are considered the best remedy prevention of poor posture. Consequently, the leading role in this belongs to the physical education teacher. In my lessons, I monitor students’ posture as they go through all sections of the curriculum throughout the school year. I give exercises where posture is formed, first of all, in walking: Normal walking. Raise your head, don’t slouch, look straight, put your shoulders back.
Walking on toes, arms in different positions.
Walking on your heels, the main thing is not to lower your pelvis, straighten up, bend over.
Walking with a rolling step. When performing a heel roll, rise high onto your toes, straighten your torso, raise your head higher.
Walk with a sharp step, raising your hip high.
I also monitor my posture when running, paying attention to the position of my back. At each lesson I conduct 5-6 exercises to develop posture. I regularly talk with students about posture and explain to them why these classes are held. I offer students sets of exercises to develop correct posture, insist on daily implementation of the sets, and give home exercises.
Methods for organizing homework. Children receive basic knowledge and skills in physical education at school. However, to have good health and physical development, school work alone is not enough. This is why it is so important to exercise on your own every day. The first step, the first step towards independent physical education, is homework. For independent home exercises, I recommend that children do feasible and safe exercises at home. For example: pulling up from a hanging position, bending and extending the arms while lying down, various drill exercises, performing various jumps outside in the autumn-spring period (standing long jumps, jumping rope), exercises to develop posture. The most important thing: I check all the exercises that I give for homework in class, some several times a day. academic year. And it immediately becomes clear how students perform the given exercises at home. I definitely encourage even a physically weak student with a good grade if he shows progress in completing homework. Homework in physical education is one of the most effective forms physical education, which allows each student to actually engage in independent activities. However, when using homework, you encounter considerable difficulties, and, perhaps, the main one is organizing control over their implementation. In order for students to systematically complete their assignments at home, students began to have a physical education notebook from the 3rd grade, where they track their completion of homework, as well as independent work. I check the notebook 2-3 times a quarter and give a grade for general notebook management and for completing homework. If a student writes “false” numbers into a notebook without doing any physical exercises, then this is immediately detected. Firstly, if there is no progress in the results shown by the student in the lessons, we can conclude that he probably does not do his homework; secondly, if anyone records “fake” progress on paper, then this number will not pass, since I check the exercises in class at least 2-3 times a quarter. Such a physical education notebook makes it possible to evaluate a student on all indicators: knowledge, motor skills, motor readiness, physical education, sports and recreational activities. To instill in schoolchildren a conscious attitude towards promoting health and their personal level of physical fitness, I constantly introduce the following program into the minds of children: “Today I do better than yesterday, and tomorrow I will do better than today.”
The tables show that the level of motor preparedness of students by the end of the school year increases significantly.
Physical culture is a complex culture of movements, knowledge about oneself and one’s development, harmonious development of physical abilities, body building, self-education, moral, psychological and spiritual development, nutrition, hardening, hygiene, daily routine, culture of other areas of a healthy lifestyle. The main thing for me as a physical education teacher is to instill in the student the habit of regular and independent physical education and sports based on the knowledge necessary for this and a healthy lifestyle. In light of this, of course, it is imperative to change for the better the attitude of some students, their parents, teachers of other disciplines, and many other people towards physical education, because without it the physical and moral health of a person is unthinkable. Unfortunately, there are still a lot of problems in solving the issues of preserving and strengthening the health of children. Only together, by joining forces, can we move towards achieving the intended goal - the formation of a healthy mentally, physically developed, socially adapted person, and the creation of health-preserving and health-enhancing learning conditions at school. Where elements of physical education can be used in addition to the physical education lesson itself - in other lessons and breaks: physical education minutes, physical education breaks, dynamic (moving) changes.
Such active recreation is designed to solve a number of problems: preventing early mental fatigue and restoring mental performance by activating cerebral circulation and switching attention; elimination of congestion in the blood circulation and respiratory system through deep breathing exercises and rhythmic alternations of contractions and relaxations of the muscles that provide accommodation of the eye; eliminating the adverse effects of prolonged stretching and relaxation of the back muscles responsible for posture and more.
Conclusion.
Widespread introduction of technical means and computer technology into the educational process, has led to an increased intensity of information flow - on the one hand. On the other hand, limited time for processing and assimilation of information, the need to memorize large volumes of material, overload curricula in combination with an imperfect diet and irrational organization of leisure time. These circumstances served as an additional reason for turning to the study of modern health technologies in the pedagogical process.
From the definition of health-saving educational technologies, it is clear that the most important goal of introducing health-saving technologies into the educational process is the formation of a culture of health. This is where the efforts of the school and family should be largely directed, taking into account the priority in this matter of upbringing over education. A culture of health should not be studied, but cultivated. The psychological basis for this is motivation to lead a healthy lifestyle. An integral part of a health culture is awareness of health issues and a healthy lifestyle. How to achieve success in life, how not to become a victim of alcohol or drugs - having joined the culture of health, a child or teenager turns to a teacher or specialist for answers to all these questions. And then the information received from them has the maximum chance of being used in practice. The circle is closed: teaching health issues, nurturing a culture of health, using health-saving technologies as the main tool of pedagogical work constitute a single whole - the road to health.
List of sources used
Anokhina I.A. Individual approach in physical education and recreation work of the preschool educational institution: Guidelines/ I.A. Anokhina. - Ulyanovsk: UIPKPRO, 2006. - 49 p.
Akhutina T.V. Health-saving teaching technologies: an individual-oriented approach // School of Health. 2000. T. 7. No. 2. P.21 – 28
Bayborodova L.V., Butan I.M., Leontyeva T.N. Methods of teaching physical education: grades 1-11: Method. - M., 2004.-205s
Bespalko V.P. Components of pedagogical technology. - M.: Education, 2009.-105 p.
Valeology. Diagnosis, means and practice of ensuring health. / Ed. I.I. Brekhman. St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1993, 269 p.
Vygotsky L.S. Pedagogical psychology/ Ed. V.V. Davydova. M.: Pedagogy, 1991, p. 324 - 341.
Zelenkevich I.B., Ivashkevich M.Z., Piliptsevich N.N. Public health care and its place in the system of public health // Issues of organization and informatization of health care. - 2001. - No. 3. - P.3-6.Can-
Kan-Kalik V.A., Nikandrov I.D. Pedagogical creativity. - M.: Pedagogy, 1990.-68 p.
Kovalko V.I. The ABCs of physical education minutes for preschoolers: Practical developments of physical education minutes, game exercises, gymnastic complexes and outdoor games (middle, senior, preparatory groups). - M.: VAKO, 2005. - 176 p.
Kovalko V.I. Health-saving technologies in primary school. Grades 1-4. M.: “VAKO”, 2004.-73s
Lomeiko V.F. Development of motor qualities in physical education lessons. M.1980. 128s.
Maksimenko A.M. Fundamentals of the theory and methodology of physical culture. - M., 2009.-345 p.
Malkova S.V. The use of health-saving technologies in the educational process in a small rural school // Priority directions for the development of education in rural areas. Uglich. 2004. 255 p. pp. 183 – 186.
Experience of physical education teachers./ Ed. Travnikova R.N., Chernova K.L. M. APP. 1962. 48p.
Selevko G.K. Modern educational technologies. M.: Public education. 2007. 255 p.
Sovetova E.V. Health technologies at school // Rostov-on-Don, 2006
Stepanov R.I. Technological approach to the humanization of education. // Science and education. - 2003. - No. 3.
Sukharev A.G. Concept of strengthening the health of children and adolescents in Russia // School of Health. 2000. T. 7. No. 2. P.29 - 34
Shebeka V.N. “Individual approach in the physical education of weakened children” / V.N. Shebeko. Contemporary issues preschool education. Materials of the MZhN scientific-practical conference dedicated to the 100th anniversary of the birth of A.V. Keneman April 10-11, 1996 - M., 1996. - P. 154-156
Shcheblanova E.I. Unsuccessful gifted schoolchildren: their problems and characteristics // School of Health. 1999. T. 6. No. 3. pp. 41-51
Shevchenko S.D. School lesson: How to teach everyone. - M.: VLADOS, 2004.-208 p.
Yanson Yu.A.: Physical education at school, a book for teachers, 2009.
Magazine “Physical Education at School”, No. 1,2,3 – 2009.
http://festival.1september.ru/articles/557275 “Health-saving technologies in physical education lessons and in extracurricular sports work” Elena Vladimirovna Akimova
http://zam-sport11.ucoz.ru/index/zdorovesberegajushhie_tekhnologii/0- 14“Creating a health-preserving environment in the classroom”
Autonomous educational institution
higher professional education
"Leningradsky State University named after A.S. Pushkin"
Boksitogorsk Institute (branch)
Final qualifying work
Pedagogical health-saving technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7
Student 4th gr.
Specialty 050720.52
A.Yu. Bazhulin
Supervisor
Physical education teacher
V.V.Eretin
Pikalevo 2013
Introduction
1.3 Means, methods and techniques of health-saving technologies
CHAPTER 2. Organization of educational activities in the conditions of health-saving technologies in the classroom
physical culture
2.3 The effectiveness of using health-saving technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5-7
Conclusion
Bibliography
Applications
Introduction
In accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education”, the health of schoolchildren is classified as a priority area of state policy in the field of education.
Health is one of the most important components of human well-being, happiness, one of the inalienable human rights, one of the conditions for successful social and economic development any country.
The issue of preserving the health of students at school today is very acute. The intensity of students' educational work is very high, which is a significant factor in weakening health and an increase in the number of various deviations in the body's condition. The causes of these deviations are a sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia), the accumulation of negative emotions without physical release, as a result of which psycho-emotional changes occur: isolation, imbalance, excessive excitability.
In connection with the deteriorating level of health of the younger generation, there is a need to organize a physical education lesson with an emphasis on solving the health-improving tasks of physical education, without disturbing the educational component of the process. Therefore, in physical education lessons it is necessary to pay special attention to the organization of health-preserving factors, which determines the relevance of the final qualifying work.
Purpose of the work: to study health-saving technologies, to consider the impact of the use of physical education and health technologies in physical education lessons on the health of students in grades 5 - 7.
Object of study: health-saving technologies in physical education lessons.
Subject of research: the influence of health-saving technologies on the health of students in physical education lessons.
Research objectives:
1. Study and analysis of literary sources on the research topic.
2. Study the principles, methods and means of health-saving technologies.
3. Consider the influence of health-saving technologies on the health of students in grades 5-7 in physical education lessons.
4. Research the practical application of physical education and health technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7.
The research hypothesis is that health-saving technologies can be effective if methods and means are correctly defined, and the principles of their use in physical education lessons are disclosed.
Theoretical basis of the study. The issues of using health-saving technologies in physical education lessons were dealt with at different times by such scientists as A.M. Maksimenko, L.P. Matveev, V.I. Lyakh, Zh.K. Kholodov, whose works formed the basis for writing this introductory note qualifying work.
Research methods: analysis of psychological, pedagogical and literature, experiment, statistical data processing.
Research base: Primary School MBOU "Secondary School No. 2" Pikalevo.
The novelty of the research is as follows:
The effectiveness of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7 has been determined;
It has been experimentally proven that the use of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7 helps to preserve and strengthen the health of students, ensures an increase in physical fitness, functional state, physical development and the level of health of students.
The practical significance of the work lies in the fact that the results of the study can be used in practical work to organize work in physical education lessons that promote the health of schoolchildren, improve indicators of physical and functional readiness, as well as develop in adolescents the interest and need for systematic physical education classes.
Structure of the final qualifying work. The final qualifying work consists of an introduction, which reflects the relevance, formulates the purpose of the research and sets the research objectives, and outlines the main ways of their implementation.
The first chapter discusses health-saving educational technologies, their classification, principles, means, methods of health-saving technologies, stages of the learning process.
The second chapter describes the organization of educational activities in the conditions of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons, the main forms of organization of training, the technology of organizing a physical education lesson, the role of the physical education teacher in promoting the health of students, and shows the effectiveness of the use of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons in grades 5-7 .
Finally, conclusions about the study are presented.
The list of references is presented by a list of literary sources used in the preparation of the final qualifying work.
The application contains practical material research.
health-saving lesson physical education
CHAPTER 1. Theoretical basis health-saving technologies
1.1 The essence of health-saving technologies in the process of physical education
The physical development of schoolchildren includes those qualitative changes that occur in strengthening and improving a person’s physical strength and health under the influence of a favorable natural environment and specially organized education. Along with the implementation of physical development, it is intended to arouse interest and need for physical education and sports, promote a deep understanding of the psychophysiological foundations of physical education and health promotion, as well as mental, moral and aesthetic development.
Physical education acts as a multifaceted process of organizing active physical culture and health activities of students, aimed at strengthening the need for physical education and sports, understanding their psychological foundations, developing physical strength and health, as well as developing sanitary and hygienic skills and healthy lifestyle habits (24 , p. 98).
An essential component of the content of physical education is the enrichment of students with a system of knowledge about the essence and social significance of physical education lessons and their influence on the comprehensive development of the individual. Active mastery of the values of physical culture can be successfully carried out if the student gets to know himself as an individual, knows his age characteristics, physical abilities and their impact on his health.
An important place in physical education is occupied by the formation in schoolchildren of sanitary and hygienic skills in organizing work and reasonable rest, proper alternation of mental activities with physical exercises and various practical activities. This includes maintaining proper hygiene of body and clothing, compliance with the requirements of the daily routine, as well as sanitary and hygienic rules in the school.
A very important content part of physical education is the development of motor skills in students, practicing and improving the external culture of behavior: posture, gait, dexterity, speed of motor reactions.
Physical education classes at school have a real chance to influence, first of all, the level of physical health of schoolchildren - the level of growth and development of organs and systems of the body, the basis of which is the functional reserves that ensure adaptive reactions.
Health-saving technologies presuppose an integrated approach to improving the health of students. The set of health-preserving measures within the framework of physical education at school includes the following types of activities:
Carrying out comprehensive diagnostics;
Organization of training sessions with a health-preserving focus;
Promotion of healthy lifestyles;
The use of physical exercise to prevent diseases;
Application of complexes of therapeutic physical culture exercises with children (4, p. 35).
Health-saving technology is a system of measures that includes the interrelation and interaction of all factors of the educational environment aimed at preserving the health of a child at all stages of his learning and development (4, p. 190). In this case, at least 4 requirements must be met:
1. Taking into account the individual characteristics of students.
2. Instilling knowledge in a child in the ability to independently protect himself from stress, grievances, insults, teaching him psychological defenses.
3. Avoid excessively debilitating physical, emotional, and intellectual stress when mastering educational material.
4. Providing an approach to the educational process that would guarantee the maintenance of only a favorable moral and psychological climate in the team (4, pp. 191-192).
Groups of health-saving technologies used in the education system, which use a different approach to health care, and, accordingly, different methods and forms of work:
1. Medical and hygienic technologies, which include a set of measures aimed at maintaining proper hygienic conditions in accordance with SanPinNov regulations, and the functioning of a medical office in schools. Creation of dental, physiotherapeutic and other medical offices to provide daily assistance to schoolchildren and teachers, conducting physical therapy classes, “mountain air” rooms, etc.
2. Physical education and health technologies that are aimed at the physical development of those involved: hardening, training strength, endurance, speed, flexibility and other qualities. Basically, these technologies are implemented in physical education lessons and in the work of sports sections.
3. Environmental health-saving technologies help to cultivate in schoolchildren a love for nature, a desire to take care of it, and familiarize students with research activities in the field of ecology, etc., all this has a powerful pedagogical impact, shaping the personality, strengthening the spiritual and moral health of students.
4. Technologies for ensuring life safety are implemented by specialists in labor protection, protection in emergency situations, architects, builders, representatives of public utilities, etc. (10, p. 135).
Based on the nature of the action, the following technologies are distinguished:
Stimulating. They allow you to activate the body’s own forces and use its resources to get out of an undesirable state. Examples could be temperature hardening, physical activity.
Protective and preventive. This is compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards and requirements. Limiting the maximum load to prevent overwork. The use of safety equipment and protective devices in gyms to prevent injury.
Compensatory-neutralizing technologies. These are physical education minutes, physical education breaks, which to some extent neutralize the adverse effects of static lessons.
Information and learning technologies. Provide students with the level of literacy necessary to effectively care for their health (10, p. 204).
Since maintaining health is considered as special case main task- retention, requirements and recommendations of these specialists are subject to mandatory consideration and integration into common system health-saving technologies. Students' literacy on these issues is ensured by studying the life safety course, teachers - life safety courses, and the director is responsible for ensuring safe conditions at school.
Health-saving educational technologies should be recognized as the most significant of all those listed in terms of the degree of impact on the health of students. Their main distinguishing feature is not the place where they are implemented, but the use of psychological and pedagogical techniques, methods, technologies, and approaches to solving emerging problems.
1.2 Principles of health-saving technologies
The goal of health-saving educational technologies is to provide the student with the opportunity to maintain health during the period of study at school, to develop in him the necessary knowledge, abilities, skills for a healthy lifestyle, and to teach him to use the acquired knowledge in everyday life. The main indicator that distinguishes all health-saving educational technologies is regular express diagnostics of the students’ condition and tracking of the main parameters of the body’s development over time (beginning and end of the school year), which allows one to draw appropriate conclusions about the students’ health status.
The goals of health-saving educational learning technologies determine the principles of learning that reflect pressing social needs. They act in organic unity, forming a system that includes general methodological and specific principles that express the specific laws of health improvement pedagogy.
General methodological principles are the basic provisions that determine the content, organizational forms and methods of the educational process in accordance with the general goals of health-saving educational technologies.
Systematic influence on the body and psyche of students can be successful only if the methodology for using health-preserving means is consistent with the laws of this application (18, pp. 75 - 76).
Let's consider the principles of health-saving technologies.
The principle of consciousness and activity - aims at developing in students a deep understanding, sustainable interest, and a meaningful attitude towards cognitive activity. Increased awareness and activity is facilitated by the teacher’s use of special methodological techniques that solve the problems of health improvement pedagogy. Realizing the health-improving effects of vigorous activity on the body, the child learns to independently and creatively solve cognitive problems.
The principle of activity - presupposes a high degree of independence, initiative and creativity in students.
The principle of clarity obliges us to build the learning process with maximum use of forms, involving human senses in the process of cognition. The principle of visualization promotes targeted influence on the functions of sensory systems involved in the cognitive process.
The principle of systematicity and consistency is manifested in the interconnection of knowledge, skills and abilities. Regularity, systematicity, and continuity in the educational process throughout the entire period of study in a comprehensive school are ensured by the principle of systematicity. Mastering the benefits of health-saving measures requires their repetition.
The principle of repetition of skills is one of the most important. As a result of repeated repetitions, dynamic stereotypes are developed. The nature of the elements of activity can manifest itself in changes in exercises and the conditions for their implementation, in a variety of methods and techniques, and in various forms of tasks.
The inclusion of variable changes in stereotypes presupposes adherence to the principle of gradualism. It assumes continuity from one stage of education to another.
The principle of accessibility and individualization has its own characteristics in the health-improving orientation of health-saving educational technologies.
The principle of individualization is carried out on the basis of general laws of training and education. Based on individual characteristics, the teacher comprehensively develops the child, plans and predicts his development. Taking into account the level of individual preparedness of the student, his motor abilities and health status, ways to improve skills and abilities, build a motor mode, and introduce him to various forms of cognitive activity are outlined. Using the child’s natural abilities, the teacher guides and stabilizes his all-round development. The purpose of the principle of accessibility and individualization is seen in the elimination of negative and harmful consequences for the students’ body due to excessive demands and tasks.
The principle of continuity expresses the laws governing the construction of health improvement pedagogy as an integral process. It is closely related to the principle of systematic alternation of loads and rest. The combination of high activity and rest in various forms of student activity increases their efficiency, which is expressed in the dynamism of natural changes in the content and form of functional load parameters from lesson to lesson, from stage to stage.
The principle of cyclicity contributes to streamlining the process of healing pedagogy. It consists of a repeating sequence of lessons, which improves the child’s preparedness for each subsequent stage of learning.
The formation of motor abilities and skills, the child’s motor abilities, and the functional capabilities of the body develop in the process of using health-saving technologies based on the principle of taking into account the age and individual characteristics of students. The principle of comprehensive and harmonious development of the individual is of utmost importance. It promotes the development of psychophysical abilities, motor abilities and skills, carried out in unity and aimed at the comprehensive - physical, intellectual, spiritual, moral and aesthetic - development of the child’s personality.
The principle of health-improving orientation solves the problem of strengthening the child’s health in the learning process.
The principle of an integrated interdisciplinary approach to teaching schoolchildren involves close interaction between teachers and medical workers.
The principle of active learning, which consists in the widespread use of active forms and methods of learning (learning in pairs, group work, gaming technologies, etc.).
The principle of connecting theory with practice calls for persistently teaching students to apply their knowledge on the formation, preservation and promotion of health in practice, using the surrounding reality not only as a source of knowledge, but also as a place for their practical application (15, pp. 124-126).
Conclusion: in the general educational process one should focus on the principles of health-saving technologies, since they are aimed at strengthening the physiological and psychological health of students and developing the cognitive activity of students. To implement these principles, means, methods and techniques of health-saving technologies are used.
1.3 Means, methods and techniques of health-saving technologies
The age of students in grades 5-7 belongs to adolescence. At this time, there is a powerful increase in vital activity and a profound restructuring of the body. Teenagers are characterized by increased activity - they want to know everything, and even more - to be able to do it. These features age development create the prerequisites for the inclusion of adolescents in active physical education and sports. The needs for motor activity, physical activity, communication and self-affirmation manifest themselves in unity, and their satisfaction occurs first. The goal of health-saving educational technologies is to provide the student with the opportunity to maintain health during the period of study at school, to develop in him the necessary knowledge, abilities, skills for a healthy lifestyle, and to teach him to use the acquired knowledge in everyday life. To achieve these goals, the following groups of means are used:
1) motor-oriented means;
2) healing powers of nature;
3) hygiene factors (13, p. 87).
The integrated use of these tools allows us to solve the problems of health improvement pedagogy.
Motor-oriented means include motor actions that are aimed at implementing the tasks of health-saving educational teaching technologies. This is movement; physical exercise; physical education minutes and active breaks; emotional release and moments of “peace” gymnastics (health-improving, finger, corrective, breathing for the prevention of colds, for vigor); physical therapy, outdoor games; specially organized physical activity of the child (health-improving physical education classes, timely development of the basics of motor skills); massage, self-massage; psycho-gymnastics, trainings, etc. (14, pp. 204-205).
The use of the healing powers of nature has a significant impact on achieving the goals of health-saving educational teaching technologies. Conducting classes in the fresh air helps to activate biological processes caused by the learning process, increase the overall performance of the body, slow down the process of fatigue, etc.
Taking into account the influence of meteorological conditions (solar radiation, exposure to air and water temperature, changes in atmospheric pressure, movement and ionization of air, etc.) on certain biochemical changes in the human body, which lead to changes in the health and performance of students, can help relieve the negative impact of training on schoolchildren.
As relatively independent means of healing, one can single out sun and air baths, water procedures, herbal medicine, inhalation, vitamin therapy (vitaminization of the diet, iodization of drinking water, use of the amino acid glycine twice a year - in December and spring in order to strengthen the memory of schoolchildren). It is possible to introduce new elements into the life of the school - herbal bars, a physiotherapy room, health training for teachers and students.
Hygienic means of achieving the goals of health-saving educational teaching technologies that promote health and stimulate the development of adaptive properties of the body include: compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements regulated by SanPiNs; personal and public hygiene (cleanliness of the body, cleanliness of places of activity, air, etc.); ventilation and wet cleaning of premises; compliance with the general regime of physical activity, diet and sleep; instilling in children basic skills in washing their hands, using a handkerchief when sneezing and coughing, teaching children basic healthy lifestyle techniques, basic first aid skills for cuts, abrasions, burns, bites; organizing the procedure for vaccinations of students in order to prevent infections; limiting the maximum level of study load to avoid overwork.
Failure to comply with hygienic requirements for conducting classes reduces the positive effect of health-saving educational teaching technologies.
One of the main requirements for the use of the above tools is their systematic and comprehensive use in the form of classes using preventive techniques; audio accompaniment of lessons, alternating classes with high and low physical activity; in the form of rehabilitation measures; through mass health events; going out into nature, excursions, through sports and health-improving technologies, the process of learning and development in working with families in order to promote a healthy image.
Methods of health-saving technologies.
Methods of health-saving educational teaching technologies are understood as methods of using means that allow solving problems of health improvement pedagogy (3, p. 193).
A teaching method is the ordered activity of a teacher aimed at achieving a given learning goal (1, p. 68). Teaching methods are often understood as a set of ways, methods of achieving goals, and solving educational problems. In health-saving educational teaching technologies, two groups of methods are used (7, p. 155).
Specific (characteristic only for the process of pedagogy of health improvement) and general pedagogical (used in all cases of training and education). Only an optimal combination of specific and general pedagogical methods in accordance with methodological principles can ensure the successful implementation of a set of tasks of health-saving educational teaching technologies.
TO general pedagogical methods include: story, conversation, discussion, exercises, visualization, practical method, game, competitive method, educational, educational and educational programs.
In the structure of methods, techniques are distinguished as an integral part in the implementation of the method. Techniques can be classified as follows:
* protective and preventive (personal hygiene and hygiene of education);
*compensatory-neutralizing (physical training sessions, gymnastics, physical therapy, trainings that allow you to partially neutralize stressful situations);
* stimulating (include elements of hardening, physical activity, psychotherapy techniques);
* informational and educational (letters addressed to parents, teachers).
The use of methods and techniques depends on the professionalism of the teacher and his personal interest.
1.4 Stages of the learning process in conditions of health-saving technologies
In the learning process, in accordance with the ideas of health-saving educational technologies, the task is to form in the student the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities for a healthy lifestyle, to teach how to use the acquired knowledge, skills and abilities, and to teach how to use the acquired knowledge in everyday life.
The entire learning process in the conditions of health-saving pedagogy includes three stages, which differ from each other both in particular tasks and in the features of the methodology (2, p. 95).
1. The stage of initial familiarization with basic concepts and ideas.
The goal is to form in the student the basics of a healthy lifestyle and achieve the implementation of basic health rules.
Main goals:
1) Form a semantic understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
2) Create basic ideas about the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
3) Achieve compliance with basic health rules (at the level of initial skill).
4) Prevent misunderstanding of the basic concepts of a healthy lifestyle.
These tasks are solved one by one. Ideas about the basic rules of health preservation are formed as a result of the teacher’s explanation, perception of the demonstrated movements of physical education complexes, viewing of visual aids, analysis of one’s own muscle and other sensations that arise during the first attempts to perform the complexes, and observations of the actions of other students. All this creates an indicative basis, without which it is impossible to master the rules of health conservation.
In-depth study stage.
The goal is to develop a full understanding of the basics of a healthy lifestyle.
Main goals:
1) Clarify your understanding of the basic rules of health conservation.
2) Achieve conscious implementation of basic health rules.
3) Formation of practically necessary knowledge, skills, rational methods of thinking and activity.
These tasks can be solved simultaneously. The effectiveness of training at this stage largely depends on the correct and optimal selection of methods, techniques and teaching aids. Using active learning methods, it is necessary, in combination with it, to widely use visualization aimed at creating feelings of a healthy lifestyle. The method of verbal influence changes its forms, the leading ones are analysis and analysis of the rules of health savings, conversation, and discussion.
At this stage, a complex of various means is widely used (motor-oriented means; healing forces of nature; hygienic factors).
The effectiveness of using various means is achieved with strict adherence to the following points: a) the goals and objectives of using a specific means in a specific lesson; b) the structural relationship of this tool and method with the main content of the lesson; c) control and self-control of compliance with health saving rules.
The stage of consolidating knowledge, skills and abilities in health conservation and their further improvement.
The goal is the ability to translate into a skill that has the ability to use it for its intended purpose.
Main goals:
1) Achieve stability and automaticity in the implementation of health rules.
2) To achieve compliance with health rules in accordance with the requirements of their practical use.
3) Ensure variable use of healthy lifestyle rules depending on specific practical circumstances.
These tasks can be solved both simultaneously and sequentially, since they are interrelated. At this stage, the number of repetitions of the use of basic concepts and ideas about a healthy lifestyle in ordinary and new, unusual conditions increases, which allows one to develop a flexible skill in applying existing knowledge in various conditions.
Thus, having studied the literature, we came to the conclusion: in order to improve knowledge, skills and abilities in health conservation, various methods and techniques are used: practical method, cognitive game, situational method, game method, competitive method, active teaching methods, educational, educational and educational programs. The teacher selects the means in accordance with specific working conditions. These could be basic movements during class; physical exercise; physical education minutes and active breaks; “minutes of peace”, various types of gymnastics (health-improving, finger, corrective, breathing, for the prevention of colds, for vigor); physiotherapy; outdoor games; specially organized physical activity of the child (health-improving physical education classes, timely development of the basics of motor skills), massage, trainings.
CHAPTER 2. Organization of educational activities in conditions of health-saving technologies in physical education lessons
In a modern school, the lesson form of teaching is the main one. This form provides for various forms of organizing the educational process: home study work (self-study), excursions, practical classes and Internship, seminars, extracurricular activities, extracurricular activities, consultations, tests, exams.
For lesson forms classes are characterized by the fact that the activities of students are controlled by a teacher who, for a strictly established time in a specially designated place, manages the educational process of a relatively constant group of students (class) in accordance with the requirements of the pedagogical laws of training and education. At the same time, the frequency of classes, their duration and relationship are strictly observed. In our country, physical education lessons are held 3 times a week and are 45 minutes long (except for first grade students) (6, p. 98).
In the theory and practice of teaching, the following classifications of lessons are traditional: according to the main didactic goal; according to the main method of carrying them out; according to the main stages of the educational process (17, p. 155).
Classification according to the main method of delivery divides them into lessons: in the form of a conversation; in the form of a lecture; in the form of an excursion; independent work students; laboratory and practical work; combinations of various forms of classes (24, p. 135).
If the classification is based on the main stages of the educational process, the following types of lessons are distinguished: introductory; initial familiarization with the material; formation of concepts, establishment of laws in practice; repetition and generalization; control; mixed or combined (24, p. 136).
IN endless stream of many lessons, one can note a certain repetition and isolate the structures of lessons that occur more often than others. Thus, the structures of lessons of various types are determined:
1) combined (mixed);
2) lessons in learning new knowledge;
3) lessons in developing new skills;
4) lessons of generalization and systematization;
5) lessons of control and correction of knowledge and skills;
6) lessons in the practical application of knowledge and skills (20, p. 56).
The objectives of the lesson, its content and structure, teaching methods - all this should be aimed at ensuring that students experience satisfaction in the process academic work at the lesson. Modern teacher free in your choice of lesson structure. It is important that the main learning goal is achieved in the lesson.
2.1 Organization of physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7
In physical education lessons, health-saving technologies in physical education are used - this is a set of techniques, methods, techniques, teaching aids and approaches to the educational process, in which at least four requirements are met:
1) Taking into account the individual characteristics of the child.
2) The teacher’s activities in the aspect of implementing health-saving technologies in physical education lessons should include familiarization with the results of medical examinations of children, taking them into account in teaching and educational work; Helping parents build healthy lives for students and families as a whole.
3) Avoid excessively debilitating physical and emotional stress when mastering educational material.
4) Providing an approach to the educational process that would guarantee the maintenance of only a favorable moral and psychological climate in the team (24, p. 204).
Currently, health-saving educational technologies used in physical education lessons in grades 5 - 7 include technologies that are based on age characteristics cognitive activity of children, learning at the optimal level of difficulty (complexity), variability of methods and forms of teaching, optimal combination of motor and static loads, learning in small groups, using visualization and combining various forms of providing information, creating an emotionally favorable atmosphere, creating positive motivation for learning (“pedagogy of success”), on cultivating students’ knowledge on health issues (22, p. 177).
It is very important for the teacher to organize the lesson correctly, because... it is the main form of the pedagogical process. The level of hygienic rationality of the lesson largely determines the functional state of schoolchildren in the process of educational activities, the ability to maintain mental performance at a high level for a long time and prevent premature fatigue. We must not forget that hygienic conditions affect the teacher’s condition and his health. And this, in turn, affects the condition and health of students. According to the Research Institute of Pediatrics, students in grades 5-7: 14% of children are practically healthy; 50% of children have deviations in the development of the musculoskeletal system; 35 - 40% of children suffer from chronic diseases (11, p. 78).
Basic modern requirements applied to a lesson with a complex of health-saving technologies:
The rational density of the lesson (the time spent by schoolchildren on academic work) should be at least 60% and no more than 75-80% (10, p. 136);
The number of types of educational activities (questioning, writing, reading, listening, telling a story, looking at visual aids, answering questions, solving examples, etc.) should be 4-7, and they should be changed every 7-10 minutes. (10, p. 139);
The lesson must include activities that promote the development of memory, logical and critical thinking;
During the lesson, at least 2 teaching technologies must be used (when choosing technologies, it is necessary to take into account whether they contribute to the activation of initiative and creative self-expression of students);
Training should be carried out taking into account the leading channels of information perception by students (audiovisual, kinesthetic, etc.);
The scientific nature of the material being studied must be monitored;
It is necessary to form external and internal motivation for students’ activities;
It is necessary to implement an individual approach to students, taking into account personal capabilities;
During the lesson it is necessary to create a favorable psychological climate and necessarily situations of success and emotional release, because the result of any work, and especially mental work, depends on the mood, on the psychological climate - in an unfriendly environment, fatigue sets in faster;
It is necessary to include in the lesson technological techniques and methods that promote self-knowledge and self-esteem of students;
To increase performance and suppress fatigue, it is necessary to include physical education lessons in the lesson, determine their place, content and duration (preferably at the 20th and 35th minutes of the lesson, lasting 1 minute, consisting of 3 light exercises with 3-4 repetitions each) (11, p. 175);
It is necessary to carry out targeted reflection throughout the lesson and in its final part.
To prepare and conduct a lesson that meets all of the above requirements, the teacher’s professional competence in matters of health-saving educational technologies is necessary, therefore there is a need for additional training for teachers of any specialty and working with different populations of students, creating conditions for an interested attitude to learning. Situations of success contribute to the formation of positive motivation for the learning process as a whole, thereby reducing emotional tension, improving the comfort of relationships among all participants in the educational process, thereby implementing the basics of health-saving technologies when organizing the educational process.
In physical education lessons, it is necessary to pay special attention to the organization of health-preserving factors.
Control tests, assignments, testing should only provide initial information for the development of individual tasks, the essence of which is that the student must move further in each period of time, which will be confirmed by the next test. If this does not happen, then the teacher must make appropriate adjustments to individual assignments. It is fundamentally important that the student does not compare with others on the principle of “better or worse than others,” but compares with himself: today I have become better than yesterday, and tomorrow I will try to become better than today. However, for this, tasks must be realistic and stimulate students to actively work. In the meantime, evaluation criteria are based on comparing the results of mastering knowledge and skills with some contrived “average” values. In this case, the strong student does not feel the need for everyday educational work, and the weak one, feeling doomed, does not feel the desire for it. And if a student does not understand the importance of educational material, then the selectively working subconscious immediately after receiving a grade helps him to quickly forget unnecessary material. In this case, the consistency in mastering the basics of knowledge is disrupted, and each new material turns out to be divorced from the previous one, independent and even far-fetched.
When conducting physical education lessons, you need to remember that the physical load on the student’s body should increase gradually, reaching a maximum in the second half of the lesson, and then gradually decrease again to the level that was at the beginning of the lesson. In accordance with this, the most typical physical education lesson scheme is the following:
Introductory part (3-5 min). The purpose of this part of the lesson is to organize students for classes, increase their attention and create a cheerful mood in the class. In the introductory part, the students are constructed and calculated, and the report is submitted to the duty officers. Then the teacher explains the objectives and content of the lesson, conducts light drills, walking, running and performing various attention exercises (21, p. 104).
The next stage of the lesson is the preparatory part (8-15 minutes). In this part of the lesson, the task is to prepare students to perform basic exercises, the comprehensive impact on the muscles and ligaments of the body is enhanced, exercises are conducted on agility, coordination of movements and the development of a sense of rhythm (21, p. 105).
Then comes the main part of the lesson (20-30 minutes). In this part of the classes, basic physical exercises are carried out: running, jumping, throwing grenades, cannonballs, climbing, games, etc. The teacher should pay special attention to the development of agility, strength, endurance, determination and the ability of students to act in a team. In order to maintain students’ attention and interest in classes, it is necessary to diversify the exercises, explain their meanings and effects on the body (21, p. 107).
The last stage of the lesson is the final part. In this part of the lesson, you should bring students to a calm state and summarize the lessons. The content of the final part is walking, elements of drill training. In physical education lessons, girls should be given slightly less workload than boys, and if possible, it is better to divide the class into two subgroups. Naturally, when conducting physical education classes, it is necessary to take into account the age of the students and prevent them from overloading and overfatigue.
2.2 The role of the physical education teacher in preserving and strengthening the health of students
Physical education occupies one of the priority places among other subjects. It lays the foundations for physical and spiritual health, on the basis of which only diversified personal development is possible. The basis of physical culture consists of appropriate methods and norms of physical activity aimed at improving the natural qualities and abilities of the individual. This is the only subject that forms in students a competent attitude towards themselves, towards their body, contributes to the development of strong-willed and moral qualities, the need to improve health and self-improvement.
A physical education teacher must be a good organizer and have a wide range of training in order to top level conduct lessons, organize and take an active part in all sports and public events together with children (inside and outside the school), organize classes in various sports sections outside of school hours, try to show students by personal example about the need and benefits of playing sports.
In many cases, the teacher’s personal example and his knowledge in the field of physical education provide strong motivation and impetus for classes.
The main task of a physical education teacher is to preserve and strengthen the health of the younger generation. Physical education is the only subject in school that performs exactly these tasks. Through his actions, a physical education teacher can destroy a young, growing organism, or can transform him from a weak, sick person into a full-fledged, healthy citizen of his country.
The teacher’s activities in the aspect of implementing health-saving technologies in physical education lessons should include familiarization with the results of medical examinations of children, taking them into account in teaching and educational work; Helping parents build healthy lives for students and families as a whole.
The criterion for the health-saving qualities of educational technologies when using them to protect against pathogenic factors will be the presence or absence of deterioration in the health of students and teachers, which is clearly related to the influence of such factors. This criterion is consistent with our current practice in the healthcare system (you should only see a doctor when you get sick). It conflicts with the principles of preventive medicine and the concept of health adopted by the World Health Organization, according to which health is not only the absence of disease, but also a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being of children's health largely depends on their attitude to physical education, Therefore, one of the teacher’s tasks is to instill interest in his subject.
The need to preserve the health of schoolchildren before school is now a paramount task. The future of our country depends on the improvement of society as a whole. Consistent, systematic work directed at the child from all sides (parents, teachers), without imposing it, but by convincing it, leads to a positive result. Appendix 1 presents the Health Passport for students in grades 5 - 7 for the 2012 - 2013 academic year. From his materials it follows that in each class the number of students ranges from 21 to 24 people. The majority of students are in the main health group (about 90%), about 6% of children belong to the preparatory group, and about 2% belong to the special group. 4% of students are exempt from physical education classes
From the diagram compiled on the basis of data from the Health Passport of students in grades 5 - 7 for the 2012 - 2013 school year and located in Appendix 2, it is clear that out of 134 students, only 42% (57 students) are healthy schoolchildren, and 58% (77 students .) are made up of students with various types diseases.
Achieving a positive pedagogical effect and high results in teaching activities is ensured by targeted health-saving technologies. The word technology in pedagogy means the totality of pedagogical processes in the physical education of schoolchildren (training, education, development).
Health-saving technologies ensure the achievement of a positive pedagogical effect and high results of teaching activities. On the other hand, it is a technique for implementing physical education, a procedural part of the physical education of schoolchildren (13, p. 78).
Pedagogical technology - main part pedagogical excellence. Pedagogically well-thought-out technology of physical education, aimed at developing the motor regime of schoolchildren, leads children to a certain level of physical development, strengthening their health, and achieving sports results. The effectiveness of the lesson primarily depends on how much the teacher will implement the plan he has outlined, apply the most rational forms of organizing the educational process and methodological techniques, use the available equipment, inventory, technical teaching aids, take into account the specifics of the location of the classes - a gymnasium or a school playground, stadium or park, flat or rough terrain. It is very important that during the lesson the teacher selects exactly those means and methods that will bring the highest results, cause student activity, and increase interest in physical education lessons. High motor density should be achieved in each lesson so that all students are actively practicing.
Depending on the objectives of the lesson, it is necessary to choose a way of organizing students’ educational work that would allow the best way solve the assigned educational tasks.
Thus, when introducing students to new material and learning relatively simple exercises that do not require special insurance and assistance, as well as when improving the performance of well-mastered movements, the frontal method of organizing the student’s work is used.
The advantages of this lesson are the maximum coverage of students with motor activity and, therefore, the greater motor density of the lesson.
One of the main tasks of a physical education teacher in grades 5-7 remains teaching motor actions determined by the content educational programs in physical education. In this process, the teacher faces problems related to the content (what to study, what to repeat) and procedural (how to organize, how to plan, what methods to use, how to control) provision of the physical education process. In learning theory, methods, methodological techniques and techniques are defined and classified.
The dosage of physical activity in the lesson requires special attention. It must be differentiated, because the solution to the health problem and the achievement of the effect of physical fitness of students primarily depends on this. In order to more or less accurately determine the load in a lesson, the teacher must take into account the health status of the students’ functional capabilities, their physical fitness, individual characteristics, as well as the degree of previous loads when studying previously covered material. During the lesson, the load can be adjusted by changing the number of repetitions, the tempo of the exercises, the size of the weights, and the duration of the tasks.
The objectives of the lesson, its content and structure, teaching methods - all this should be aimed at ensuring that students experience satisfaction in the process of learning in the lesson. A modern teacher is free in his choice of lesson structure. It is important that the main learning goal is achieved.
Thus, it can be argued: in order to organize and conduct lesson forms of classes, it is characteristic that the activities of students are controlled by a teacher who, for a strictly established time in a specially designated place, manages the educational process of a relatively constant group of students (class) in accordance with the requirements of pedagogical patterns of training and education, while the frequency of classes, their duration and interrelation are strictly observed. Scheme of conducting a physical education lesson: introductory part, preparatory part, main part of the lesson, final part of the lesson. One of the main tasks of a physical education teacher in grades 5-7 is teaching motor actions determined by the content of educational programs in physical education.
2.3 The effectiveness of using health-saving technologies in physical education lessons of grades 5-7
In the first chapter, we examined the principles, means, methods, structure of health-saving technologies and revealed that health-saving technologies provide schoolchildren with the opportunity to maintain and improve their health during the period of study at school, form in them the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities for a healthy lifestyle, teach them to use the acquired knowledge in everyday life.
The level of physical development and state of health have a huge impact on the development of a student’s mental performance.
Having examined health-saving technologies, we came to the conclusion that these technologies can be used as a means of preserving the health of schoolchildren and increasing their performance in physical education classes.
Similar documents
Features of conducting physical education lessons in grades 8-9. Evaluation of the use of various methods of training endurance in physical education lessons, which allows to increase the level of development of conditioning abilities in students in grades 8-9.
thesis, added 05/26/2015
Analysis of pedagogical technology for constructing annual lesson plans and conducting game-oriented physical education lessons in grades 6-7 high school. Study of the influence of physical education lessons on the level of physical fitness of students.
thesis, added 09/29/2011
The essence and features of modern pedagogical technologies. The effectiveness of using multimedia in the educational process. Formation of a healthy lifestyle in physical education lessons using health-saving technologies.
course work, added 04/20/2016
Distinctive features organization of the pedagogical process in a rural school. The role and place of physical education in an educational institution. Features of the use of pedagogical technologies in physical education lessons in urban and rural schools.
abstract, added 05/10/2016
The concept of aesthetic education in psychological, pedagogical and methodological literature. Means of aesthetic education in physical education lessons. Methods of introducing musical accompaniment into practice in physical education lessons.
thesis, added 05/28/2015
Studying compensation with the help of computer technologies for the lack of visual aids in a physical education lesson. Characteristics of the use of color, graphics, presentations, animation, and sound to recreate the real environment of sports competitions.
course work, added 06/21/2011
The concept of independence in pedagogical literature. Psychophysiological characteristics of younger schoolchildren. Physical education lessons as a form of education. Exercises to develop independence among 1st grade students in physical education lessons.
course work, added 09/06/2015
Features of the physical and physiological development of 5th grade students. Means of physical education, forms of its organization. Stages empirical research Features of teaching physical culture and physical education to 5th grade students.
thesis, added 11/17/2014
Implementation of health-saving educational technologies in the educational process. Their features in chemistry lessons as a factor in increasing students’ learning motivation. Technologies for optimal organization of the educational process and physical activity of schoolchildren.
thesis, added 08/05/2013
Self-improvement and self-knowledge in physical education lessons. Developing self-confidence and confidence in one’s actions and abilities. Features of will formation. The role of physical education in self-esteem. Spiritual and moral education person.